Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Humoral vaccine responses to SARS-Cov-2 vaccines are impaired and short lasting in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs). Concerns have been raised regarding their protection against severe COVID-19 disease. The study aim was to evaluate humoral response and safety of repeated vaccination in IMID patients.
Methods: The prospective observational Nor-vaC study (NCT04798625) enrolled adult patients on immunosuppressive therapy for inflammatory joint- and bowel diseases. Healthy controls were health care workers from participating hospitals. All participants received standard vaccines according to the national vaccination program with three doses in patients and two doses in controls. The third dose was offered to IMID patients >4 weeks after the second dose. Anti-Spike antibodies were assessed 2-4 weeks, and 12 weeks following each dose. Levels were compared across groups by Mann-Whitney U tests and multivariate linear regression was used to identify predictors of response.
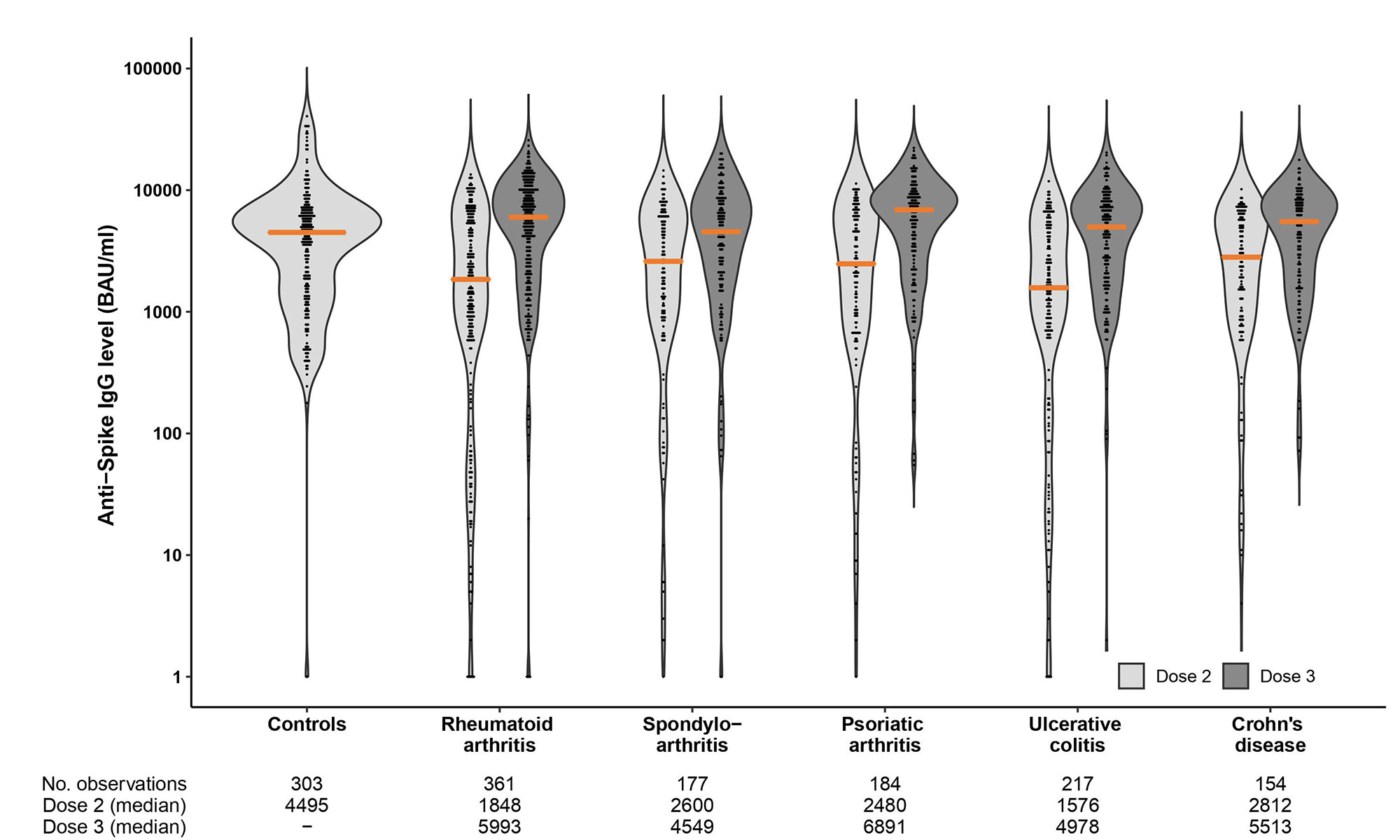
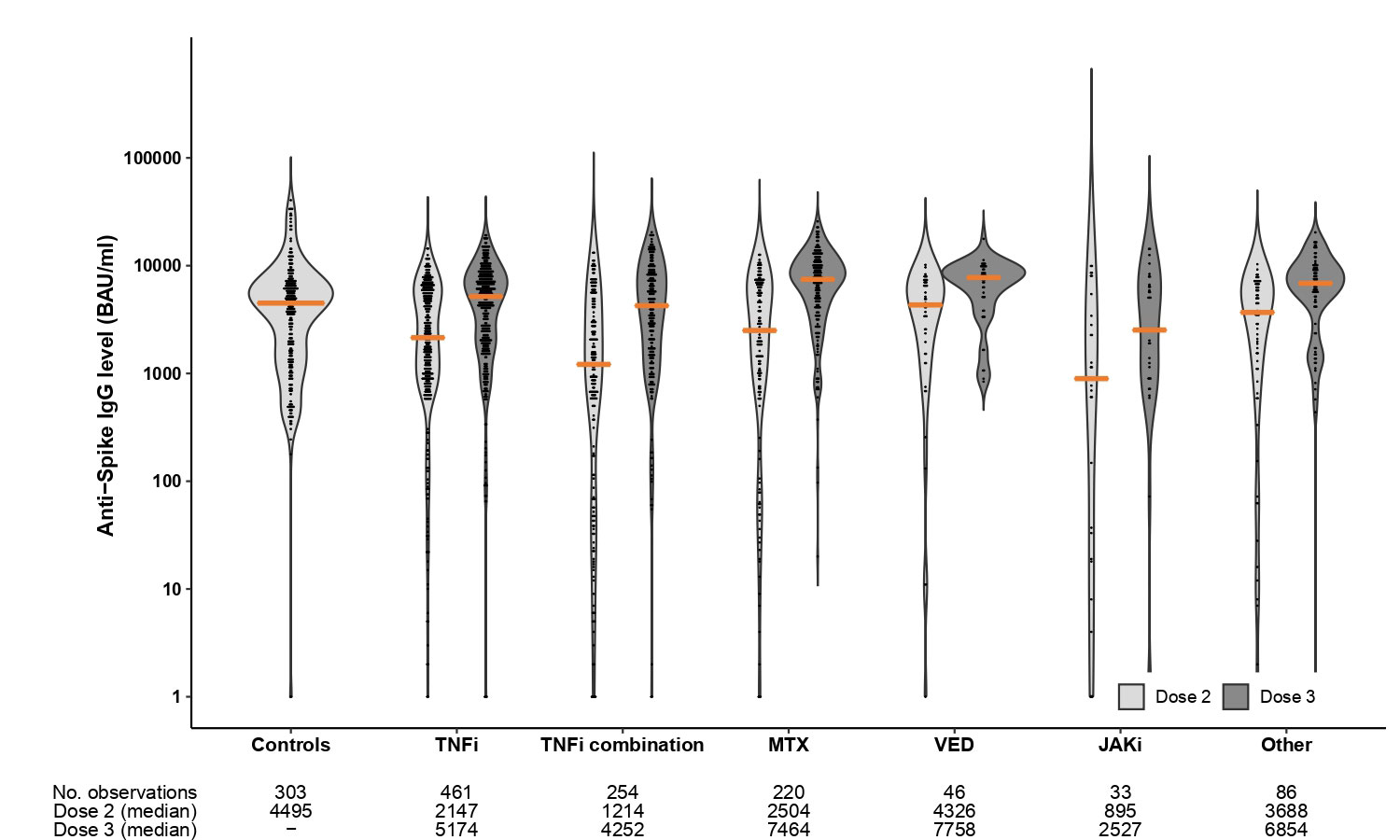
Results: A total of 1100 patients (366 rheumatoid arthritis, 177 spondyloarthritis, 184 psoriatic arthritis, 156 ulcerative colitis and 217 Crohn’s disease) (median age 54 years [IQR 43-64]; 55 % women) and 303 healthy controls (median age 43 years [IQR 33-55]; 75 % women) were included in these analyses. Following three-dose vaccination, patients achieved median (IQR) antibody levels of 5720 BAU/ml (2138-8732) compared to 4495 (1591-6639) in controls receiving two doses, p=0.27. Anti-Spike antibody levels increased with median 1932 BAU/ml (IQR 150–4978) after the third dose. Factors associated with high antibody levels following the third dose were; use of methotrexate in