Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Genetic risk factors may explain why only a small proportion of patients taking statins develop severe cases of anti-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGCR) immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM). A high prevalence of HLA-DRB1*11:01 carriers has been described in patients with anti-HMGCR IMNM. However, it is unknown whether this allele is specifically associated with anti-HMGCR IMNM or if it is also associated with non-immune-mediated statin myotoxicity.
The main objective is to elucidate whether Anti-HMGCR IMNM and non-immune-mediated statin myotoxicity exhibit a different HLA-DRB11 association.
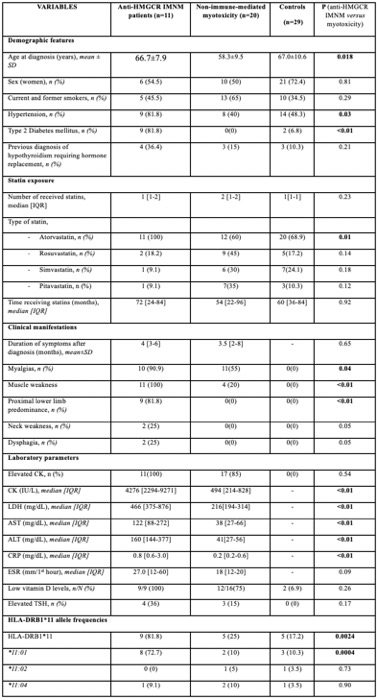
Methods: HLA-DRB1 typing was performed using the Luminex 100 system in 11 patients with anti-HMGCR IMNM diagnosis, 20 patients with non-immune- mediated statin myotoxicity and 29 ethnically matched controls receiving statins without myotoxicity. Comparisons were performed between the three groups.
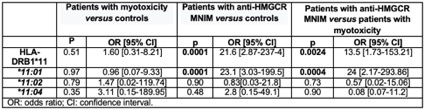
Results: Demographic, clinical features and laboratory abnormalities were different between anti-HMGCR IMNM patients and non-immune-statin myotoxicity (Table 1). HLA-DRB1*11 phenotype frequency was significantly increased in patients with anti-HMGCR IMNM compared to controls (81.8% versus 17.2%, respectively; p < 0.001; odds ratio-OR [95% confidence interval-CI] =21.6 [2.87-237.4]). Remarkably, a higher proportion of HLA-DRB1*11 carriers was observed in anti-HMGCR IMNM patients when compared to non-immune-mediated statin myotoxicity (81.8% vs 25%; p < 0.001; OR [95% CI] =13.5 [1.73-153.21]). This association was mainly due to the HLA-DRB1*11:01 allele. Patients with non-immune-mediated statin myotoxicity and controls did not exhibit HLA-DRB1*11 allele differences (Table 2).
Conclusion: We found that HLA-DRB1*11, particularly the HLA-DRB1*11:01 allele, is strongly associated with anti-HMGCR IMNM while this association was not observed in patients with non-immune-mediated statin myotoxicity. HLA-DRB1*11:01 might be useful as a specific genetic marker to identify those patients at high risk of anti-HMGCR IMNM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Corrales Selaya C, Prieto-Peña D, Ocejo-Viñals g, Secada Gómez C, Corrales-Martínez a, Ibarbia C, Salmón-gonzalez Z, Martín-millan M, Portilla-González V, mota-perez N, sebastian-mora gil M, Batista-liz J, Pulito-Cueto V, Lopez-mejias R, Blanco-Alonso R, Hernandez J. HLA-DRB1*11:01 Association Differenciates Anti-hmgcr Immune-mediated Necrotizing Myopathy from Non-immune Mediated Statin Myotoxicity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hla-drb11101-association-differenciates-anti-hmgcr-immune-mediated-necrotizing-myopathy-from-non-immune-mediated-statin-myotoxicity/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hla-drb11101-association-differenciates-anti-hmgcr-immune-mediated-necrotizing-myopathy-from-non-immune-mediated-statin-myotoxicity/