Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: 5T095: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorder – Basic Science (2744–2749)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Autoimmune responses to DNA topoisomerase-I (TOP1) are found in a subset of patients with scleroderma at high risk for interstitial lung disease (ILD) and mortality. Anti-TOP1 antibodies (ATA) are associated with specific HLA-DRB1 alleles, and the frequency of HLA-DR-restricted TOP1-specific CD4+ T cells is associated with the presence, severity, and progression of ILD. Although this strongly implicates the presentation of TOP1 peptides by HLA-DR in scleroderma pathogenesis, the processing and presentation of TOP1 has not been studied.
Methods: We developed a novel natural antigen processing assay (NAPA) which relies on the sensitivity and specificity of the cellular MHC class II antigen processing machinery. Monocyte-derived dendritic cells were generated from six SSc patients with anti-Topo-I antibodies (ATA) and pulsed with Topo-I protein. HLA-DR:peptide complexes were isolated by immunoprecipitation and eluted peptides were analyzed by mass spectrometry. We then examined the ability of these naturally presented putative epitopes to induce CD4+ T cell activation, as measured by upregulation of the early activation marker CD154 in PBMCs from ATA-positive (n=11) and ATA-negative (n=11) SSc patients.
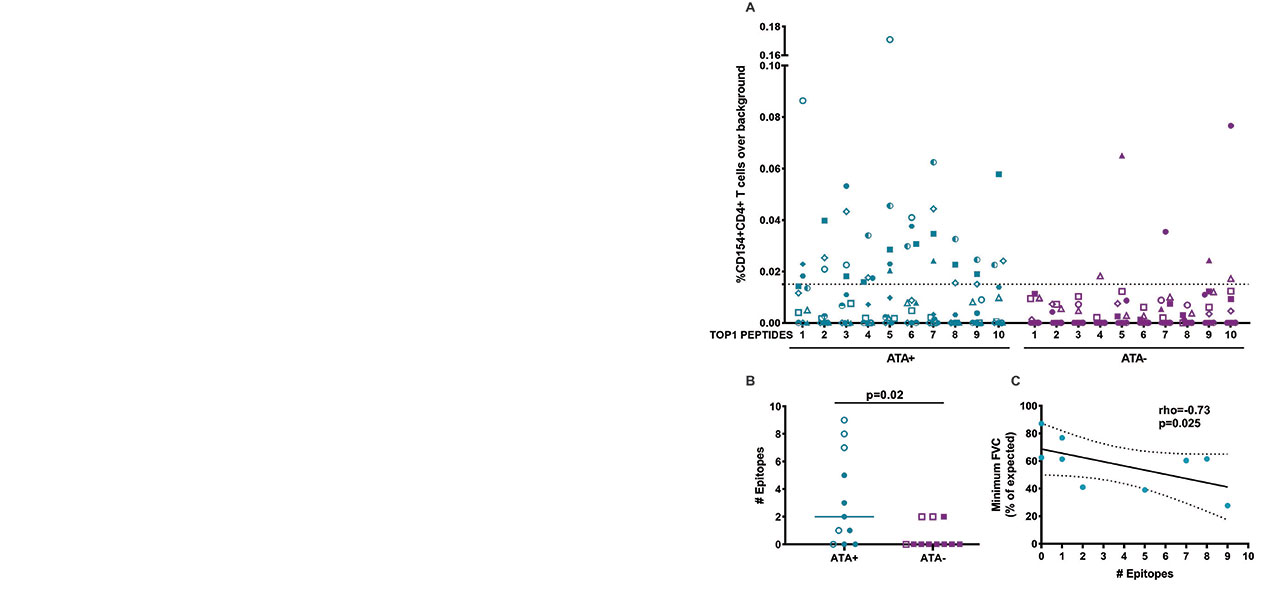
Results: Using NAPA, we found that presentation of TOP1 epitopes was restricted to only 10 hot spots within TOP1, across patients with different HLA-DR variants. Further analysis revealed shared peptide-binding motifs within the HLA-DRβ chains of ATA-positive patients and a subset of TOP1 epitopes with distinct sets of anchor residues capable of binding to multiple different HLA-DR variants. The naturally presented TOP1 peptides elicited robust CD4+ T cell responses in ATA-positive patients, and the number of epitopes recognized correlated with the severity of lung fibrosis (Figure 1).
Conclusion: This study suggests a mechanism in which autoimmunity to TOP1 in scleroderma is driven by the presentation of a communal set of TOP1 peptides in patients with diverse HLA-DRB1 alleles.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tiniakou E, Fava A, McMahan* Z, Gurh T, O'Meally R, Shah A, Wigley F, Cole R, Boin F, Darrah E. Identification of Naturally Presented Peptides of the Autoantigen Topoisomerase-I Reveals a Common Pathogenic Mechanism in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-naturally-presented-peptides-of-the-autoantigen-topoisomerase-i-reveals-a-common-pathogenic-mechanism-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-naturally-presented-peptides-of-the-autoantigen-topoisomerase-i-reveals-a-common-pathogenic-mechanism-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/