Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: Abstracts: T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) is a potentially fatal complication of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA). Gene expression pathway analyses have identified altered Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling in sJIA and MAS. Repeated administration of CpG, a TLR-9 agonist, induces an MAS-like phenotype in mice; fulminant disease is induced with co-administration of intereukin-10 receptor blocking antibody (αIL10R). IL10 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine that induces T cell immune tolerance. Deficient production of IL10 by antigen presenting cells drives pathology in sJIA patients and animal models of the disease. Polymorphisms in the IL10 gene family confer susceptibility to sJIA. We hypothesized that IL10 inhibits T cell activation (TCA) in TLR-9-induced inflammation, and that TCA contributes to hypercytokinemia in TLR-9-induced inflammation.
Methods: Five experimental groups of C57Bl6 mice were studied: 1) untreated, negative controls; 2) MAS: treated with CpG 50 μg intraperitoneally (ip) every other day for 5 doses days -8 – 0; 3) CpGHi: treated with CpG 500 μg ip on day 0; 4) CpGHi+αIL10R: treated with CpG 500 μg plus αIL10R 1000 μg (both ip) on day 0; 5) αCD3ε (positive controls): treated intravenously with 50 μg of anti-CD3ε stimulating antibody on day 0. On day 1 following completion of treatment animals were sacrificed. Spleens were harvested and digested, and leukocytes were isolated. Cells were cultured in brefeldin A to entrap expressed products intracellularly or were stained directly post-isolation. Stained cells were analyzed with flow cytometry. Cytokine-driven-TCA was quantified by CD69 staining on flow cytometry. T cell receptor-mediated- (TCR-) TCA was quantified by Nur77 staining on flow cytometry. Data were analyzed using one-way Analysis of Variance with Šídák post-hoc tests.
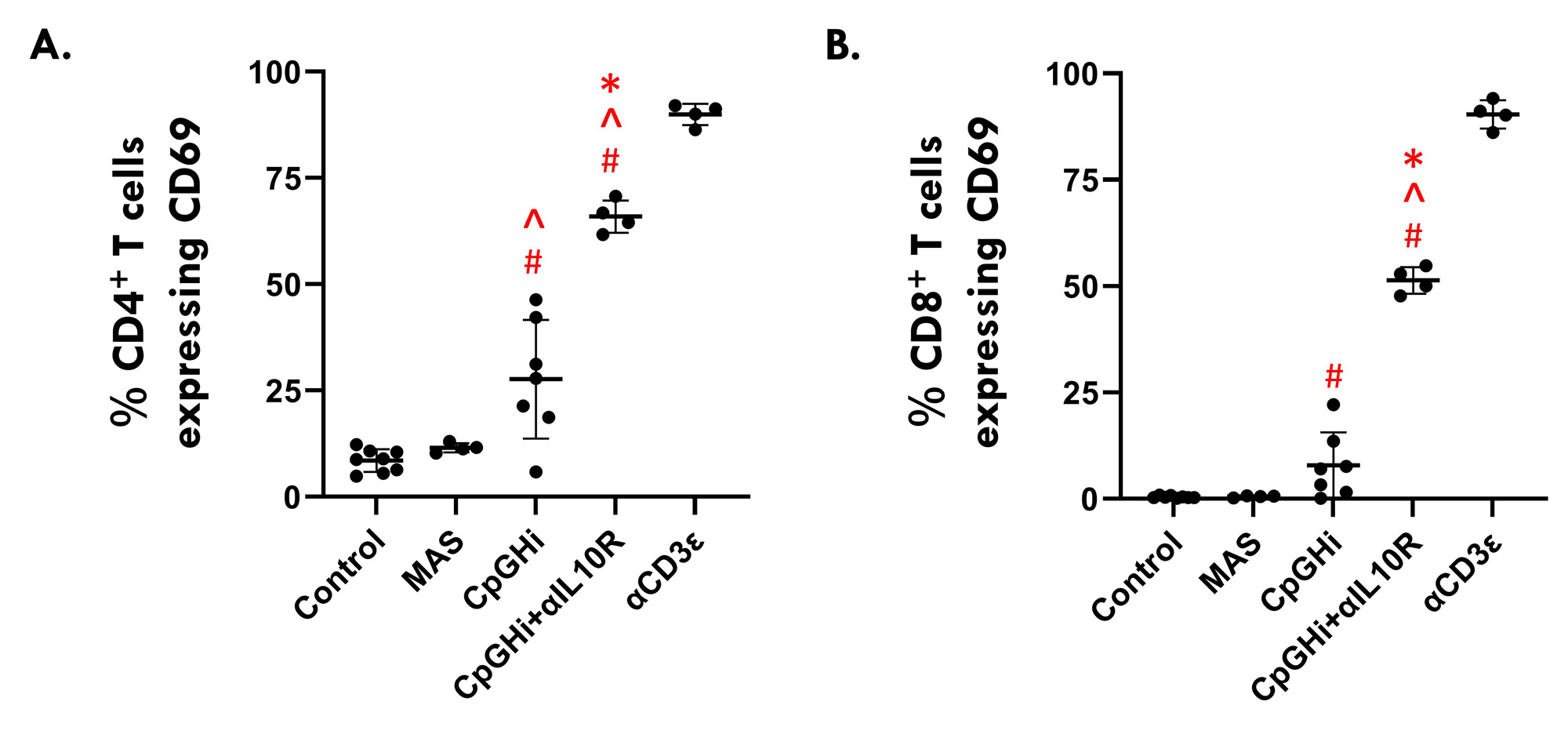
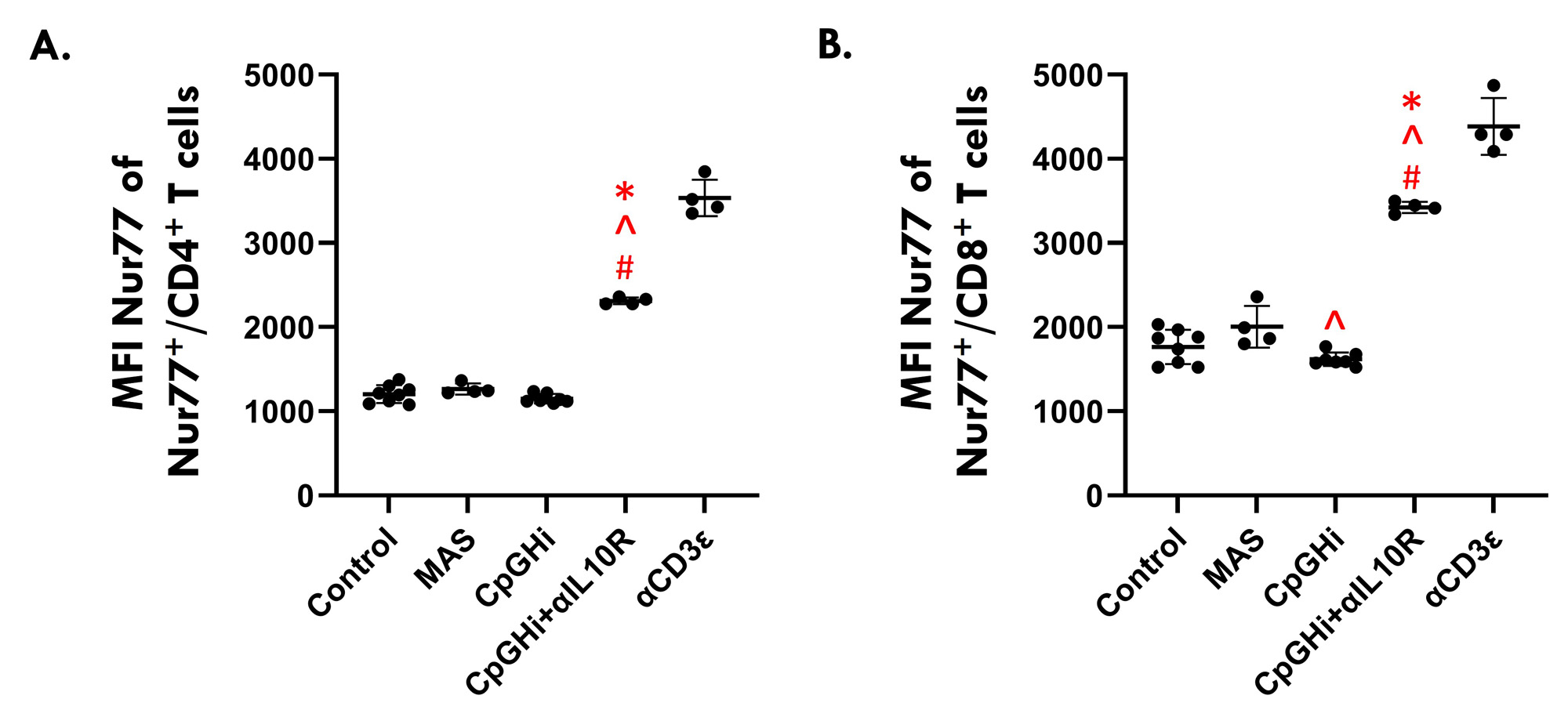
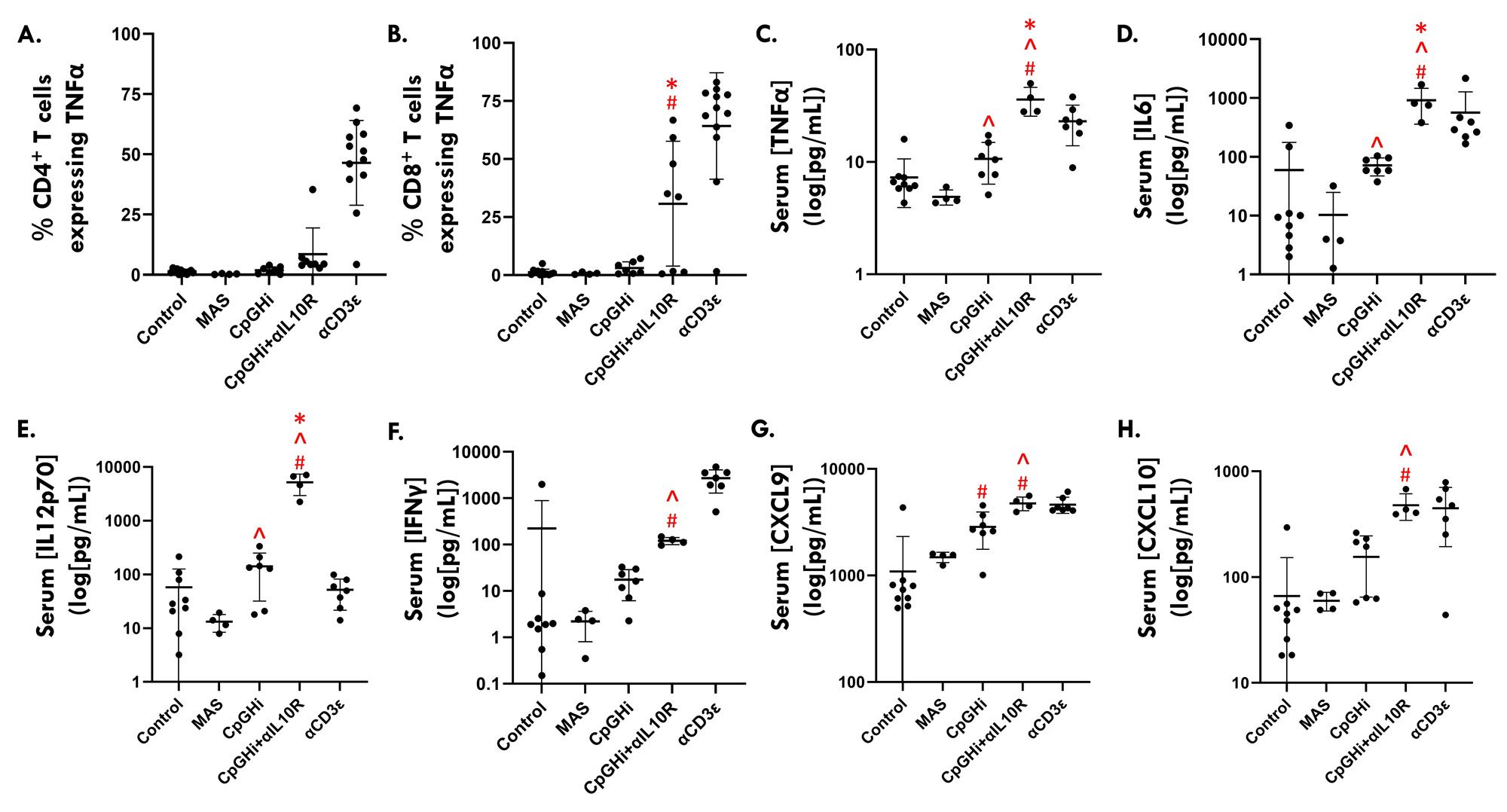
Results: MAS exposure did not affect cytokine-driven-TCA. CpGHi-exposure increased cytokine-driven-TCA in CD4+ T cells compared to MAS-exposed mice and untreated controls (Fig. 1, p < 0.05). CpGHi+αIL10R exposure increased cytokine-driven-TCA compared to MAS- and CpGHi-exposed mice, and untreated controls (Fig. 1, p < 0.05). MAS exposure did not affect TCR-TCA. CpGHi exposure increased TCR-TCA compared to MAS-exposed mice and untreated controls (Fig. 2, p < 0.05). CpGHi+αIL10R exposure increased TCR-TCA compared to MAS- and CpGHi-exposed mice, and untreated controls (Fig. 2, p < 0.05). CpGHi+αIL10R