Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Clinical Poster II: Biomarkers and Outcomes
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
iC3b/C3 Ratios More Strongly Correlate with SLE Disease Activity in African-Americans Compared with Whites
Background/Purpose: Complement activation is a hallmark of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) pathophysiology. iC3b is a complement split product of C3b formed during complement activation. We have previously found that iC3b/C3 ratios associated with both active disease and clinically meaningful changes in SLE disease activity. Since SLE is more severe in nonwhite populations, we hypothesized that iC3b/C3 ratios would be a more sensitive marker of disease activity and examined this relationship in African-American (AA) and white subjects with SLE.
Methods: 159 adult SLE (92 AA and 67 white) patients were enrolled. C3 and C4 were measured by nephelometry; iC3b by a lateral flow assay. SLE disease activity was measured using the SLEDAI 2K Responder Index-50 (S2K RI-50). Statistical analyses were performed using SAS v9.4. Multilevel regression models examined associations with SLE disease activity. Ordinal logistic regression models with generalized estimating equation (GEE) modeling examined associations with clinically meaningful changes since the outcome variable is ordinal. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were estimated using Proc GLIMMIX and Proc GENMOD.
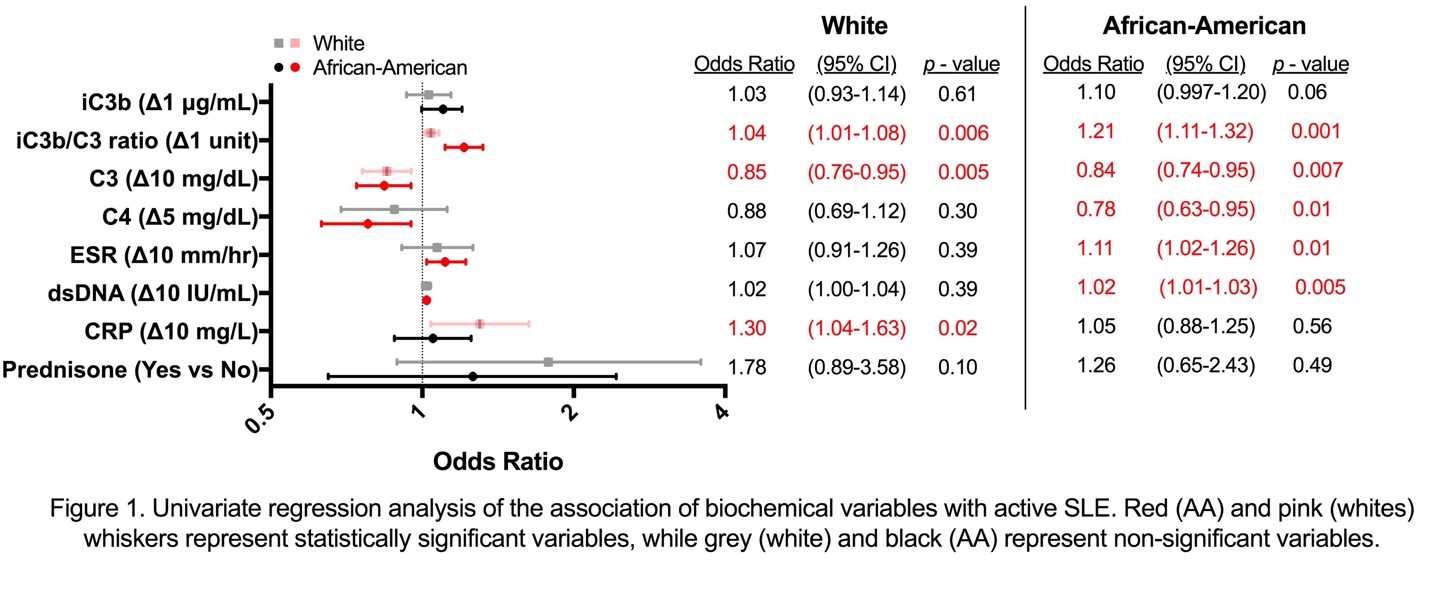
Results: Both iC3b/C3 ratios and C3 associated with active disease in AA and whites in univariate regression analysis, although association of the iC3b/C3 ratio was stronger in AA (Figure 1). In AA, active disease also associated with C4, ESR, and dsDNA levels, whereas it was CRP in whites. Association of iC3b/C3 ratios was independent of other variables in multiple regression analysis (AA: OR=1.48, 95% CI=1.21-1.82; whites: OR=1.17, 95% CI=1.02-1.34).
