Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Ianalumab (VAY736), a B cell activating factor receptor (BAFFR) targeting mAb, depletes B cells via both antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity and blockade of BAFF:BAFFR mediated survival signals. The aim of the study was to assess changes in B cell subsets, whole blood transcriptome and serum proteome in patients with SLE, treated with ianalumab to characterize pharmacodynamic (PD) effects, disease modification and clinical response signatures.
Methods: A randomized, parallel group, double blind, placebo (PBO) controlled phase 2 trial (NCT03656562) evaluated PD and preliminary clinical efficacy of ianalumab (n=34, 300 mg monthly SC injection) vs PBO (n=33) in patients with moderate to severe SLE. Blood samples were collected in both groups at baseline (BL) through Week (W) 28 (double blind) up to W52 (open label) and W68 (post treatment). Cellular analysis was performed by flow cytometry, whole blood transcriptome analysis by Illumina Stranded kit, and soluble proteins by SomaScanTM.
Results: A marked reduction in total CD19+ B cell counts and double negative, naïve and memory B cells, and plasmablasts/plasma cells with ianalumab was seen at both W28 and W52 vs PBO or BL and up to W68, demonstrating durability of ianalumab PD effects post treatment.
Transcriptome analysis identified a set of 231, differentially expressed genes at both W28 and W52 in ianalumab treated patients (fold change >1.5; P< 0.05), mostly related to B cell and neutrophil. Further pathway analysis of modulated transcripts identified downregulation of IFN response and inhibition of apoptosis peaking at W28, while B cell receptor signaling, Fcγ receptor and neutrophil degranulation were downregulated at both timepoints with further downregulation at W52 indicating exposure-dependent differences. At W68, 73 B cell related genes (eg. CD19 and FCRL members) remained downregulated, showing durability of PD effects post ianalumab treatment and suggesting lasting depletion of tissue resident B cells.
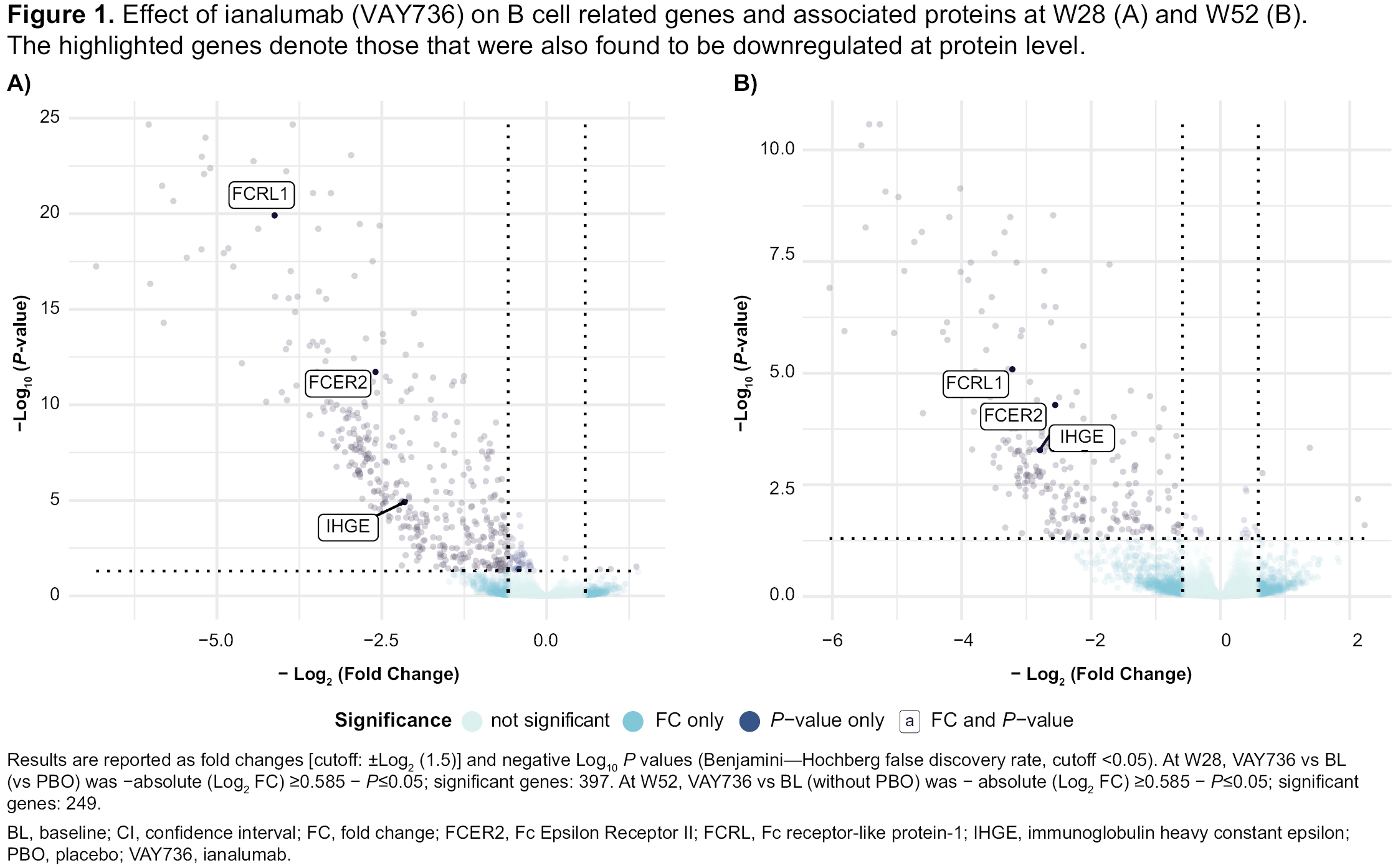
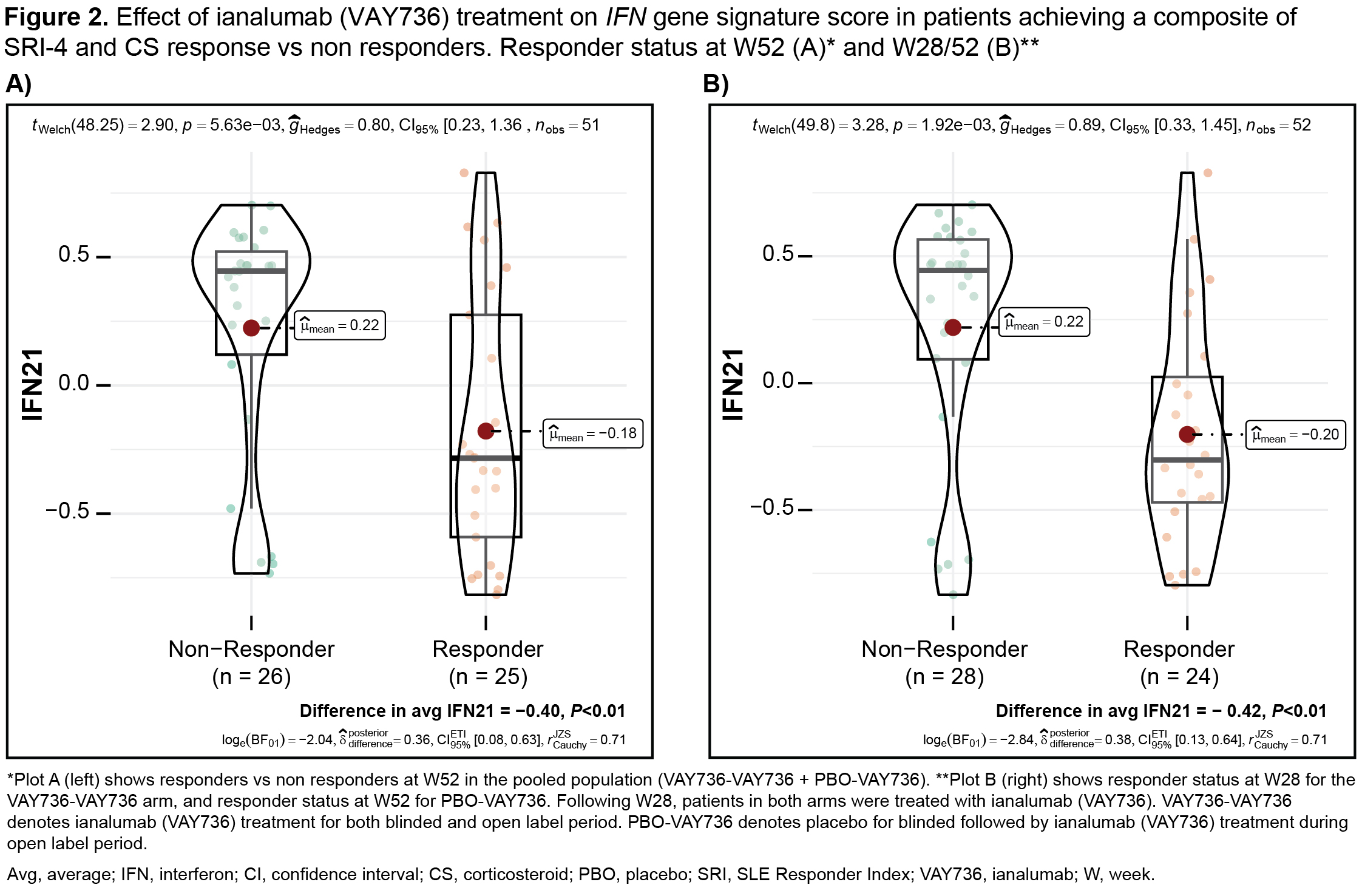
