Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is a pivotal therapy for lupus nephritis (LN) as it contributes to 65% lower mortality and 84% lower renal damage compared to HCQ non-users. End-stage renal disease (ESRD) due to LN is a leading cause of renal transplantation and almost 30% of patients suffer from LN recurrence after renal transplant. Yet, the impact of post-transplant HCQ use on LN recurrence, and patient and graft survival has not been elucidated. Therefore, this study aims to examine the role of post-transplant HCQ use on LN recurrence, and patient and renal graft survival. We also examined other predictors of post-transplant patient and graft survival. We hypothesized that post-transplant HCQ use will predict lower LN recurrence, and better patient and graft survival.
Methods: Using a comprehensive transplant database, we identified all patients with ESRD due to LN who underwent renal transplant between 1994-2016 at an academic center. Data, including patient, lupus, and transplant characteristics, were extracted from this database. Post-transplant medication HCQ use and biopsy confirmed LN recurrence were abstracted. Primary outcomes were all-cause mortality and graft failure, defined as re-transplant or dialysis. Cox proportional hazards models were used to examine predictors of patient and graft survival. Fisher test was used to examine association between LN recurrence and HCQ use.
Results: Overall, we identified 205 patients undergoing renal transplant for ESRD due to LN. The mean age of 43 years, 78% were white female, and only 34% of the patients were on HCQ after transplant. The post-transplant LN recurrence rate was 14%, with 52% of recurrences occurring in HCQ non-users (p 0.09).
Patient Survival: We identified 47 deaths (23%) during 11-year post-transplant follow up, with 79% of deaths occurring in HCQ non-users. Stratified survival analysis by HCQ use highlighted significantly lower mortality in HCQ users compared to non-users (10/47 vs. 37/47, p < 0.0001) (Figure 1). We found that HCQ use predicted 40% lower mortality compared to non-users and a trend was noted on multivariable analysis (HR 0.6, CI 0.3-1.2, p 0.1; Table 1). Post-transplant graft failure predicted 51-fold higher mortality risk in our cohort (HR 51, CI 7-77, p 0.0001) (Table 1). Age ≥ 45 years predicted 4-fold higher mortality (HR 3.5, CI 1.8-6.6), and non-white race predicted 2-fold higher mortality (HR 2.3, CI 1.1-4.7).
Graft Failure: We identified 99 graft failures (48%) during post-transplant follow up. Stratified graft survival analysis revealed significantly lower graft failure in post-transplant HCQ users compared to non-users (29/99 vs 70/99, p < 0.0001) (Figure 2). Multivariable analysis showed post-transplant LN recurrence predicted 2-fold higher graft failure risk (HR 1.7, CI 1.02-3, p 0.04; data not shown).
Conclusion: HCQ use predicted higher post-transplant LN patient and renal graft survival. LN recurrence was a strong predictor of graft failure, and renal graft failure predicted 51-fold higher post-transplant mortality. Future efforts should prospectively examine the impact on post-transplant HCQ use on graft and patient outcomes.
