Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Employing
genome-wide gene transcription on a unified platform, to identify molecular signatures
for predicting therapeutic effects for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with three
biologics, infliximab (IFX), tocilizumab (TCZ), and abatacept (ABT).
Methods: Two hundred and
three RA patients who were methotrexate-inadequate response and the first
biologic administered were enrolled (IFX: 139, TCZ: 34, ABT: 30). Whole blood
gene transcription data of each patient were obtained using a unified platform,
Agilent Whole Genome Microarray 44K prior to administration of drugs. Using
gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA), a priori defined functional set of genes,
such as Reactome pathways and blood cell subtype-specific transcripts, were
analyzed to find the difference of biological characteristics between remittors
and non-remittors based on CDAI at 6th month of treatment. “Signature scores”
of the gene sets derived from the GSEA results was calculated for each patient
and then was reviewed using logistic regression and ROC analysis.
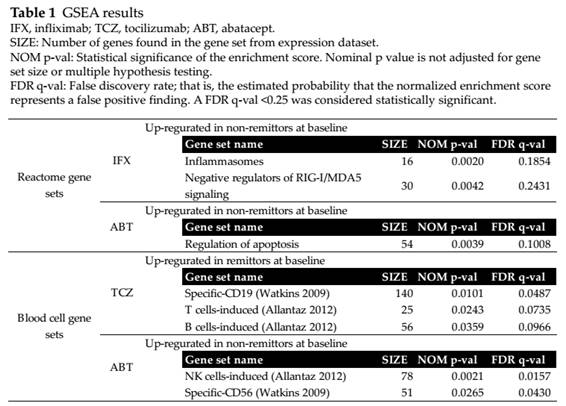
Results: Based on GSEA,
innate immunity pathways (inflammasomes and negative regulators of RIG-I/MDA5
signaling) were significantly upregulated in baseline peripheral blood of
non-remitters in IFX (table 1). In TCZ, genes specifically expressed in B or T
cells were significantly upregulated in remitters. Apoptosis related or NK
cells-specific genes were related with ABT treatment outcome. Univariate
logistic regression of signature scores supported the GSEA results.
Multivariate logistic regression adjusting to clinical background showed
inflammasomes genes for IFX, CD19 cells-specific genes for TCZ, CD56
cells-specific genes for ABT as significant independent predictive factors. The
AUCs of ROC curve of each signature score were 0.638 (95% CI: 0.538-0.739), 0.769
(95% CI: 0.596-0.943), and 0.764 (95% CI: 0.575-0.953) for IFX, TCZ, and ABT,
respectively.
Conclusion:
We
have shown a long sought objective means to predict the therapeutic effects of
biologics using multiple expression markers expressed in peripheral blood. Each
signature is shown to be associated with biological function underlying the
therapeutic mechanism.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nakamura S, Iijima H, Hata Y, Ishizawa Y, Lim CR, Matoba R, Suzuki K, Amano K, Takeuchi T. Identification of the Gene Expression Signatures Predicting the Responses to Three Biologics (infliximab, tocilizumab, and abatacept) in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-the-gene-expression-signatures-predicting-the-responses-to-three-biologics-infliximab-tocilizumab-and-abatacept-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-the-gene-expression-signatures-predicting-the-responses-to-three-biologics-infliximab-tocilizumab-and-abatacept-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/