Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) offer promising results for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients in general, but a substantial percentage of patients do not respond to them. It is important to predict the response before the treatment so that unnecessary adversities for the patients and costs for the healthcare system can be avoided. We developed a model to predict remissions in patients treated with bDMARDs and to identify important clinical features associated with remission using several machine learning (ML) models system that works with readily-available demographic and clinical factors for prediction of response to DAS-28.
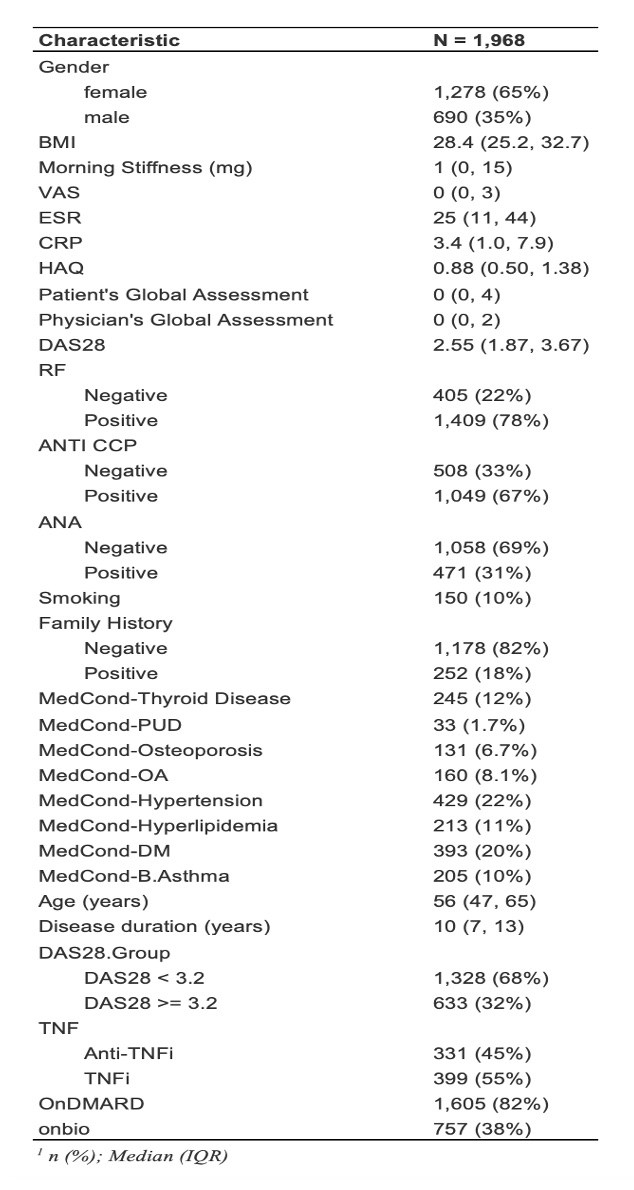
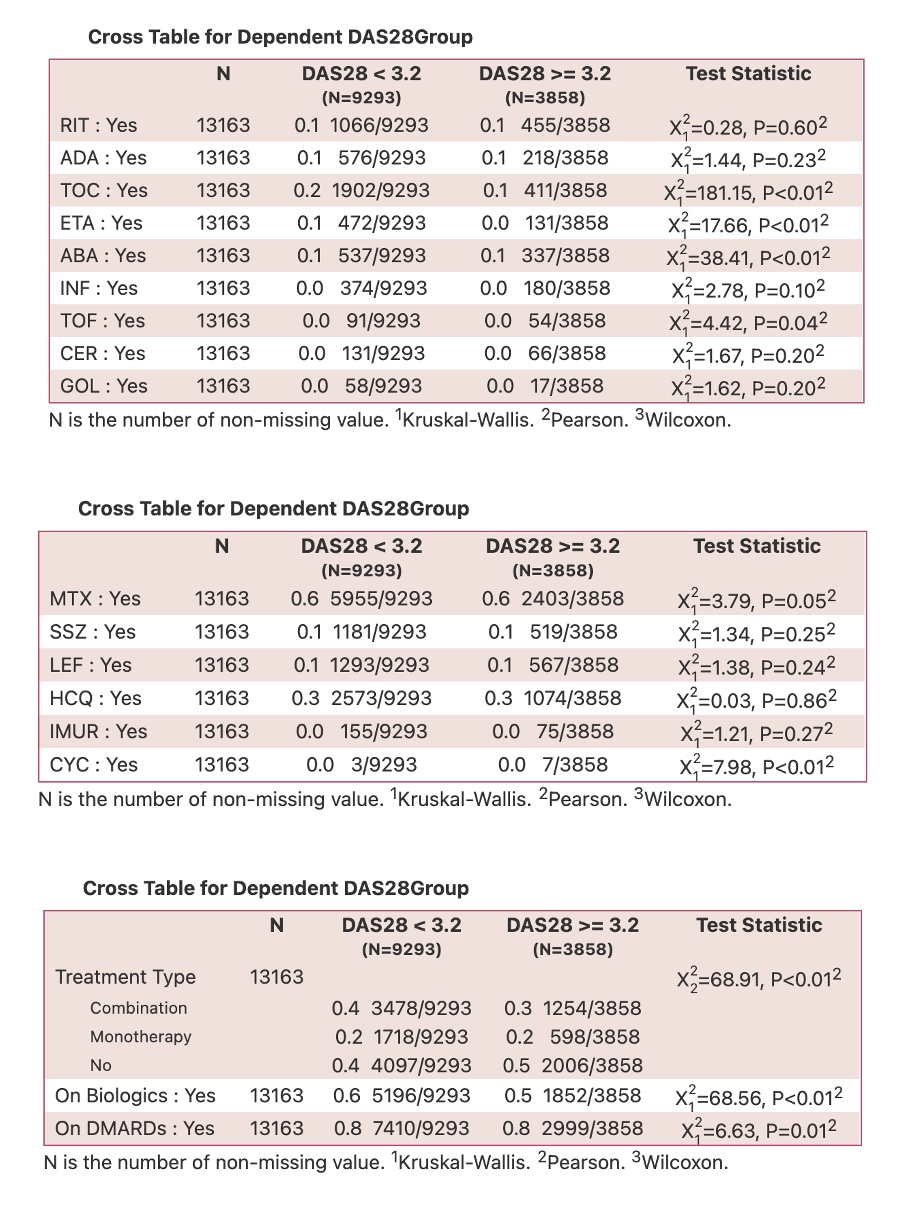
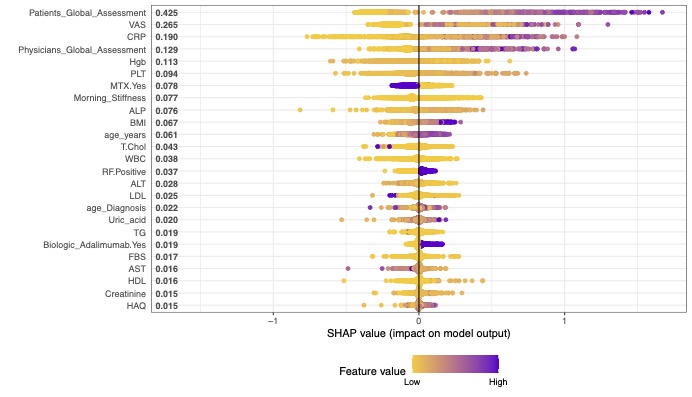
Methods: We gathered the follow-up data of 1,000 patients treated with bDMARDs (etanercept, adalimumab, golimumab, infliximab, abatacept, and tocilizumab) from KRRD. Patients were recruited from public hospitals in Kuwait between February 2013 to September 2022. Remission (DAS-28 less than 2.6) was predicted at 1-year follow-up using baseline clinical data obtained at the time of enrollment. Machine learning methods system (including: lasso, ridge, support vector machine, random forest, XGBoost, and Shapley additive explanation (SHAP)) were used for the predictions.