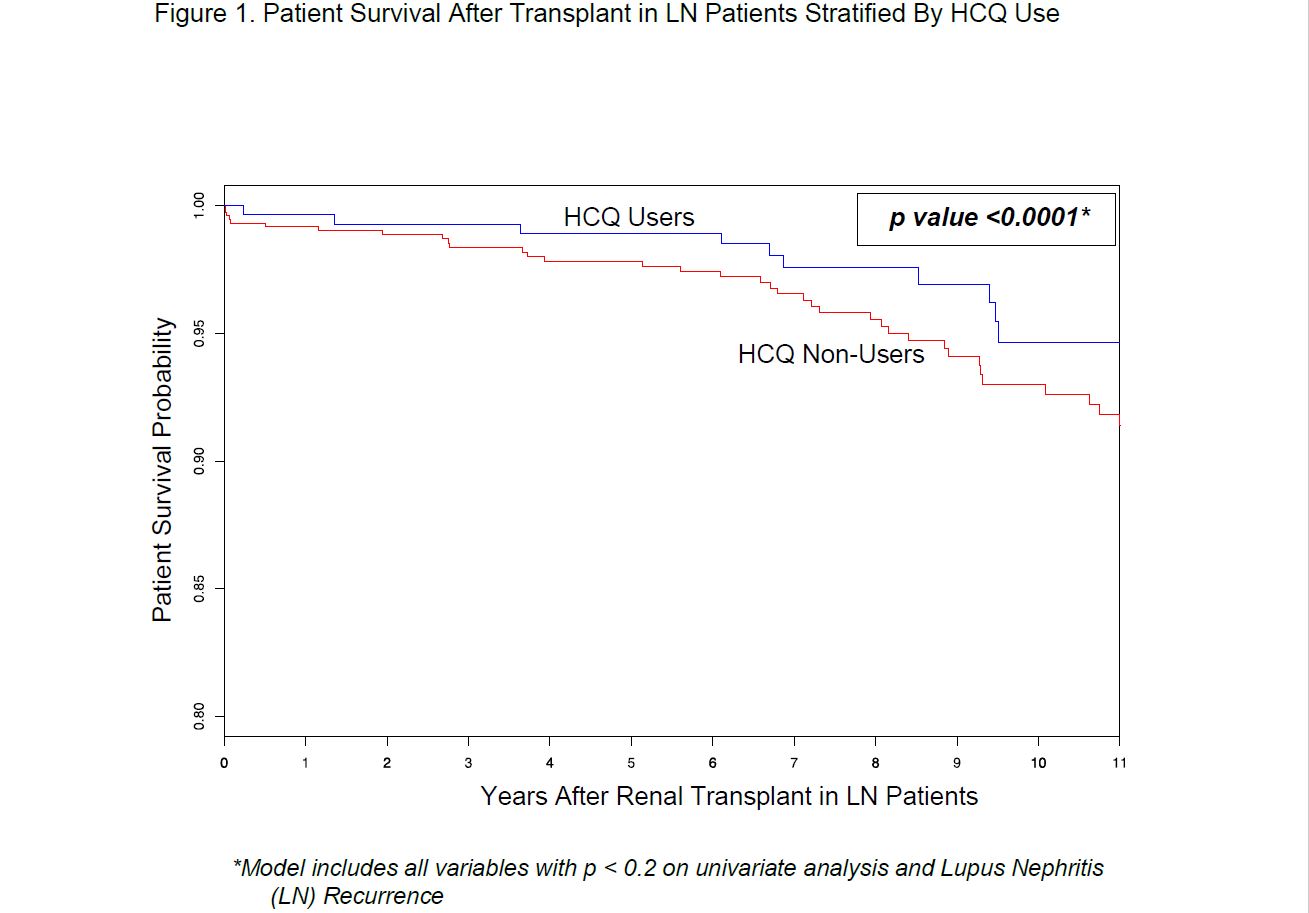 Figure 1. Patient Survival After Transplant in LN Patients Stratified By HCQ Use
Figure 1. Patient Survival After Transplant in LN Patients Stratified By HCQ Use
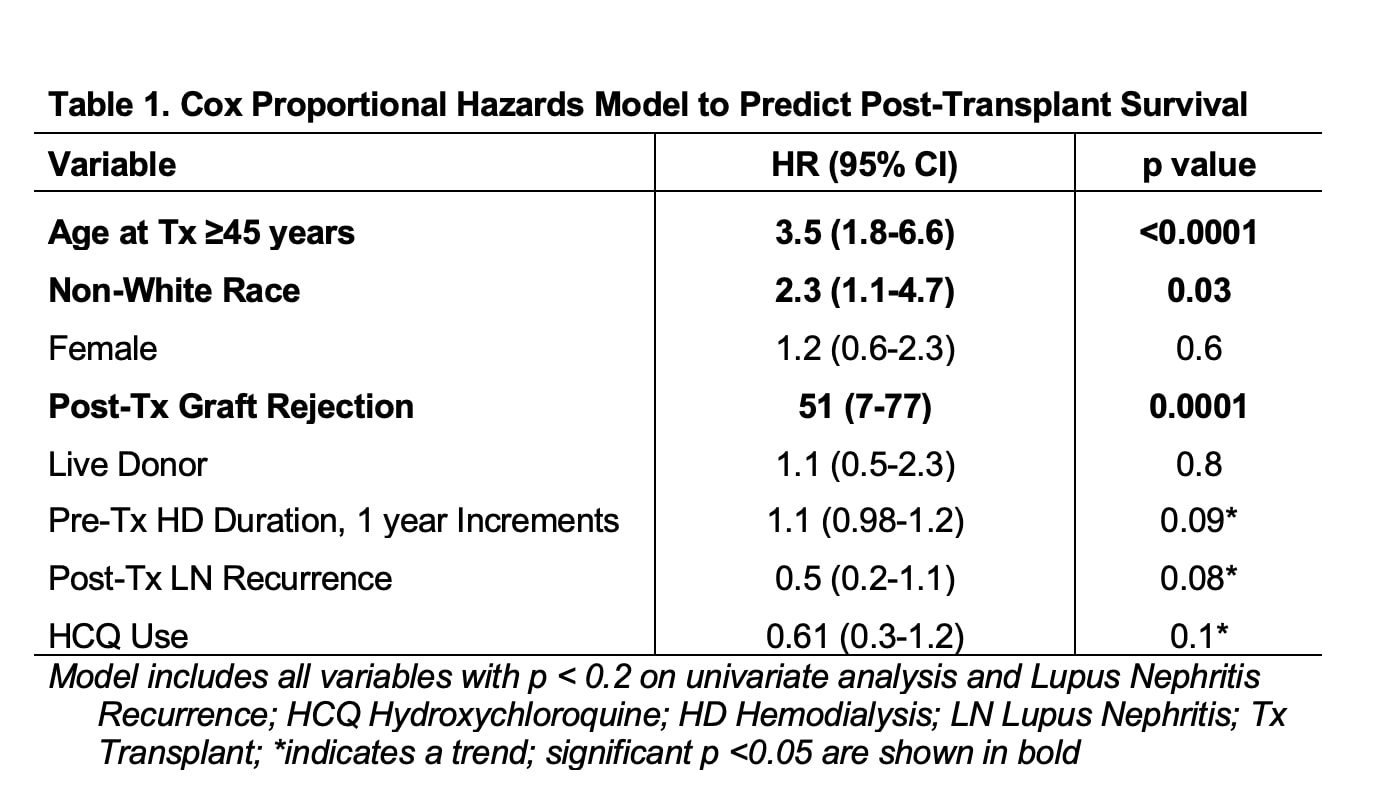 Table 1. Cox Proportional Hazards Model to Predict Post-Transplant Survival
Table 1. Cox Proportional Hazards Model to Predict Post-Transplant Survival
