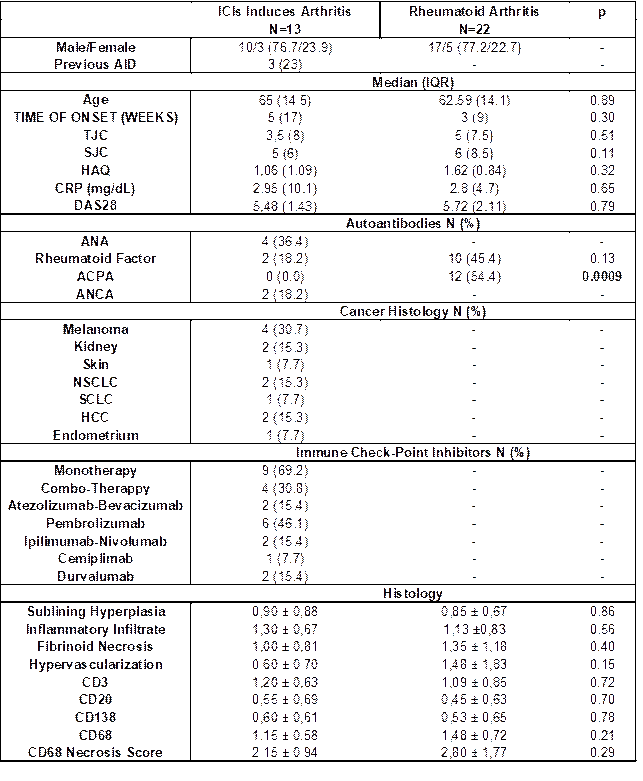Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The increasing use of Immune Check-Point Inhibitors (ICIs) to treat malignancy focused attention on immune-related adverse events (irAEs). ICIs-induced arthritis is the most common rheumatic irAEs. Its prevalence is usually underestimated, and the pathogenesis remains unknown (1). Ultrasound (US) Guided Synovial Biopsy (USGSB) has been proven a safe and reliable procedure in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), enlarging the understanding of synovitis in RA. To our knowledge, no studies analyzed the histology of ICIs-induced arthritis. This study aimed to describe ICIs-induced arthritis comprehensively, from the clinical presentation to the histological assessment, comparing the results with the clinical and histological characteristics of an Early RA (ERA) Cohort.
Methods: Oncological patients in treatment with ICIs have been enrolled. Patients were referred to our attention by their oncologist to the appearance of signs and/or symptoms suggestive of arthritis. Each patient received a complete rheumatological evaluation including joint counts and research of autoantibodies (ANA, RF, and ACPA antibodies). An ultrasound-guided synovial biopsy of a small joint or a knee mini arthroscopy was performed. Synovial samples were analyzed for histology (Synovial Hyperplasia, Fibrinoid Necrosis, Hypervascularization, Inflammatory Infiltrate) and IHC (CD3, CD20, CD138, and CD68) on a semiquantitative 0-3 scale. US was systematically performed including scanning of 38 joints (shoulder, elbow, knee, wrist, MCP, IFP, and MTP joints). Synovitis was defined according to the OMERACT guidelines definition (2). As a control, we enrolled age and sex-matched untreated ERA patients.
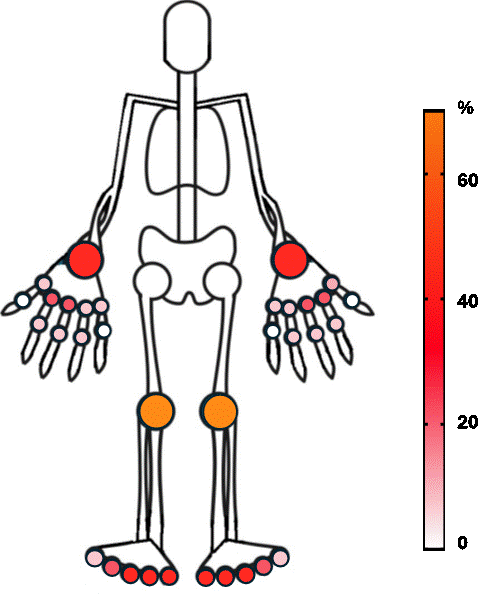
Results: Up to now, thirteen patients were included [M/F (10/3), median age 65 years (IQR14.5)]. The clinical, serological, and demographic characteristics are reported in Table 1 including the compared ERA cohort. Six patients (46.1%) were positive for ANA or RF. One patient suffered from monoarthritis, 5 (38.4%) from oligoarthritis, and the remaining 7 (53.8%) from polyarthritis. The systematic US pre-biopsy evaluation (Figure 1) demonstrated the presence of any grade synovitis in 23.4% of analyzed joints; the most commonly involved was the knee, followed by wrist, elbow, MCP2, MCP3, and MTP 2-5. The knee was by far the most biopsied joint (69.2%). The histology of ICIs-induced arthritis demonstrated high-grade synovitis: we did not identify any significant difference for any variable. Histology and IHC results did not correlate with the baseline disease severity (DAS28, TJC, SJC, CRP).
Conclusion: In our cohort, as in previous studies ICIs induced arthritis manifested as an oligo-polyarthritis, clinically similar to RA; small and large joints were similarly involved. Histology is not specific to ICI-induced arthritis and to date does not have a diagnostic value. However, the resemblance to ERA suggests common pathogenic mechanisms. Considering the low numerosity of the cohort, we did not identify any correlation between disease activity and histological assessment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Francesco N, Tatiana S, Adrien N, Christine G, Frank A, Jean-François B, Frank C, Yvan B, Patrick D, Laurent M. Immune Checkpoint–Induced Arthritis: A Comprehensive Single Cohort Descriptive Analysis from Clinical Evaluation to Histology [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immune-checkpoint-induced-arthritis-a-comprehensive-single-cohort-descriptive-analysis-from-clinical-evaluation-to-histology/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immune-checkpoint-induced-arthritis-a-comprehensive-single-cohort-descriptive-analysis-from-clinical-evaluation-to-histology/