Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments III: Predictors of Treatment Response (2003–2007)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-4:50PM
Background/Purpose: Despite the existence of guidelines for DMARD treatment of RA, a more individualized approach to treatment is needed to maximize efficacy while minimizing risk of adverse events. In phase 3 trials, sarilumab, an IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) inhibitor approved for treatment of moderate to severe RA, has been shown to be superior to both placebo (clinical trials MOBILITY [NCT01061736] and TARGET [NCT01709578]) and the TNF-α inhibitor adalimumab (MONARCH [NCT02332590]). However, the characteristics of patients who are most likely to benefit from sarilumab treatment remain poorly understood. Here, we describe the application of machine learning to select from a predefined set of patient characteristics that could facilitate the choice between anti-IL-6R and anti-TNF-α treatment, using data from the sarilumab clinical development program.
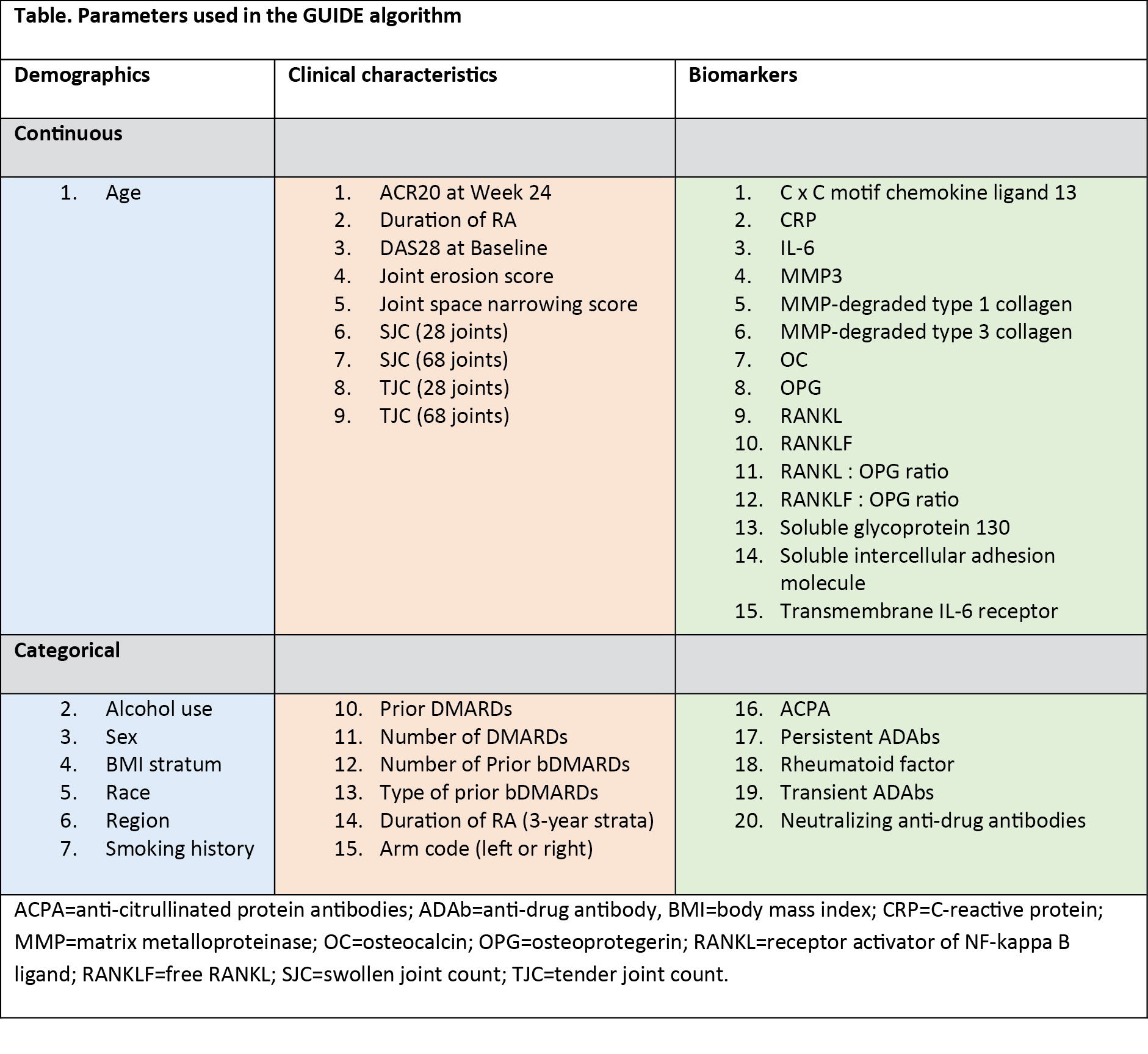
Methods: A decision tree classification approach was used to build predictive models on ACR response criteria at Week 24 in patients from MOBILITY, using the Generalized, Unbiased, Interaction Detection and Estimation (GUIDE) algorithm (Version 27.9; available as free software). A total of 17 categorical and 25 continuous baseline variables were included as candidate predictors, chosen based on subject matter expertise. These included protein biomarkers, disease activity scoring, and demographic data (Table). The endpoints used were ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 at Week 24. The resulting rule was validated through application on independent data sets from MOBILITY (N=1197; sarilumab [150 mg and 200 mg combined], 799; placebo, 398), TARGET (N=546; sarilumab [150 mg and 200 mg combined], 365; placebo, 181), and MONARCH (N=369; sarilumab, 184; adalimumab, 185), as well as on the tocilizumab-calibrator study ASCERTAIN (NCT01768572; N=202; sarilumab [150 mg and 200 mg combined], 100; tocilizumab, 102). The analysis focused on the 200 mg sarilumab dose.
Results: The most successful GUIDE model was trained against the ACR20 response. Out of the 42 candidate variables, the combined presence of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) and CRP >12.3 mg/L was identified as a predictor (ie, rule) of better treatment outcomes with sarilumab. Rule-positive patients (34-51% in sarilumab groups across the 4 trials) had more severe disease and poorer prognostic factors at baseline. Rule-positive patients had a better outcome than rule-negative patients for most endpoints assessed, with the exceptions observed in patients with inadequate response to TNF inhibitors (TARGET; Figure 1). In addition, rule-positive patients had a better response to sarilumab but an inferior response to adalimumab, with the exception of HAQ-Disability Index minimal clinically important difference endpoint (Figure 2), equivalent to an approximately 5-fold difference in the chance of achieving ACR70 (34% versus 7%).
Conclusion: Machine learning ascertained a simple selection rule, ACPA positivity and CRP >12.3 mg/L, to identify patients with an increased chance of achieving clinical response with sarilumab. If verified in prospective studies, this rule could facilitate treatment decision-making for patients with RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rehberg M, Giegerich C, Praestgaard A, van Hoogstraten H, Iglesias-Rodriguez M, Curtis J, Gottenberg J, Schwarting A, Castañeda S, Rubbert Roth A, Choy E. Identification of a Rule to Predict Response to Sarilumab in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Machine Learning and Clinical Trial Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-a-rule-to-predict-response-to-sarilumab-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-machine-learning-and-clinical-trial-data/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-a-rule-to-predict-response-to-sarilumab-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-machine-learning-and-clinical-trial-data/