Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) occurs in over 50% of SLE patients, contributing significant morbidity and mortality. Despite a generally accepted treatment goal of Complete Renal Response (CRR) at one year, concerns for damage accrual remain, raising the question of whether a more stringent proteinuria goal renal remission (RR) should be pursued.
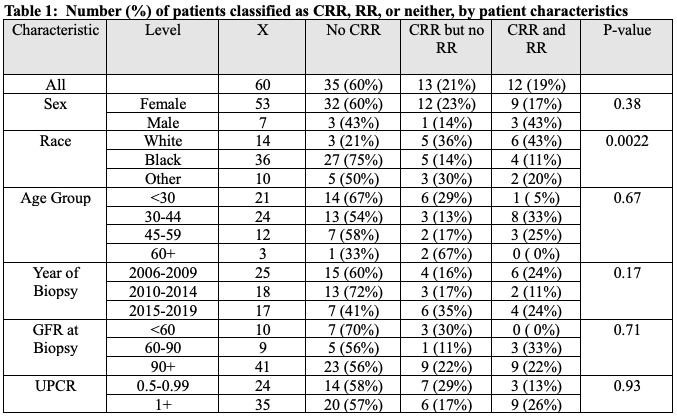
Methods: CRR at one year after renal biopsy, was defined as urine protein creatinine ratio (UPCR) ≤ 0.50 g/g, and < 10 mg/day of prednisone. RR at one year after renal biopsy, was defined as UPCR ≤ 0.20 g/g, and < 5mg/ day of prednisone. We identified patients with biopsy classes: III, IV, or mixed III+V or IV+V per International Society of Nephrology/ Renal Pathology Society (ISN/RPS) classification criteria. Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) was assessed at baseline and approximately 3 years post-baseline using the 2021 CKD-EPI formula without race. Based on these measures, three long-term outcomes were evaluated: mean 3-year GFR, change in GFR, and proportion with a 30% decline in eGFR from baseline.
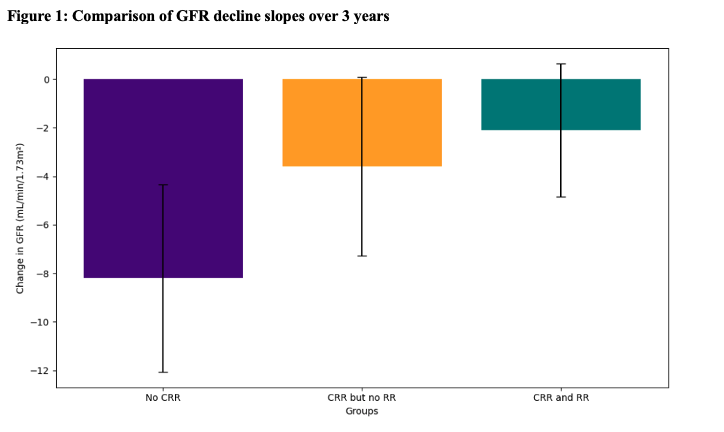
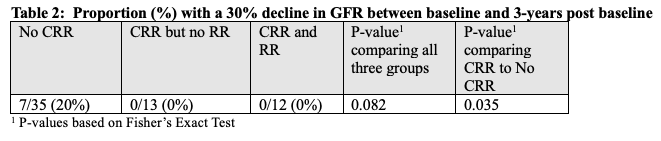
Results: 60 patients had a qualifying biopsy and at least 3 years of follow-up data. Patient demographics and characteristics are summarized in Table 1. CRR was achieved in 25 patients (40%) and RR in 12 patients (19%) one year after biopsy. White patients were more likely to achieve RR (43%) compared to Black patients (11%). Compared to patients who did not achieve CRR, both CRR and RR demonstrated a higher eGFR and smaller declines in GFR at the 3-year assessment, but these differences were not statistically significant (Figure 1). There was a statistically significant difference in the proportion who had a 30% decline in eGFR (Table 2). No differences were observed between those who achieved RR and those who achieved CRR but not RR, with respect to three-year outcomes.
Conclusion: Renal remission is rare at one year (only 19% of our patients). Both RR and CRR had lower GFR decline compared to non-responders. In fact, compared to non-responders, patients with either CRR or RR did not experience a 30% decline in GFR, which was statistically significant.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Guerra Sayre J, Fava A, Goldman D, Magder L, Petri M. How Do Lupus Nephritis Patients Who Achieve Renal Remission Fare? A 3-year Comparison in Terms of GFR Decline [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-do-lupus-nephritis-patients-who-achieve-renal-remission-fare-a-3-year-comparison-in-terms-of-gfr-decline/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-do-lupus-nephritis-patients-who-achieve-renal-remission-fare-a-3-year-comparison-in-terms-of-gfr-decline/