exposure increased the proportion of CD8+ T cells expressing TNFα compared to untreated controls and CpGHi-exposed mice (Fig. 3B, p < 0.05), but not MAS-exposed mice. CpGHi+αIL10R exposure increased serum concentrations of TNFα, IL6, and IL12 compared to MAS- and CpGHi-exposed mice, and untreated controls (Fig. 3C-E, p < 0.05). CpGHi+αIL10R exposure increased serum concentrations of IFNγ, CXC-motif chemokine ligand 9 (CXCL9), and CXCL10 compared to MAS-exposed mice and untreated controls (Fig. 3F-H, p < 0.05).
Conclusion: IL10 prevents TLR-9-induced TCA. TCA contributes to TLR-9-induced hypercytokinemia. The established, non-infectious model of MAS with repeated administration of low-dose CpG does not adequately capture the contribution of T cells to the development of fulminant disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Eremita M, Geier O, Hui-Yuen J, Taylor M. IL10 Inhibits Toll-like Receptor-9-induced T Cell Receptor-mediated T Cell Activation in Macrophage Activation Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/il10-inhibits-toll-like-receptor-9-induced-t-cell-receptor-mediated-t-cell-activation-in-macrophage-activation-syndrome/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/il10-inhibits-toll-like-receptor-9-induced-t-cell-receptor-mediated-t-cell-activation-in-macrophage-activation-syndrome/