Results: The ranges for accuracy and area under the receiver operating characteristic of the newly developed machine learning model for predicting remission were 52.8–72.9% and 0.463–0.719, respectively. The Shapley plot in XAI showed that the impacts of the variables on predicting remission differed for each bDMARD. The most important features were age for adalimumab, rheumatoid factor for etanercept, erythrocyte sedimentation rate for infliximab and golimumab, disease duration for abatacept, and C-reactive protein for tocilizumab, with mean SHAP values of − 0.250, − 0.234, − 0.514, − 0.227, − 0.804, and 0.135, respectively.
Conclusion: Our proposed machine learning model system successfully identified clinical features that were predictive of remission in each of the bDMARDs. This approach may be useful for improving treatment outcomes by identifying clinical information related to remissions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alsaber A, AlHerz A, Alawadhi B, Setiya P, MOHAMMED K, Al-Awadhi A, Al-Kandari W, Hasan E, Mokaddem K, Ghanem A, Bartella Y, Hussain M, Alhadhood N, Ali Y, Nahar E, Aldei A, Alenizi A, Hayat S, Abutiban F, Abutiban F. Identifying Important Clinical Features for Predicting Remission in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Biologics Using Machine Learning Model [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identifying-important-clinical-features-for-predicting-remission-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-biologics-using-machine-learning-model/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identifying-important-clinical-features-for-predicting-remission-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-biologics-using-machine-learning-model/