Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Treatments, Outcomes, & Measures
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex autoimmune disease with a fluctuating course of disease activity and progression. Although treatments have improved substantially in recent years thanks to the development of novel drugs, response is not guaranteed. Also, response is often monitored in a binary, and not a dynamic way, resulting in loss of information about the level of response. The aim of this study was to identify heterogeneity in Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28) in response to tocilizumab in RA patients and investigate molecular and clinical factors which may cause this.
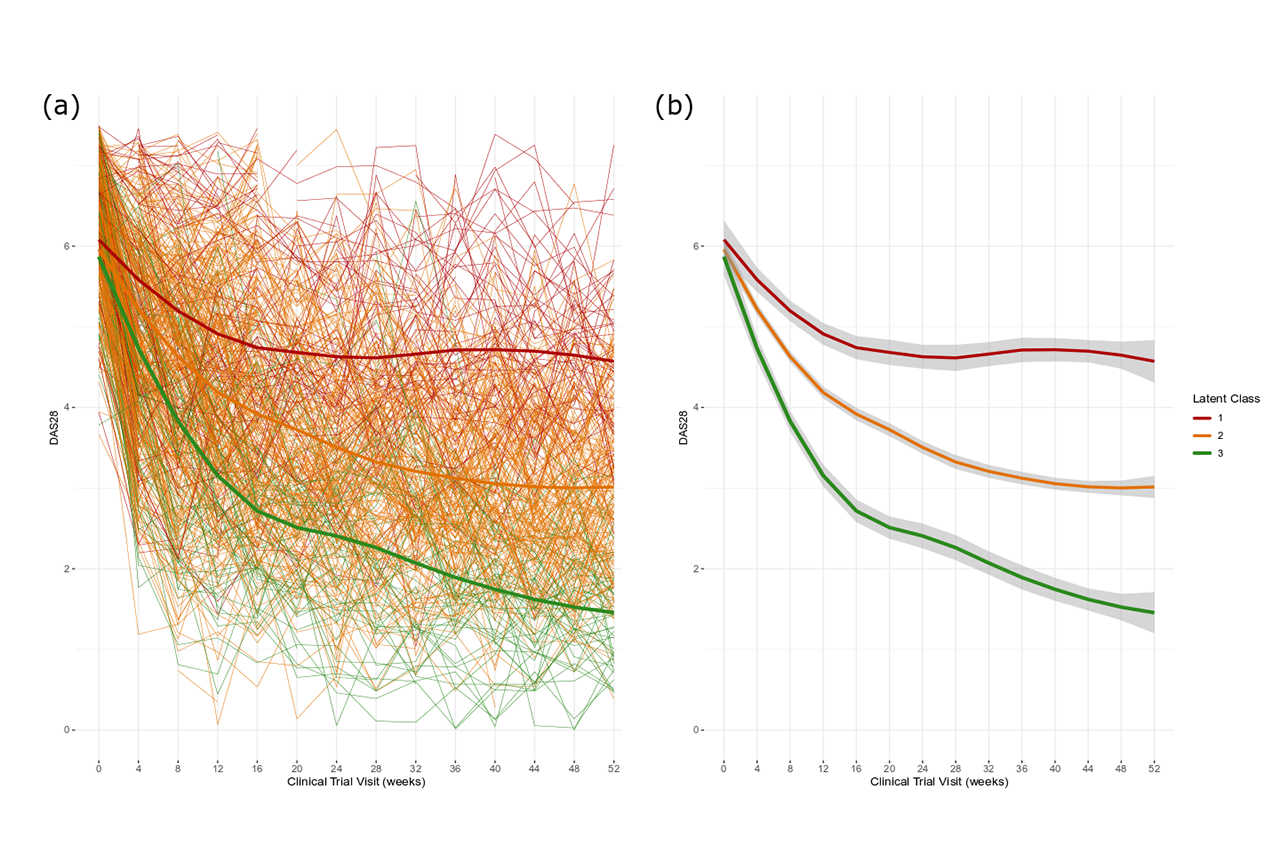
Methods: Longitudinal clinical and biochemical data, as well as baseline demographics for 485 RA patients receiving 4 or 8 mg/kg tocilizumab in combination with MTX, were extracted from the LITHE phase III clinical study (NCT00106535), and post-hoc and exploratory analysis was conducted. Latent class mixed models were used in order to identify distinct trajectories of patients’ disease activity using DAS28 after the initiation of treatment. The optimal number of classes was selected using Bayesian Information Criteria (BIC) and Akaike Information Criteria (AIC). Longitudinal and cross-sectional measurements were then analysed using linear mixed effects models in order to characterise patients by serological biomarker levels, and other clinical factors, and identify correlations between drug response and patient characteristics.
