Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0380–0422) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is the result of the complex interplay between genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors leading to immune dysregulation, synovial membrane inflammation, and disability. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are non-coding RNA molecules that alter mRNA expression, affecting multiple molecular pathways. Growing evidence suggests that miRNAs are implicated in the onset and development of RA but studies about their association with disease activity are scant. We conducted a pilot study to identify miRNAs differentially expressed in patients with RA and applied Artificial Neural Network (ANN) analysis to build a classificatory model that explored the association between levels of differentially expressed miRNAs and disease activity using Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI).
Methods: We recruited 43 subjects, 18 healthy controls (HC), and 25 RA patients. Serum from all participants was collected, exosomes isolated, and miRNAs extracted. Using the Nanostring nCounter miRNA expression panel, levels of 800 miRNAs were determined. We identified 9 miRNAs using nSolver software analysis that had the largest difference (top 10%) between groups and a RA:HC ratio in the top 50%. In subsequent analysis, we also included 4 previously reported RA-relevant miRNAs. The 13 miRNA panel showed good discrimination between RA and HC (Figure 1A). We used the Mann-Whitney t-test to identify mean differences and Pearson correlation to assess the association between miRNA levels and CDAI. ANN analysis was used to build a classificatory model. All analysis was carried out with SPSS v.28, p≤0.05 was considered statistically significant, and Pearson correlation coefficients were important when p<0.05 and/or the effect size (ES) was moderate or high (ES >0.3).
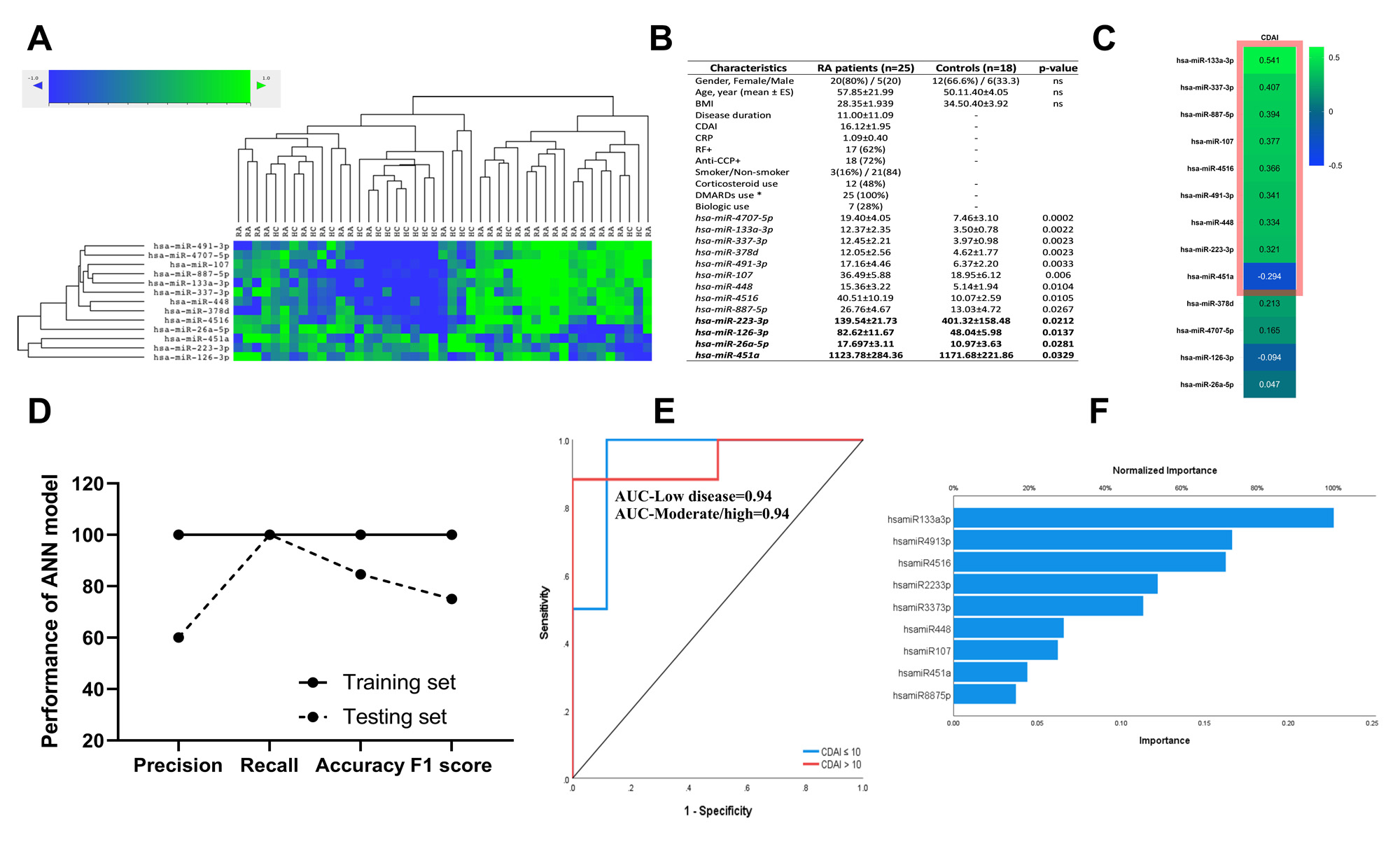
Results: Of the 13 identified RA-relevant miRNAs in this study (Figure 1A, B), 9 correlated with CDAI (Figure 1C). These 9 miRNAs, miR -133a-3p, miR-337-3p, miR -887-5p, miR-107, miR-4516, miR-491-3p, miR-448, miR-223-3p, and miR-451a, were further selected for the ANN analysis. 70% of the sample was used to train the ANN model and 30% to test it. The training set scored 100% in all performance metrics (Figure 1D), whereas the testing set performed 80% in recall and accuracy, 60% in precision, and 75% in F1 score. The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) illustrates the diagnostic ability of the model expressed as low (CDAI≤10) and moderate/high (CDAI >10) disease activity. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) is 0.94 indicating excellent classificatory prediction for the model (Figure 1E). The 4 miRNAs that most contributed to the model were miR-133a-3p, miR-491-3p, miR-4516, and miR-223-3p (Figure 1F).
Conclusion: Our study for the first time describes miR-133a-3p, miR-491-3p, and miR-4516 as differentially expressed in RA. We also described 9 miRNAs not previously correlated with RA disease activity. An ANN model built with these 9 miRNAs had an excellent classificatory capacity for RA patients with low or moderate-high disease activity, therefore providing a new set of potential biomarkers as a starting point to assess RA disease activity and response to treatment in future studies.
-A- Unsupervised hierarchical cluster analysis of 13 exosomal miRNA levels in RA patients and healthy controls (HC). -B- Demographics data and miRNA levels in RA patients and HC. -C- Heatmap of Pearson correlation coefficients between 13 miRNAs levels and CDAI numeric values.Statistical significant correlations (p<0.05 and/or ES≥0.3) are enclosed in a pink-colored box. -D-. Performance of the ANN model classifying disease activity of RA patients based on miRNAs. -E- ROC curve for the ANN Model and AUC values to predict disease activity levels. -F- Normalized contribution of each miRNAs to the ANN model.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rodriguez Alvarez M, Delgado-Cruzata L, Tryfonos A, Almodovar N, Bravo T, Kabani N. Identification of Disease Activity-related miRNAs Through Artificial Neural Network Analysis in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-disease-activity-related-mirnas-through-artificial-neural-network-analysis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-disease-activity-related-mirnas-through-artificial-neural-network-analysis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/