Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Aspects and Treatment IV
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is an immune-mediated inflammatory disorder of spine and sacroiliac joints, which could lead to bony fusion of vertebral joints. TNF-blockers have a high efficacy in treating AS, yet up to 40% of AS patients show poor or even no response to this treatment. We aim to build an approach to predict the response prior to clinical treatment.
Methods: Ninety-two AS patients undergoing etanercept treatment were recruited and patients who did not fulfill BASDAI50 or ASAS40 at week 12 after starting treatment were considered poor-responders. The IgG galactosylation (IgG-Gal) ratio was calculated and candidate SNPs in patients treated with etanercept were examined. Machine-learning models and cross-validation were conducted to predict responsiveness.
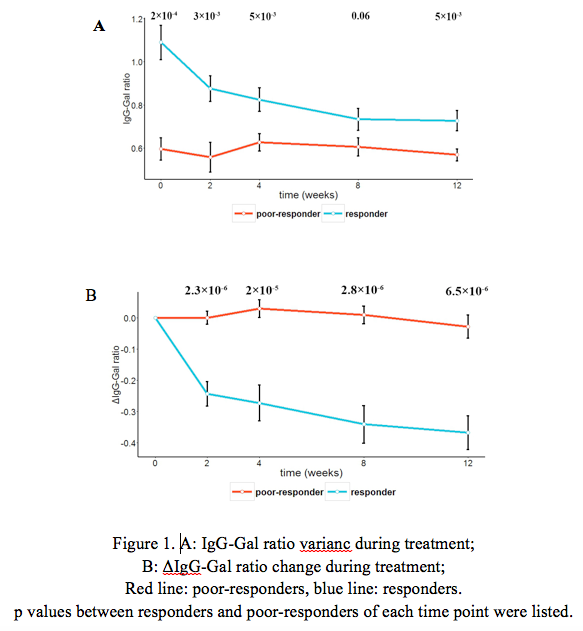
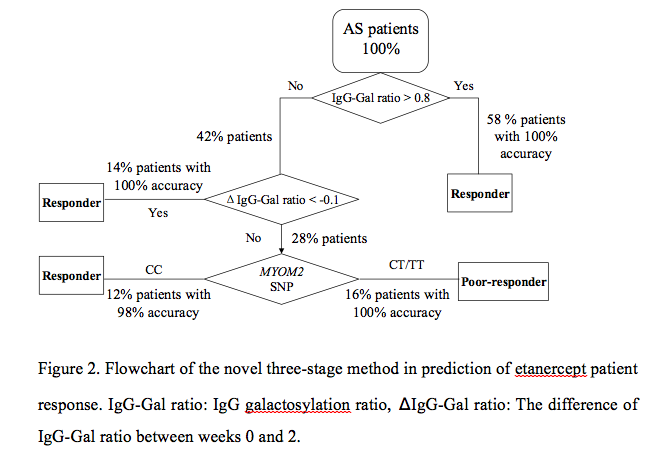
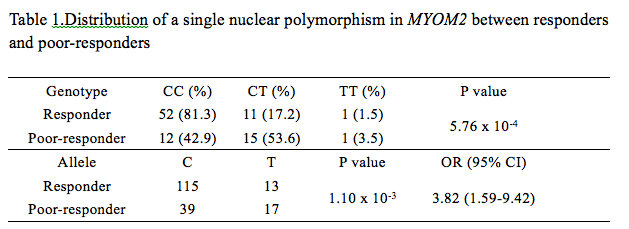
Results: Both IgG-Gal ratio at each drug delivery and differential IgG-Gal ratios between week 0 and weeks 2, 4, 8, 12 showed significant differences between responders and poor-responders (Fig. 1A, B). AUC of the IgG-Gal ratio prediction model was 0.8 after cross-validation, significantly higher than current clinical indices, including CRP, ESR, BASDAI, BASFI and ASDAS. In addition, one MYOM2 SNP was found significantly associated with drug response (Table 1) (p=0.000576). Thus, a three-stage approach consisting of baseline IgG-Gal ratio, differential IgG-Gal ratio in 2 weeks, and the MYOM2 SNP genotype was conducted as follows (Fig. 2): Stage I: The IgG-Gal ratio of all AS patients were evaluated prior to etanercept treatment. Patients whose IgG-Gal ratio values were over 0.8 were predicted to be responders. Stage II: The others were examined after one dose of etanercept and repetitive IgG-Gal ratio evaluation was performed at week 2, among which patients whose ¦¤IgG-Gal ratio value were below -0.1 were predicted to be responders. Stage III: The remains were subjected to MYOM2 SNP genotyping, revealing patients with CT/TT genotype to be poor-responders and patients with CC genotype to be responders.
Conclusion: We propose a novel three-stage approach to combine genetic markers and post-translational modifications to predict precisely the response to the TNF blocker (Etanercept) in AS patients with an accuracy of 100% for poor-responders and 98% for responders.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liu J, Ren S, Niu Z, Zhu Q, Wan W, Han J, Ma Y, Pu W, Li Y, Xu X, Wang Y, Zhao D, Zhang H, Qian F, Zhou X, Reveille JD, Jin L, He DY, Zou H, Gu J, Wang J. IgG Galactosylation Status Combined with MYOM2 SNP Precisely Predicts Anti-TNF Response in Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/igg-galactosylation-status-combined-with-myom2-snp-precisely-predicts-anti-tnf-response-in-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/igg-galactosylation-status-combined-with-myom2-snp-precisely-predicts-anti-tnf-response-in-ankylosing-spondylitis/