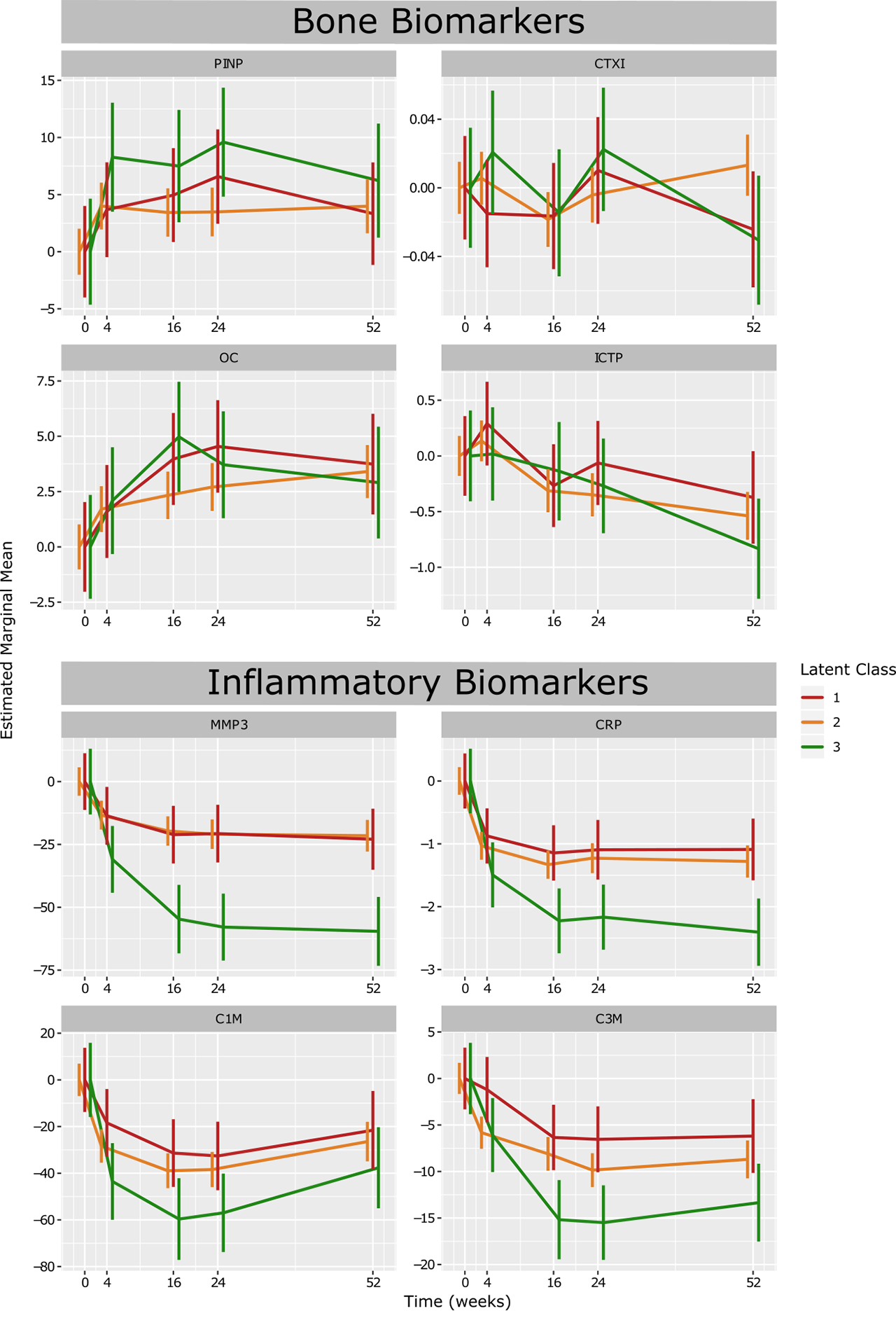
Results: Trajectory analysis identified three distinct response subgroups of patients: class 1 (n = 85, 25.9%), class 2 (n=338, 63.9%) and class 3 (n=62, 10.4%). All groups started with a high DAS28 on average (DAS28 > 5.1). Class 1 showed the least reduction in DAS28, with a significantly higher proportion of patients seeking escape therapy (p < 0.001). Class 3 showed significantly higher rates of improvement in DAS28 achieving remission status, as well as having the highest rates of patients achieving ACR response levels (p < 0.001). Biomarkers associated with inflammation, MMP-3, CRP, C1M, and C3M, were markedly decreased from baseline levels in class 3 in response to treatment compared to the other classes.
Conclusion: Identification of more distinct patient populations of drug response may allow for more targeted therapeutic treatment regimens. Treatment strategies should consider the initial state of disease severity as well as clinical and biochemical disease parameters to achieve optimal response rates.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Blair J, Bager C, Tang M, Karsdal M, Bay-Jensen A, Brunak S. Identification of Heterogenous Treatment Response Trajectories to anti-IL6 Receptor Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-heterogenous-treatment-response-trajectories-to-anti-il6-receptor-treatment-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-heterogenous-treatment-response-trajectories-to-anti-il6-receptor-treatment-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/