Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Hypertrophic pachymeningitis (HP) is an inflammatory disorder causing focal and diffuse thickening of the dura mater. It is realized that anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) contributes to the development of HP, whereas the epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of patients with HP in the whole population of AAV are still uncertain. In this study, we demonstrated the characteristics of patients with HP compared with those of patients without HP in AAV.
Methods: We retrospectively investigated the clinical records of 39 Japanese patients with AAV (18 men and 21 women). Among them, patients with associated HP were detected. To determine the characteristics of HP in AAV, the epidemiological and clinical data from patients with HP were statistically compared with those from patients without HP.
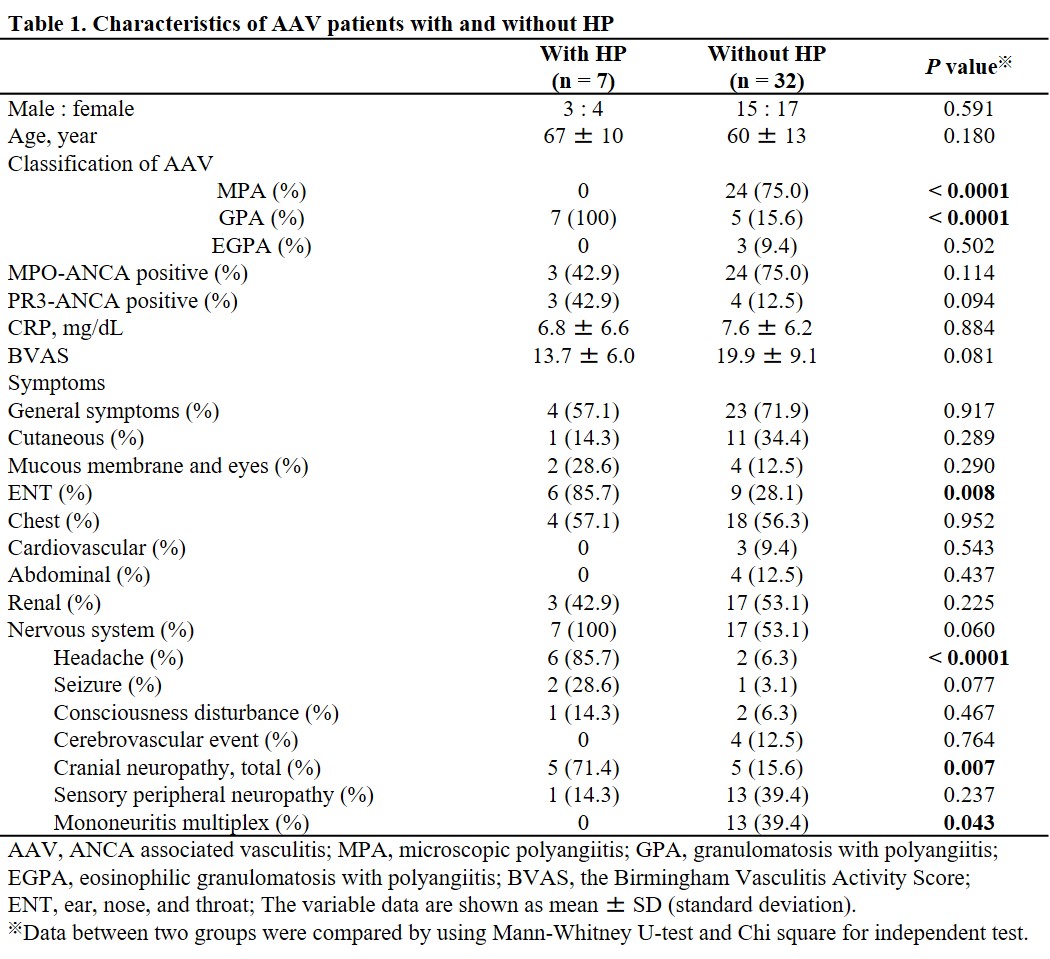
Results: Of 39 patients with AAV, 7 (17.9%) had associated HP. All patients with HP were classified as having granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), whereas only 5 of 32 patients without HP were diagnosed as having GPA (P < 0.0001) (Table 1). The frequencies of myeloperoxidase (MPO)-ANCA and proteinase 3-ANCA positivity in patients with HP were equivalent, while MPO-ANCA positivity was obviously dominant in patients without HP. HP occurred as the initial clinical episode of AAV in 3 patients (7.7% of all AAV). Frequent significant characteristics of patients with HP were headache, cranial neuropathy, and paranasal involvement (P < 0.05), and histopathological findings from paranasal involvement were useful for the diagnosis of GPA in some patients with HP. Combination therapy of corticosteroid and an immunosuppressant, such as methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, or rituximab, was effective for achieving remission and improving radiographic findings of HP.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first study that has described the epidemiological analyses of HP in the whole population of AAV. We conclude that the epidemiological features of AAV patients with HP are different from those of patients without HP. The geographical studies of AAV indicated that the predominance of microscopic polyangiitis and MPO-ANCA positivity as epidemiologically specific to Japan, whereas GPA and PR3-ANCA positivity are dominant in European countries. However, the epidemiology of patients with HP is similar to that of patients in European countries. In addition, HP impacts the diagnosis of AAV because it could be an initial clinical sign of disease as well as associated with frequent existence of granulomatous lesions in the respiratory tract.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shimojima Y, Kishida D, Hineno A, Yazaki M, Sekijima Y, Ikeda SI. Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis in a Population with Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: A Retrospective Study in a Single Japanese Institution [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hypertrophic-pachymeningitis-in-a-population-with-anti-neutrophil-cytoplasmic-antibody-associated-vasculitis-a-retrospective-study-in-a-single-japanese-institution/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hypertrophic-pachymeningitis-in-a-population-with-anti-neutrophil-cytoplasmic-antibody-associated-vasculitis-a-retrospective-study-in-a-single-japanese-institution/