monotherapy, self-reported pause in medication in relation to vaccination, the interval between the vaccine doses and vaccination with mRNA-1273 or a combination of vaccines. The percentage decline per day in anti-Spike antibody levels was significantly higher following the second (0.45%) than the third vaccine dose (0.35%), p< 0.001. Adverse events were reported by 488 (53%) and 464 (47%) patients after second and third dose, respectively, and by 196 (78%) controls. Disease flares were reported by 50 (5%) and 70 (7%) patients following the second and third dose.
Conclusion:
This study suggests that a third vaccine dose for immunosuppressed patients closes the gap in serological response between patients and the healthy population. Antibody levels following the three-dose regimen in IMID patients were comparable to healthy controls vaccinated twice, and no new safety issues emerged. This finding was consistent across all diagnoses and treatment groups, supporting repeated vaccination of IMID patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jyssum I, Tveter A, Sexton J, Christensen I, Mjaaland S, Warren D, kvien T, Bjørlykke K, Kro G, Jahnsen J, Munthe L, Haavardsholm E, Grødeland G, Provan S, Jørgensen K, Goll G, Syversen S. Immunogenicity and Safety of a Three-dose SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Strategy in Patients with Immune-mediated Inflammatory Diseases on Immunosuppressive Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunogenicity-and-safety-of-a-three-dose-sars-cov-2-vaccination-strategy-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-on-immunosuppressive-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunogenicity-and-safety-of-a-three-dose-sars-cov-2-vaccination-strategy-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-on-immunosuppressive-therapy/