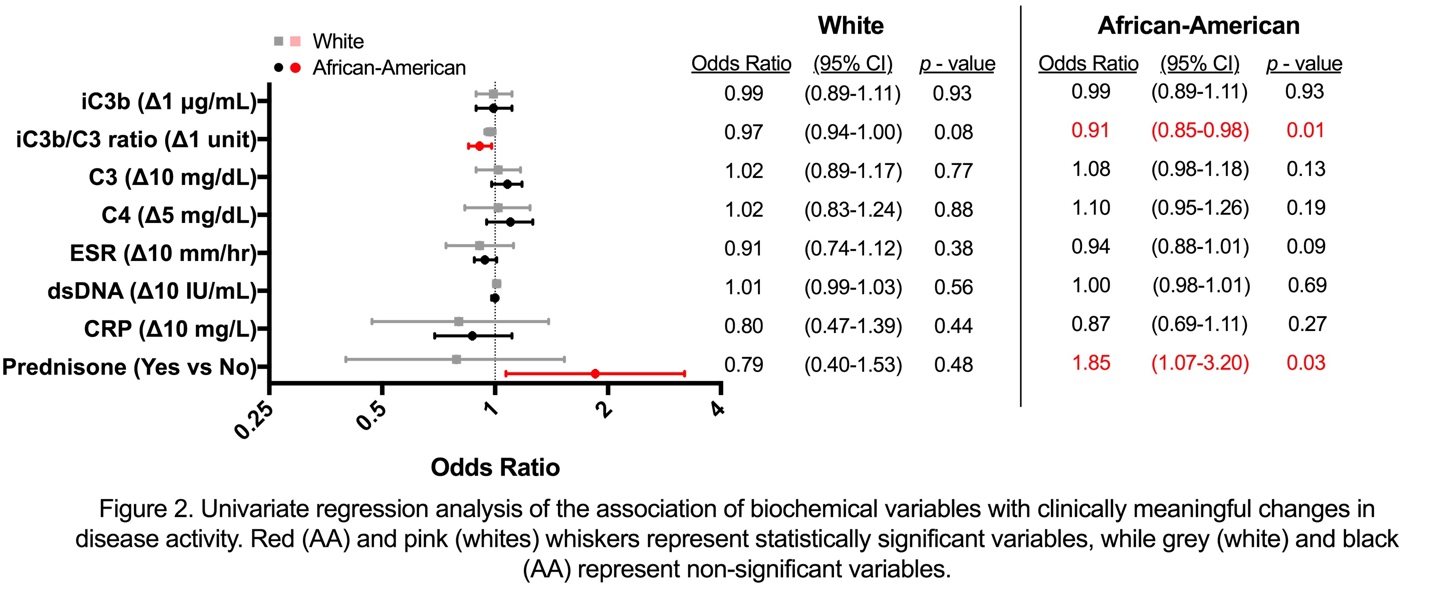
We next examined whether there were differences in clinical meaningful changes in disease activity and iC3b/C3 ratios with race. In univariate regression analysis, iC3b/C3 ratios were associated with clinically meaningful changes in disease activity in AAs; less so in whites. (Figure 2). In multiple regression analysis, an association was demonstrated in both races; stronger in AA (AA: OR=0.89, 95% CI=0.83-0.96, whites: OR=0.92, 95% CI=0.88-0.97).
Conclusion: iC3/C3 ratios were more strongly associated with active SLE and clinically meaningful changes in disease activity in AA compared with whites. This likely reflects either racial differences in complement activation or disease phenotypes. Our data suggest that the iC3b/C3 ratio is a valuable biomarker in AA SLE patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sen D, Strand V, Mathis N, Fu Q, Kim A. iC3b/C3 Ratios More Strongly Correlate with SLE Disease Activity in African-Americans Compared to Whites [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ic3b-c3-ratios-more-strongly-correlate-with-sle-disease-activity-in-african-americans-compared-to-whites/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ic3b-c3-ratios-more-strongly-correlate-with-sle-disease-activity-in-african-americans-compared-to-whites/