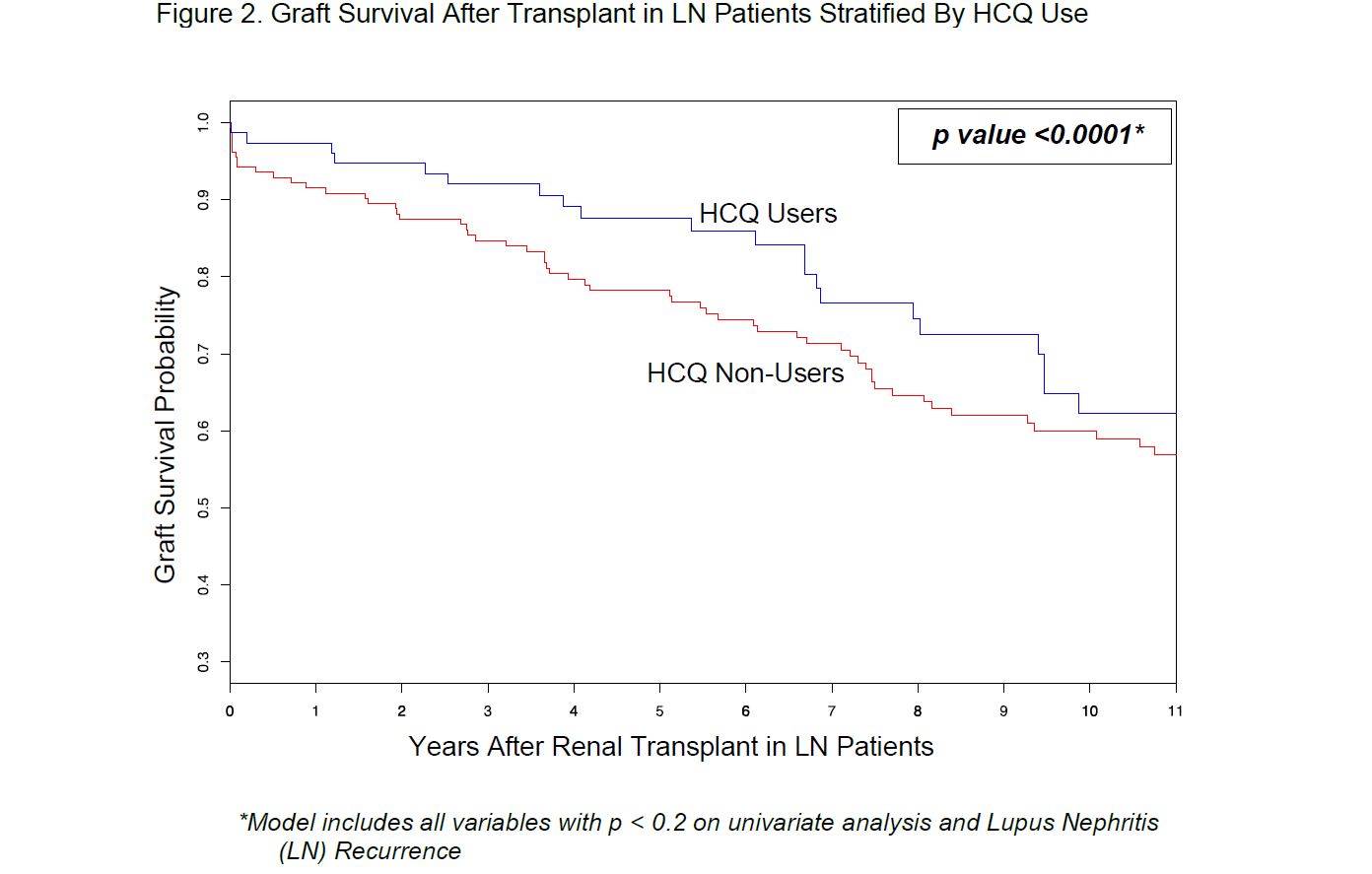 Figure 2. Graft Survival After Transplant in LN Patients Stratified By HCQ Use
Figure 2. Graft Survival After Transplant in LN Patients Stratified By HCQ Use
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Garg S, Singh T, Panzer S, Bartels C. Hydroxychloroquine Use Predicts Significantly Higher Patient and Graft Survival in Post-Renal Transplant Lupus Nephritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hydroxychloroquine-use-predicts-significantly-higher-patient-and-graft-survival-in-post-renal-transplant-lupus-nephritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hydroxychloroquine-use-predicts-significantly-higher-patient-and-graft-survival-in-post-renal-transplant-lupus-nephritis-patients/
