Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1913–1944) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: IgG4 immunoglobulin-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a rare, systemic immune-mediated fibro-inflammatory process with an unclear etiology and pathophysiology with the capacity of affecting multiple organs. It exhibits common pathophysiological, serological, and clinical characteristics.
Objectives: To describe clinical presentation, evolution, and treatment heterogeneity among a series of IgG4-RD cases and to compare the accuracy of the last two most recent IgG4-RD classification and diagnostic criteria.
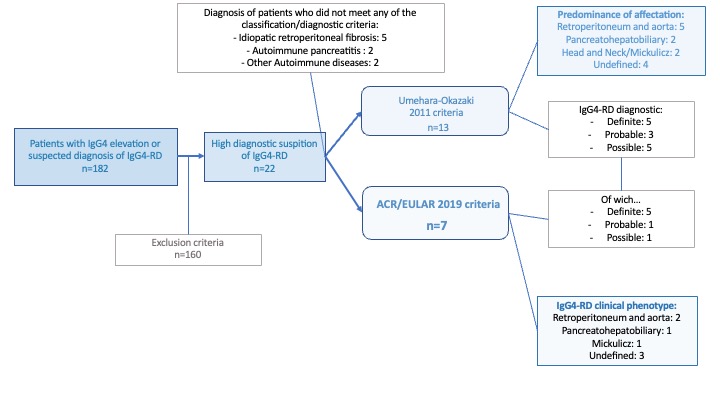
Methods: A single-center retrospective cross-sectional study was conducted, encompassing patients with a suspected diagnosis of IgG4-RD from various hospital departments (Rheumatology, Digestive Medicine, Internal Medicine and Pneumology). The study period lasted from January 2010 to August 2022. Exclusion criteria were applied to patients who were ultimately diagnosed with other pathologies, and for those patients who remained with a suspected diagnosis of IgG4-RD, the Umehara-Okazaki 2011 and ACR/EULAR 2019 criteria were subsequently employed.
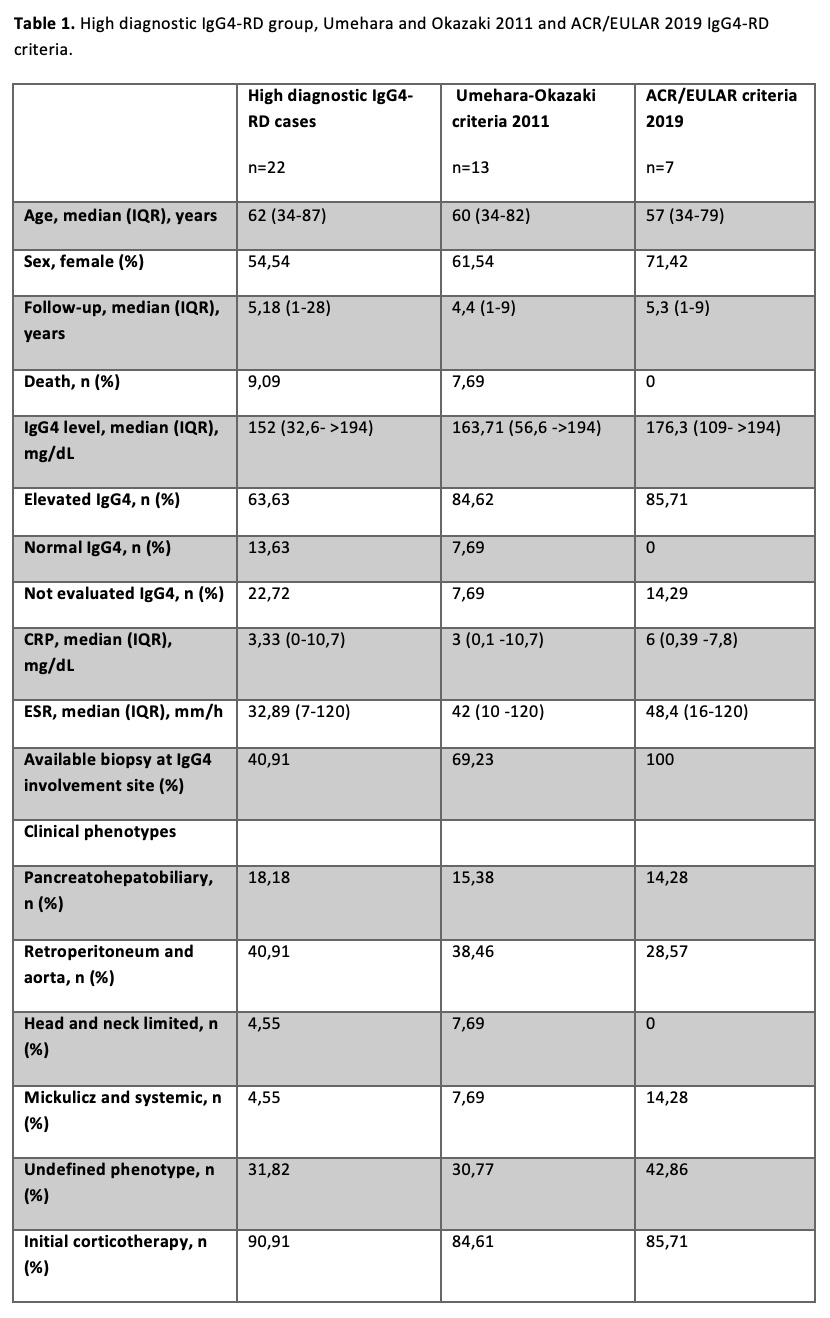
Results: A total of 182 patients with elevated IgG4 and/or a suspected diagnosis of IgG4-RD were initially collected. After applying the exclusion criteria, 22 potential cases of IgG4-RD were described (Table 1). The Umehara and Okazaki 2011 diagnostic criteria were applied, resulting in the classification of 13 patients (mean age :60 years; 57% women); with 5 being classified as definitive disease, 3 as probable disease, and 5 as possible disease. One death was recorded in this group, which was related to heart failure. Furthermore, the ACR/EULAR 2019 classification