Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative musculoskeletal disease causing chronic disability and elevated social costs worldwide. Its multifactorial origin contributes to different OA phenotypes and at present no biomarker can predict individual response to treatments such as autologous blood-derivative platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection. Our aim is to define the peripheral blood profile – inflammatory versus mechanical – of knee OA patients treated with PRP injection, based on the analysis of serological and cellular biomarkers, to predict the response to this regenerative treatment
Methods: Patients with Kellgren and Lawrence radiological grade 2-3 of knee OA were enrolled as per protocol and IRB rules. Prior to PRP knee injection by nSTRIDE (Zimmer Biomet, USA) we obtained 30 ml of blood to characterize i) the immunophenotype of adaptive and innate immune cells (CD3, CD4, CD8,Treg, CD19, CD14, CD56; central and effector memory cells); ii) inflammatory (Wnt and IL-1 pathway, pentraxin3-PTX3) and antioxidant (DPP3/Keap1/Nrf2) pathways, by multiparametric FACS analysis, qPCR, ELISA, and enzymatic assays. Patients were followed for 12 months after PRP knee injection to define responders vs non-responders based on clinical and patient-reported-outcomes and correlate the response to PRP with the specific OA phenotype.
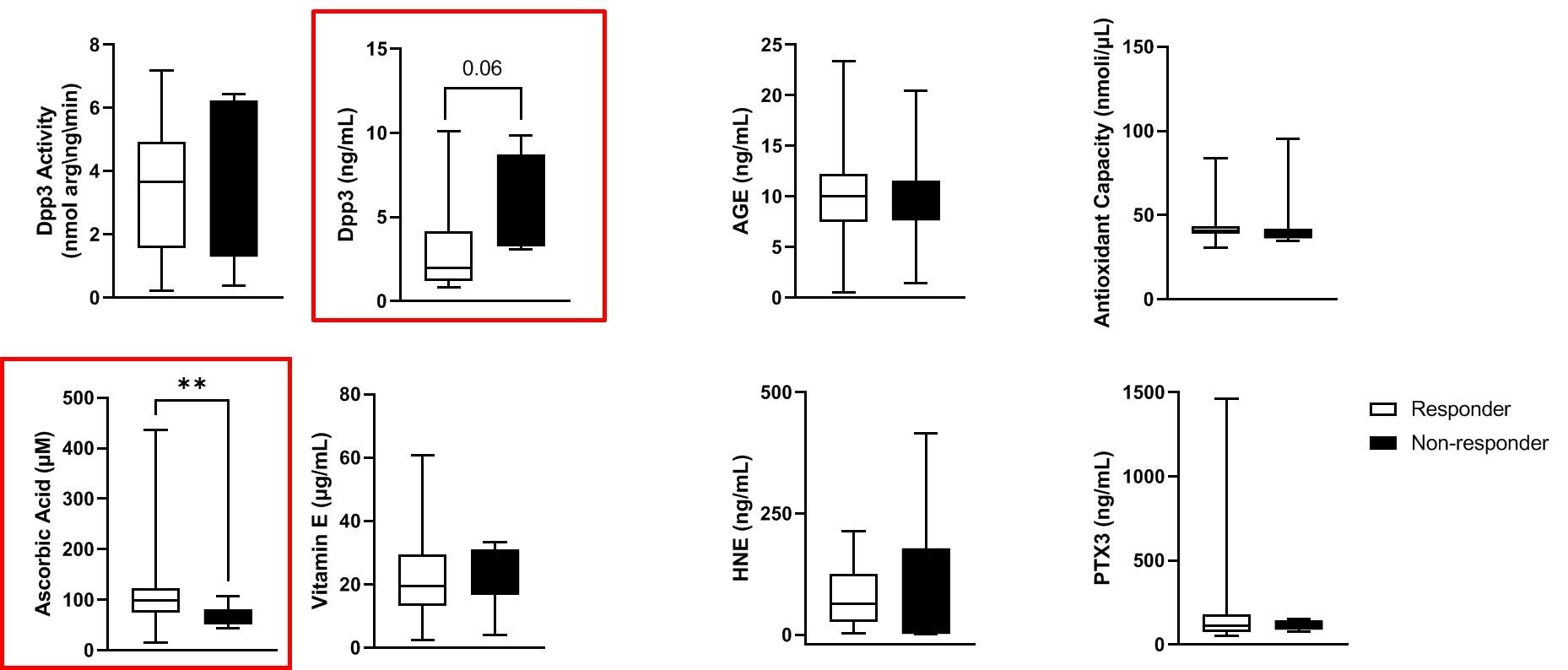
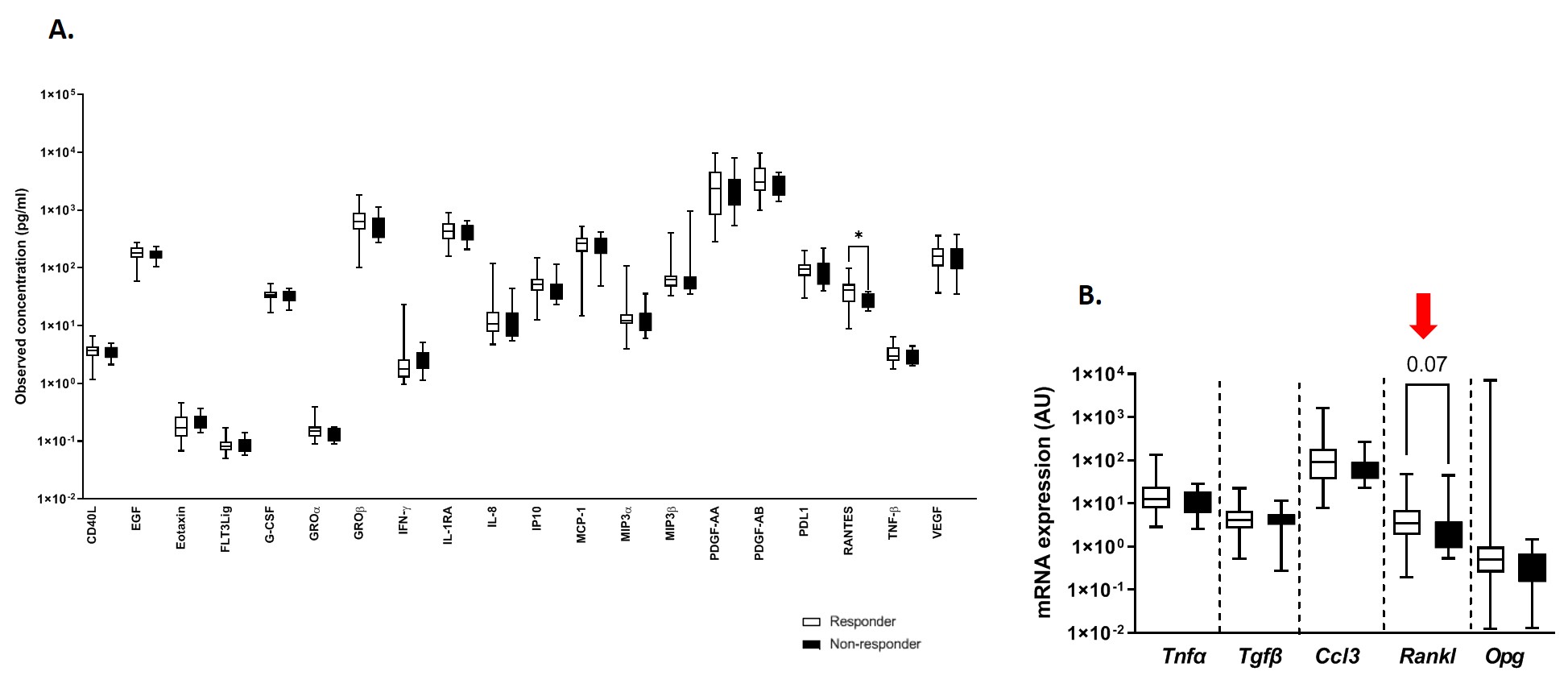
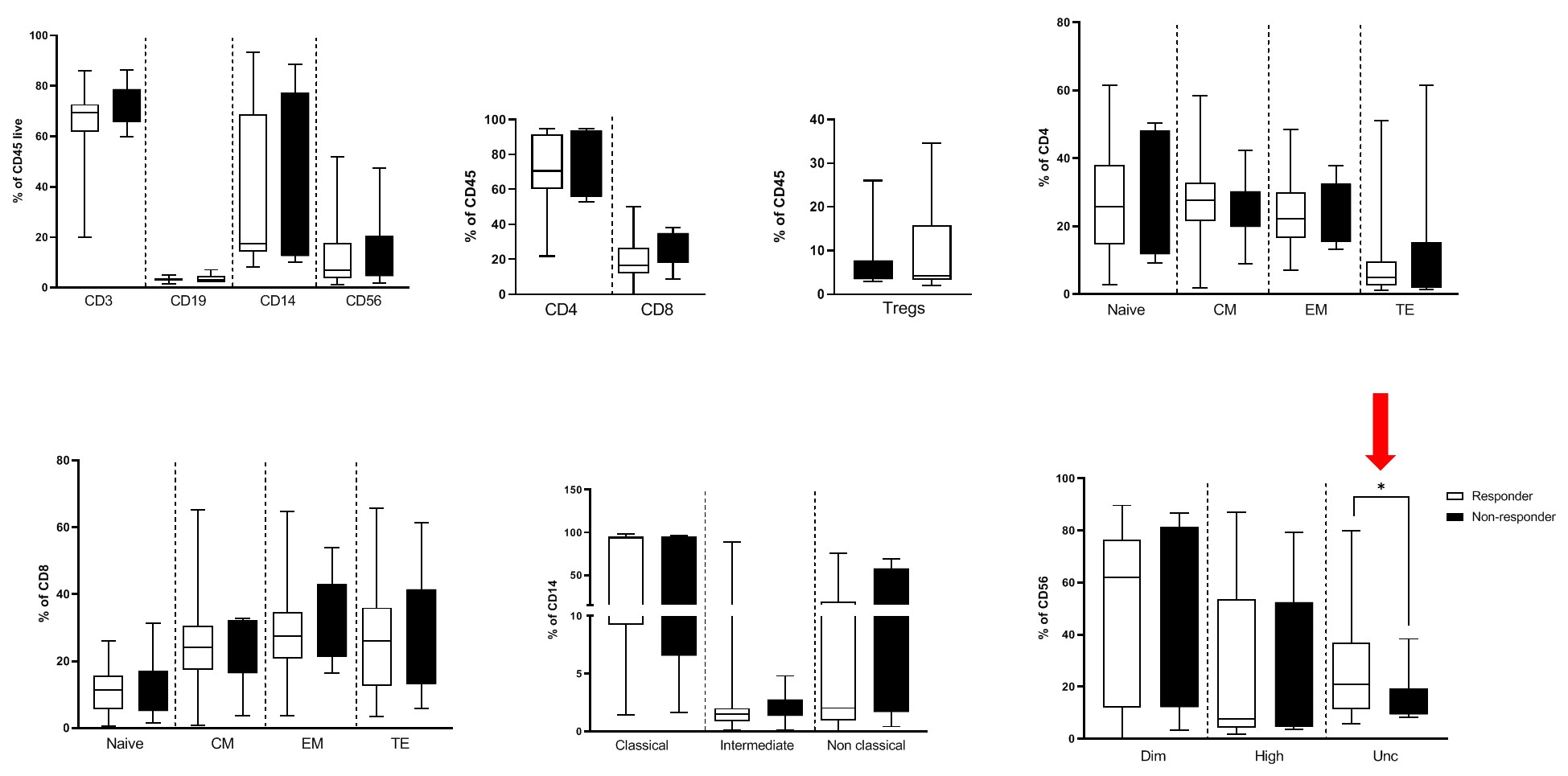
Results: We enrolled 105 knee OA patients (41 male, 64 female) treated with a single PRP injection; 58 patients completed the 12-month follow-up period and were included in the analysis (47 responders, 11 non-responders). No significant changes were observed in responders vs non-responders as for sex, age and clinical features associated with knee OA. We measured the oxidative status of OA patients, in particular the presence of products of advanced glycation, HNE and DPP3, by ELISA and we detected a significantly lower level of ascorbic acid concentration (p < 0.01) and a trend toward increase of DPP3 levels in non-responder OA patients (p 0.06; Fig. 1). The analysis of a panel of 20 cytokines (detectable in our samples out of 46 cytokines tested by Bioplex) showed higher levels of RANTES (CCL5) in the responders (p < 0.05; Fig.2A), and we were able to identify the activation of components such as RANKL (p 0.07; Fig. 2B) associated with response to PRP injection by real time qPCR on PBMCs. By FACS on PBMCs we could identify a subset of NK cells (CD56dimCD16negative), a population still under study with unknown specific functions, significantly associated with response to PRP injection in knee OA patients (p < 0.05; Fig.3).
Conclusion: Our immunological analysis for the characterization of knee OA patients responding and non-responding to PRP injection shows that high levels of RANTES (CCL5) and RANKL activation may be related with response to PRP treatment.
Acknowledgements. Grant number GR-2019-12370692 (Italian Ministry of Health)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tonutti A, Granata V, Marrella V, Sobacchi C, Ragusa R, Monferini M, sconza C, rani N, Di Matteo B, Selmi C, Ceribelli A. Immunobased Profiling of Knee Osteoarthritis Patients to Predict Response to Regenerative Treatment with Autologous Blood-derivative Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunobased-profiling-of-knee-osteoarthritis-patients-to-predict-response-to-regenerative-treatment-with-autologous-blood-derivative-platelet-rich-plasma-injection/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunobased-profiling-of-knee-osteoarthritis-patients-to-predict-response-to-regenerative-treatment-with-autologous-blood-derivative-platelet-rich-plasma-injection/