Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster I: Strategy and Epidemiology
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tocilizumab, anti-interleukin 6 receptor (IL-6R) therapy, is an effective treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, a significant amount of patients do not respond adequately long term and would most likely benefit from changing treatment at an early time point. Biomarkers reflecting joint tissue degradation (e.g. C1M) are direct measures of joint health and have been shown to be prognostic of structural progression, as well as pharmacodynamics markers of tocilizumab response. We investigated whether lack of early changes in biomarkers, in response to tocilizumab, were predictive of lack of long-term (52 week) clinical benefit.
Methods: Pooled biomarker data from the two treatment arms (4 and 8 mg/kg tocilizumab + MTX) were included in this reanalysis of the LITHE (a phase III randomized placebo controlled study, NCT00106535) biomarker study (N=380). Patients had moderate-severe RA and were DMARD-IRs. Biomarkers reflecting tissue degradation were selected; type I, II, III, IV and VI collagen metabolites C1M, C2M, C3M, C4M and C6M. Missing biomarker data (<5%) were imputed using KNN. Patients were dichotomized into quartiles using 16-week %-suppression in the biomarkers. Long-term clinical benefit was assessed by ACR20 and ACR50 at week 52. Escape patients were annotated as ACR non-responders. Mann-Whitney was used to compare level of biomarker suppression between responders and non-responders. Logistic regression was used to predict lack of response, adjusting for age, sex, BMI and baseline biomarker level.
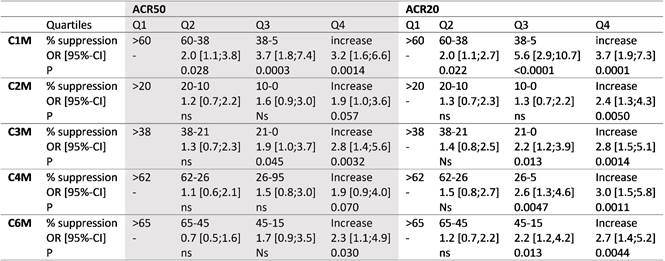
Results: There were a total of 196 (50.5%) ACR20 and 266 (70.0%) ACR50 non-responders at week 52. There were significant differences in the median levels of biomarker suppression between ACR non-responders and responders: i) C1M; ACR20, 28 vs. 47% (p=0.0004), ACR50, 34 vs. 45% (p=0.02), ii) C2M; ACR20, 7 vs. 13% (p=0.007), ACR50, 8 vs. 13% (p=0.02), iii) C3M; ACR20, 14 vs. 28% (p=0.0008), ACR50, 17 vs. 30% (p=0.009), iv) C4M; ACR20, 20 vs. 30% (p=0.0001), ACR50, 22 vs. 29% (p=0.04), and v) C6M; ACR20, 36 vs. 53% (p=0.0004), ACR50, 37 vs. 56% (p=0.004). C1M was the best marker for prediction of whom would not respond to tocilizumab. Patients with a 38 to 60% suppression in C1M were 2.0 times more likely to achieve an ACR50, whereas patient with less than a 38% suppression were 3.2 to 3.7 more likely not to achieve an ACR50 response and 3.7 to 5.6 more likely not to achieve an ACR20 response (table). The remaining markers could predict lack of ACR50 with ORs from 1.9 to 2.9 and ACR20 with ORs from 2.4 to 3.0, if the marker actually increased from baseline to 16 weeks (Q4, table).
Conclusion: We found that lack of early inhibition in tissue turnover biomarkers, especially C1M, were predictive of long term lack of clinical benefit. This indicates that biomarkers associated with joint tissue health may be used as patient monitoring and risk-assessment tool for anti-IL6 effect.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bay-Jensen AC, Thudium CS, Christiansen C, Karsdal MA. Identification of Tocilizumab Treated RA Patients, Whom Are Not Likely to Show Long-Term Clinical Benefit; Reanalysis of the Biomarker Sub-Study of LITHE [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-tocilizumab-treated-ra-patients-whom-are-not-likely-to-show-long-term-clinical-benefit-reanalysis-of-the-biomarker-sub-study-of-lithe/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-tocilizumab-treated-ra-patients-whom-are-not-likely-to-show-long-term-clinical-benefit-reanalysis-of-the-biomarker-sub-study-of-lithe/