criteria were applied to the same patient cohort (Table 1), resulting in the diagnosis of 7 patients (mean age:57 years; 71% women) with a mean follow-up of 5.3 years. In this group, 85.71% of patients had elevated IgG4 levels (mean: 176.3 mg/dL). Retroperitoneal fibrosis and aortitis were the most prevalent form of presentation for both groups (2011 and 2019 criteria) accounting for 38.5% and 28.6% respectively. Initially, 85.71% of the patients finally diagnosed with IgG4-RD received corticosteroids followed by other immunosuppressants such as Azathioprine, Methotrexate, Rituximab, surgical treatment, or maintenance doses of corticosteroids.
Conclusion: IgG4-RD is a recently recognized entity that exhibits significant heterogeneity in clinical, analytical, and histopathological presentation. Differences arise when utilizing different diagnostic criteria.
The most recent and stringent ACR/EULAR 2019 classification criteria allow for a more accurate classification of patients by emphasizing histopathology, different forms of presentation, and analytical data. Therefore, on many occasions, a multidisciplinary approach is often necessary.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martínez Calabuig P, Fragio J, Gonzalez Mazarío R, Rueda Cid A, Sanmartín Martínez M, Salvador Maicas L, Abenza Barberá L, Sabater Abad M, Sierra Rivera A, Castelló Miralles I, Lerma Garrido J, Molina Almela C, Balaguer Trull I, Campos Fernández C. IgG4-related Disease: 2010-2022 Case Review and Comparative Evaluation of Diagnostic Criteria [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/igg4-related-disease-2010-2022-case-review-and-comparative-evaluation-of-diagnostic-criteria/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/igg4-related-disease-2010-2022-case-review-and-comparative-evaluation-of-diagnostic-criteria/