Proteomics analysis revealed a set of 9 differentially expressed (fold change >1.5; P< 0.05) B cell and neutrophil biology related proteins with overlap of changes at transcript level (Figure 1); 4 of these (eg. FCRL1 and 4) were further downregulated by W52 vs W28 demonstrating exposure dependent effects and remained downregulated by W68 indicating durability of PD effects. Patients achieving a composite of SLE Responder Index (SRI-4) and CS response at W52 on ianalumab independent of exposure duration had a significant decrease in transcriptional IFN gene signature score vs non responders (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Ianalumab treatment of patients with SLE led to a profound B cell depletion with durable reduction in B cell and neutrophil pathways, indicating durability of PD effects post ianalumab treatment and suggesting lasting depletion of tissue resident B cells. At W52, responders of SRI-4 with sustained, tapered and CS showed a significant decrease in the IFN gene signature score vs non responders. As neutrophils associate with extracellular trap formation and contribute to autoantibody and type I IFN production, our results also provide further characterization of disease modification pathways by ianalumab.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rowlands M, Dörner T, Miranda D, McMullen J, Santos da Costa A, Sommer U, Hillenbrand R, Nogueira da Costa A, Bonal C, Isnardi I, Khokhlovich E, J Oliver S. Ianalumab Induced Durable Depletion of Circulating B Cell Subsets and Associated Changes in B Cell and Neutrophil Transcriptomic and Proteomic Profiles in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: 52-Week Treatment Results from a Phase 2 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ianalumab-induced-durable-depletion-of-circulating-b-cell-subsets-and-associated-changes-in-b-cell-and-neutrophil-transcriptomic-and-proteomic-profiles-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-5/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ianalumab-induced-durable-depletion-of-circulating-b-cell-subsets-and-associated-changes-in-b-cell-and-neutrophil-transcriptomic-and-proteomic-profiles-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-5/