Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) on immunosuppressive therapy have impaired humoral immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. This study aimed to assess serologic response in IMID patients receiving four vaccine doses and the serologic response to COVID-19 infection in patients following three vaccine doses compared to healthy controls.
Methods: The ongoing prospective, observational Nor-vaC study includes patients with inflammatory joint and bowel diseases on immunosuppressive therapy. In the present analyses we included patients receiving four SARS-CoV-2 vaccine doses (vaccine group), or three vaccine doses followed by COVID-19 infection (COVID-19 group), as well as healthy controls receiving three doses (control group). Anti-Spike antibody levels were analyzed 2-4 weeks following each vaccine dose and/or COVID-19 infection by an in-house bead-based assay. The main outcome was anti-Spike antibody levels following four-dose vaccination and COVID-19 infection in the vaccine- and COVID-19 group respectively, and following three vaccine doses in healthy controls. Levels were compared across groups by Mann-Whitney U test.
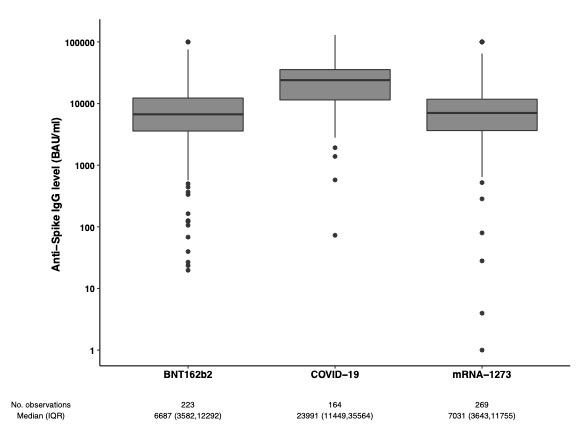
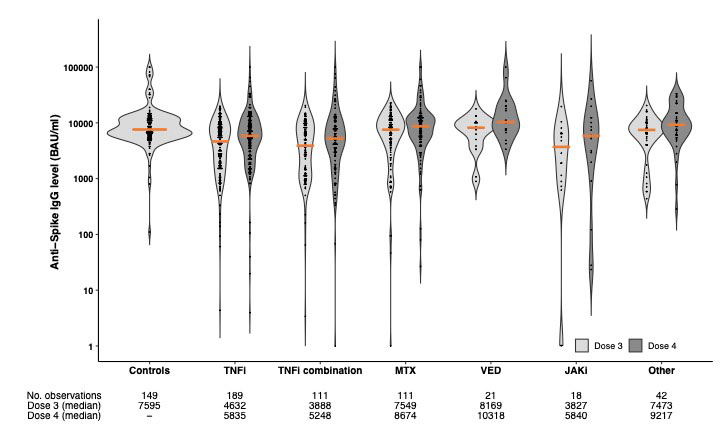
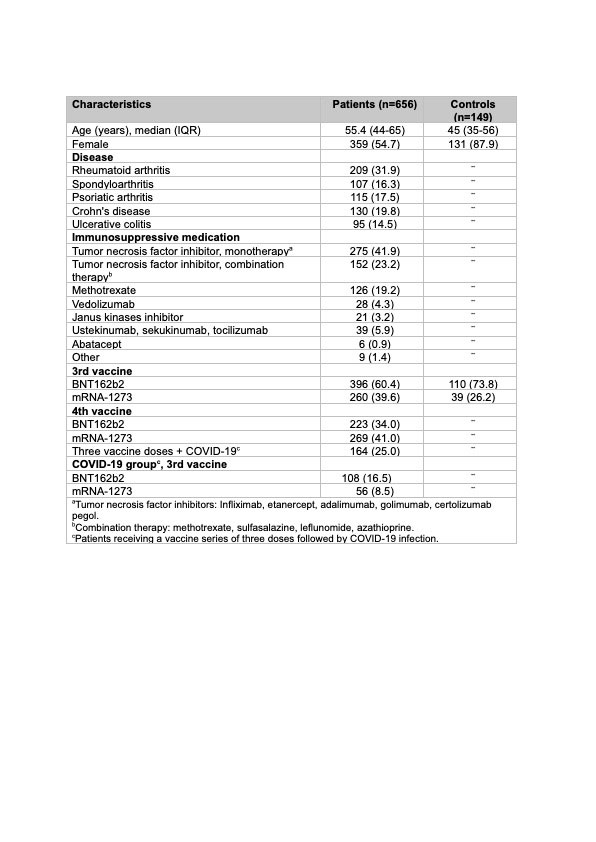
Results: Overall, 656 patients (209 rheumatoid arthritis, 107 spondyloarthritis, 115 psoriatic arthritis, 130 Crohn’s disease and 95 ulcerative colitis) (median [IQR] age 55 years [44-65]; 55% women) and 149 healthy controls (45 years [35-56]; 88% women) were included. Ongoing immunosuppressive medication is shown in the Table. Of the patients, 492 (75%) received the fourth vaccine dose (223 (45%) BNT162b2 (full dose), 269 (55%) mRNA-1273 (half-dose)), and 164 (25%) received three vaccine doses (all full dose) followed by COVID-19 infection. In the controls, the third dose comprised 110 (74%) BNT162b2 and 39 (26%) mRNA-1273 vaccines (Table). In the COVID-19 group, anti-Spike antibody levels were three times higher than in the vaccine group; median [IQR] 23991 BAU/ml [11449-35564] vs 6846 BAU/ml [3593-12073], p < 0.001 (Figure 1). In the vaccine group, anti-Spike antibody levels were significantly higher following the fourth dose than after the third dose; median [IQR] 6846 BAU/ml [3593-12073] vs 6016 BAU/ml [1857-9453], p < 0.0001, but significantly lower than antibody levels in healthy controls following the third dose (7595 BAU/ml [5915-12001], p=0.002) (Figure 2). In the vaccine group, no difference was found regarding anti-Spike levels following a full fourth dose of BNT162b2 vs half-dose mRNA-1273 vaccine (median [IQR] 6687 BAU/ml [3582-12292]) vs. 7031 BAU/ml [3643-11755]), p=0.98 (Figure 1).
Conclusion: COVID-19 infection after three vaccine doses induces a robust serologic response in IMID patients, with immunization efficacy even better than a fourth vaccine dose in this study. Repeated vaccination of IMID patients improves humoral immunity, but anti-Spike antibody levels were lower in patients following the fourth dose, than in healthy controls vaccinated with three doses. There was no significant difference in humoral immune responses between half dose mRNA-1273 vs full dose BNT162b2 as the fourth vaccine dose.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ørbo H, Bjørlykke K, Sexton J, Tveter A, Jyssum I, Christensen I, Warren D, Kvien T, Chopra A, Kro G, Jahnsen J, Munthe L, Haavardsholm E, Grødeland G, Provan S, Jørgensen K, Syversen S, Goll G. Humoral Immune Responses Following Four SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Doses or COVID-19 Infection in Patients with Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases on Immunosuppressive Therapy: A Prospective Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/humoral-immune-responses-following-four-sars-cov-2-vaccine-doses-or-covid-19-infection-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-on-immunosuppressive-therapy-a-prospective-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/humoral-immune-responses-following-four-sars-cov-2-vaccine-doses-or-covid-19-infection-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-on-immunosuppressive-therapy-a-prospective-cohort-study/