Abstract
Background/Purpose : Our objective was to prospectively determine the prognostic significance of laboratory variables regarding thrombotic events during follow-up, including novel assays IgG antibodies directed against domain I of ß2-glycoprotein I (antiDI) and IgG anti-phosphatidylserine–prothrombine (antiPS-PT) antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and/or antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL).
Methods : We performed a prospective cohort study in a French University Hospital and tertiary care center. Consecutive patients with SLE and/or aPL without ongoing anticoagulant treatment were enrolled. The outcome was the time to the first incident thrombotic event. Blood was drawn at baseline. ELISA antiDI and antiPS-PT antibodies assays were performed together with traditional assays (lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin and anti-ß2-glycoprotein I antibodies).
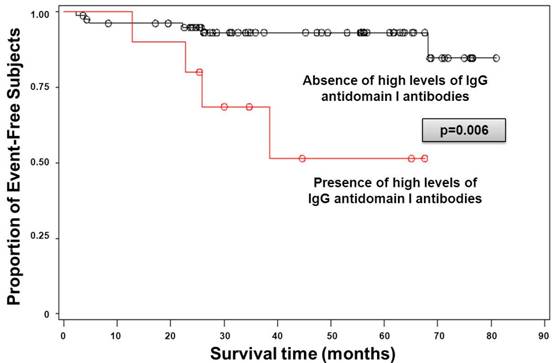
Results : Ninety-two patients (median age 40 years [interquartile range IQR: 29-58]; 74 women) were followed-up for a median duration of 35 months (IQR: 26-62; 320 patient-years). Thrombosis during follow-up occurred in 11 patients (2 strokes, 1 myocardial infarction, 1 splanchnic arterial thrombosis, 2 pulmonary embolisms, 2 deep vein thromboses, 3 small vessels thromboses). Triple positivity, high levels of antiDI and of antiPS-PT antibodies were found in 17, 10 and 13 patients respectively. In univariate analysis, high levels of antiDI (HR=6.41 [CI95%; 1.72-23.89], p=0.006) and antiPS-PT antibodies (HR=3.62 [CI95%, 1.06-12.37], p=0.04) were significantly predictive of incident thrombotic event while triple positivity did not reach statistical significance (HR=3.09 [CI95%; 0.90-10.66], p=0.07). In multivariate analysis (stepwise method), high levels of antiDI antibodies remained the only laboratory variable significantly predictive of incident thrombotic events overtime.
Conclusion : High levels of IgG antibodies directed against the domain I of the ß2-glycoprotein I are significant predictors of thrombosis in patients with aPL and/or SLE.
Disclosure:
S. Zuily,
None;
B. de Laat,
None;
F. Guillemin,
None;
P. Kaminsky,
None;
H. Kelchtermans,
None;
R. Albesa,
Inova Diagnostics, Inc.,
3;
G. L. Norman,
Inova Diagnostics, Inc.,
3;
A. C. Rat,
None;
P. de Groot,
None;
T. Lecompte,
None;
V. Regnault,
None;
D. Wahl,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/igg-antibodies-directed-against-domain-i-of-s2-glycoprotein-i-are-significant-predictors-of-thromboembolic-events-in-patients-with-antiphospholipid-antibodies-a-prospective-cohort-study/