Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Metabolomics is an emergent research field within the omics sciences aimed at characterizing the metabolome in complex biological samples. It provides a powerful approach to identify physiopathological processes and metabolites can be useful biomarkers in clinically relevant applications. The present study represents the first metabolomic analysis on a large cohort including multiple immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs). Its objective is the identification of diagnostic and activity biomarkers through the analysis of the whole urine metabolome of 6 IMIDs.
Methods:
Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) data of urine samples was acquired among 6 IMID cohorts (n=200 Spanish patients per cohort) including: rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriasis (PS), psoriatic arthritis (PA), Crohn’s disease (CD), ulcerative colitis (UC) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Each IMID cohort was selected in order to include low and high activity patients according to the consensus activity indexes of each disease. Distributions of sex, age, extraction time and fasting time were matched between these cohorts to avoid false positive associations due to these confounding variables. 1H-NMR data of 100 control individuals was also acquired in this study. Spectral processing was performed using Focus. Mann-Whitney U test was used to evaluate potential diagnostic and activity biomarkers. A multivariate analysis (i.e. logistic regression) was also performed to avoid false positive associations due to confounding epidemiological or clinical variables. A clustering analysis was also conducted to evaluate disease similarity according to the urine metabolome.
Results:
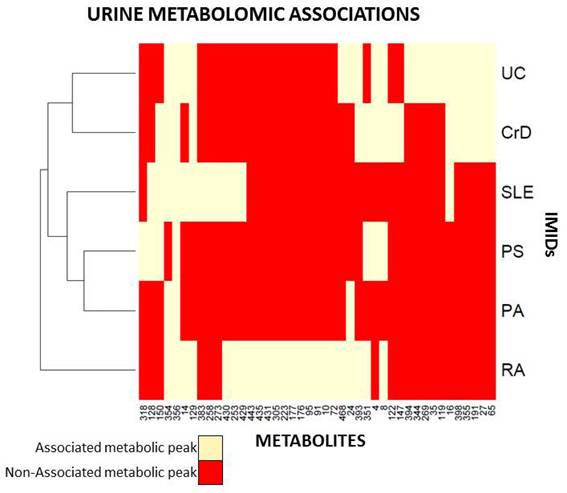
After processing the spectral data n=473 peaks were identified. This set was reduced to n=145 peaks after applying several quality control filters. The statistical analysis identified 45 metabolic peaks significantly associated (P-Value<1E-4) in at least one of the performed disease diagnostic or activity tests (Figure 1). When analyzing each IMID cohort separately, RA, CD and UC obtained the largest number of diagnostic biomarker candidates: n=27, n=18 and n=21 respectively. Interestingly, CD and UC shared common metabolic disturbances although differential biomarkers between them were also identified. PS and PA showed a little impact on their metabolic profiles. On the other side, when comparing low to high disease activity patients a lower number of significant associations were observed, mainly related to CD and RA.
Conclusion:
A significant number of diagnostic biomarker candidates have been identified on this first large cohort of IMIDs. Several candidates were found to be global IMID biomarkers and could target the common inflammatory process shared by these diseases. RA showed the largest burden on urine metabolic disturbances and interesting activity biomarkers were identified for RA and CD.
Figure 1. Urine metabolomic associations
Disclosure:
A. Alonso,
None;
J. Tornero,
None;
A. Fernandez Nebro,
None;
J. D. Cañete,
None;
E. Domènech,
None;
J. P. Gisbert,
None;
C. Ferrándiz,
None;
E. Fonseca,
None;
V. García,
None;
F. Blanco,
None;
J. Rodriguez,
None;
J. Gratacós,
None;
P. Carreira,
None;
T. Julia,
None;
R. Tortosa,
None;
M. A. López-Lasanta,
None;
X. Correig,
None;
S. Marsal,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-diagnostic-and-activity-metabolomic-urine-biomarkers-in-six-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases/