Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Limited information is available regarding how medical comorbidities affect the outcomes of total knee arthroplasty (TKA). The association of medical comorbidities with post-TKA outcomes may vary by the primary underlying cause leading to TKA. We evaluated the association of hypothyroidism with TKA outcomes, overall and by the primary diagnoses categorized as knee osteoarthritis (OA), avascular necrosis (AVN), fractures, and inflammatory arthritis including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), or spondylarthritis (SpA) (ankylosing spondylitis (AS), psoriatic arthritis (PsA)).
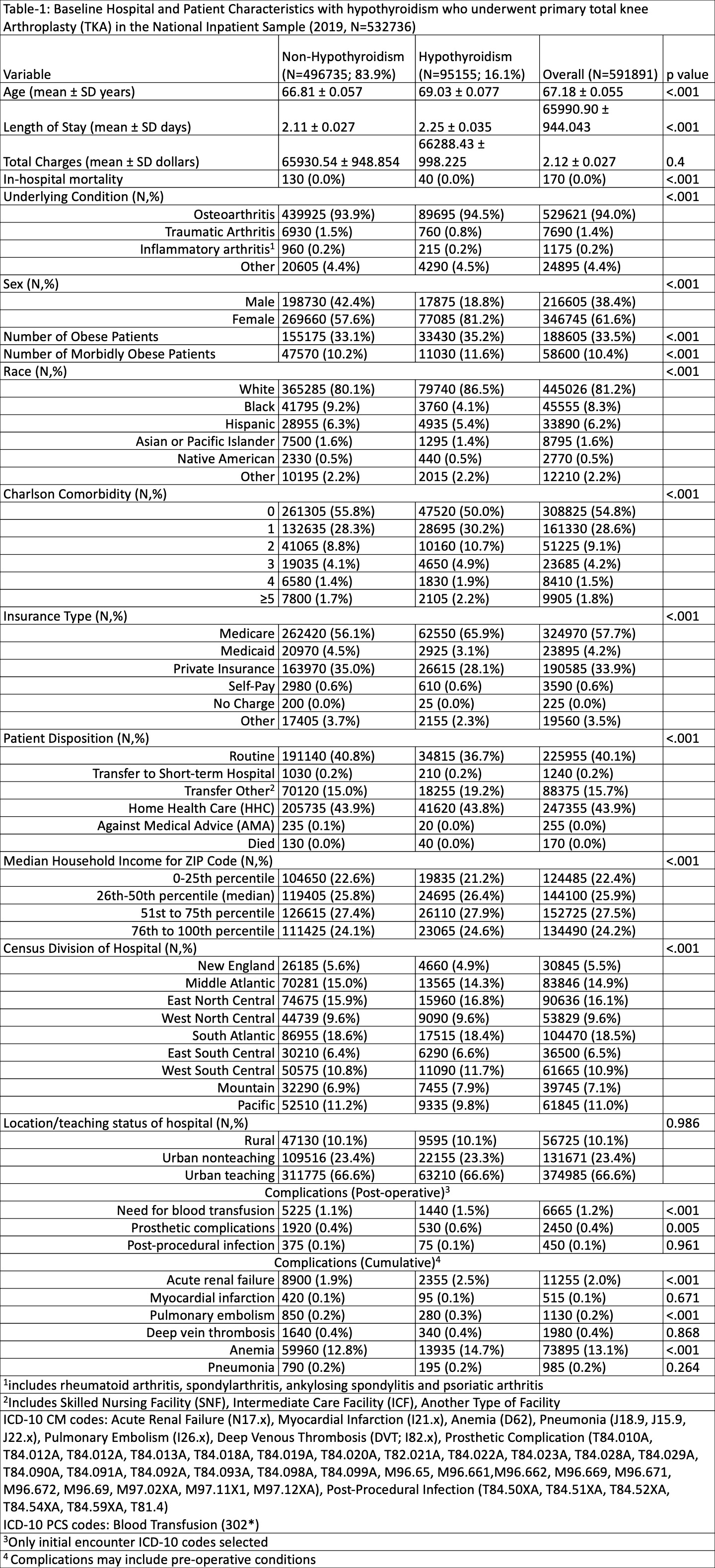
Methods: We identified all patients in the 2019 national inpatient sample (NIS) that received primary TKA and stratified them based on primary diagnoses. The population was stratified into knee OA (N=529,621), traumatic arthritis (N=7,690) and inflammatory arthritis (RA, AS, or PsA; N=1,175) and other diagnoses. Hypothyroidism was determined using secondary diagnoses. We assessed clinical and healthcare utilization outcomes as endpoints using multivariable-adjusted regression analyses adjusted for race, age, sex, hospital bed size, census region and teaching status.
Results: Total cohort population was 563,381 Mean age was 67.18 years, 61.6% were female, and mean length of stay was 2.12 days.
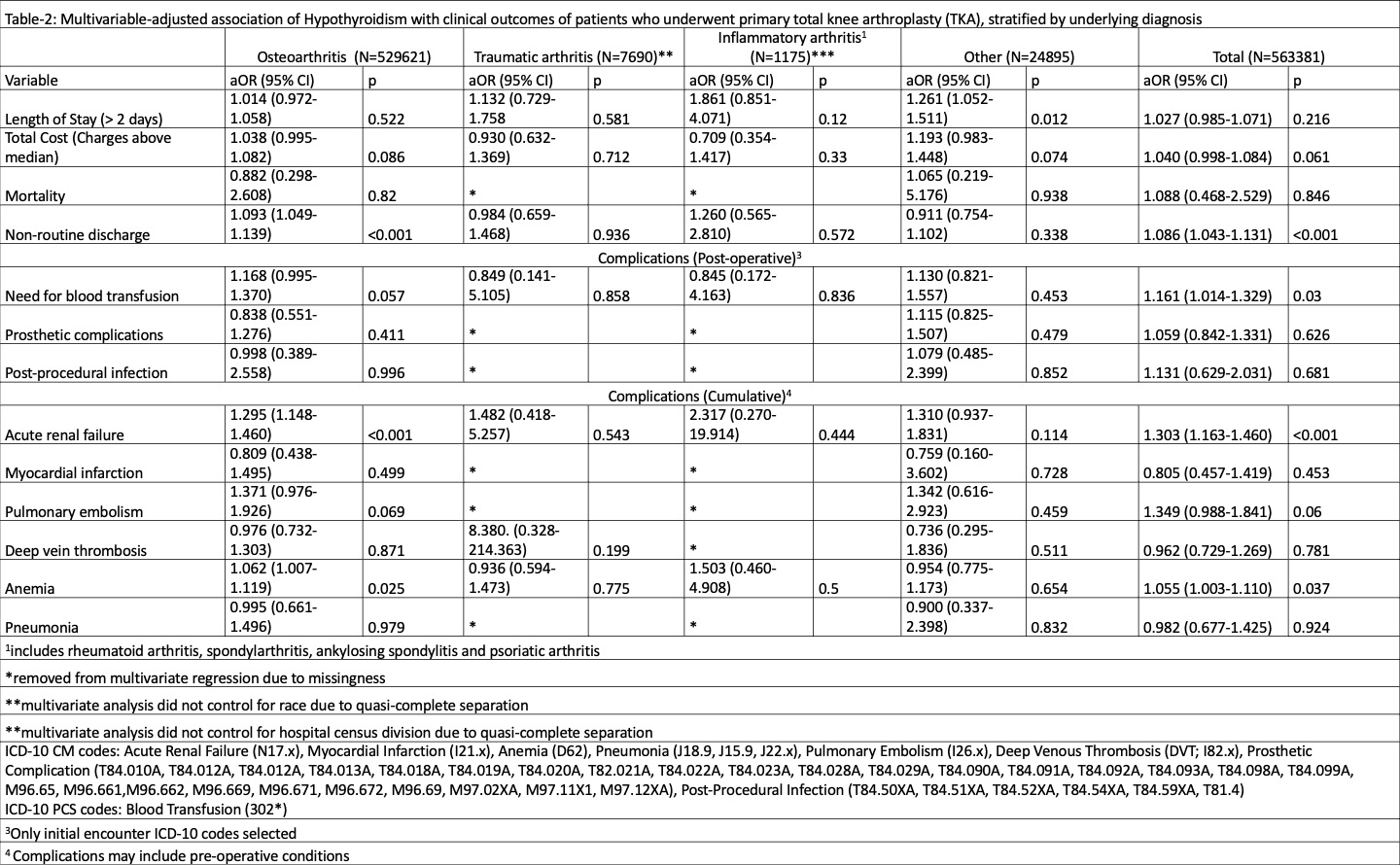
Overall, hypothyroidism was associated with increased adjusted odds of non-routine discharge, blood transfusion, acute renal failure (ARF), and anemia (p≤0.037 each). In the knee OA cohort, hypothyroidism was associated with increased adjusted odds of non-routine discharge, ARF, and anemia (p≤0.025 each). Hypothyroidism was not associated with any complications or adverse patient outcomes in the traumatic or inflammatory arthritis cohorts.
Conclusion: Hypothyroidism impacts TKA outcomes, particularly in patients with knee OA. These findings hold crucial implications for patient care and guidance for orthopedic surgeons, emphasizing the necessity for thorough preoperative evaluations and care plans. By better understanding these risks, we can enhance patient outcomes and streamline surgical protocols.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chandrupatla S, Rumalla K, Singh J. Hypothyroidism Is Associated with Worse Clinical and Utilization Outcomes After Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hypothyroidism-is-associated-with-worse-clinical-and-utilization-outcomes-after-primary-total-knee-arthroplasty/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hypothyroidism-is-associated-with-worse-clinical-and-utilization-outcomes-after-primary-total-knee-arthroplasty/