Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Immunogenicity is a leading cause of treatment failure to TNF inhibitors, and also affects drug safety. Variations in HLA class II genes have been suggested to predispose to anti-drug antibody formation (ADA), but characterization of biologically relevant HLA haplotypes, based on high-resolution genotyping, is lacking. The aim was to assess associations between HLA loci and formation of ADA to infliximab across different immune mediated inflammatory diseases.
Methods: Patients with immune mediated inflammatory diseases on infliximab therapy (N=612; 181 spondyloarthritis, 120 rheumatoid arthritis, 72 psoriatic arthritis, 114 ulcerative colitis, 80 Crohn’s disease and 45 psoriasis) participating in the Norwegian Drug Monitoring (NOR-DRUM) trials (1, 2) were included in the present analyses. Neutralizing ADA were assessed with an automated fluorescence assay at each infusion. Next generation sequencing-based HLA typing was performed (Histogenetics®). Associations with ADA formation were assessed at locus, allele, haplotype and amino acid level. Peptide binding predictions for infliximab were performed.
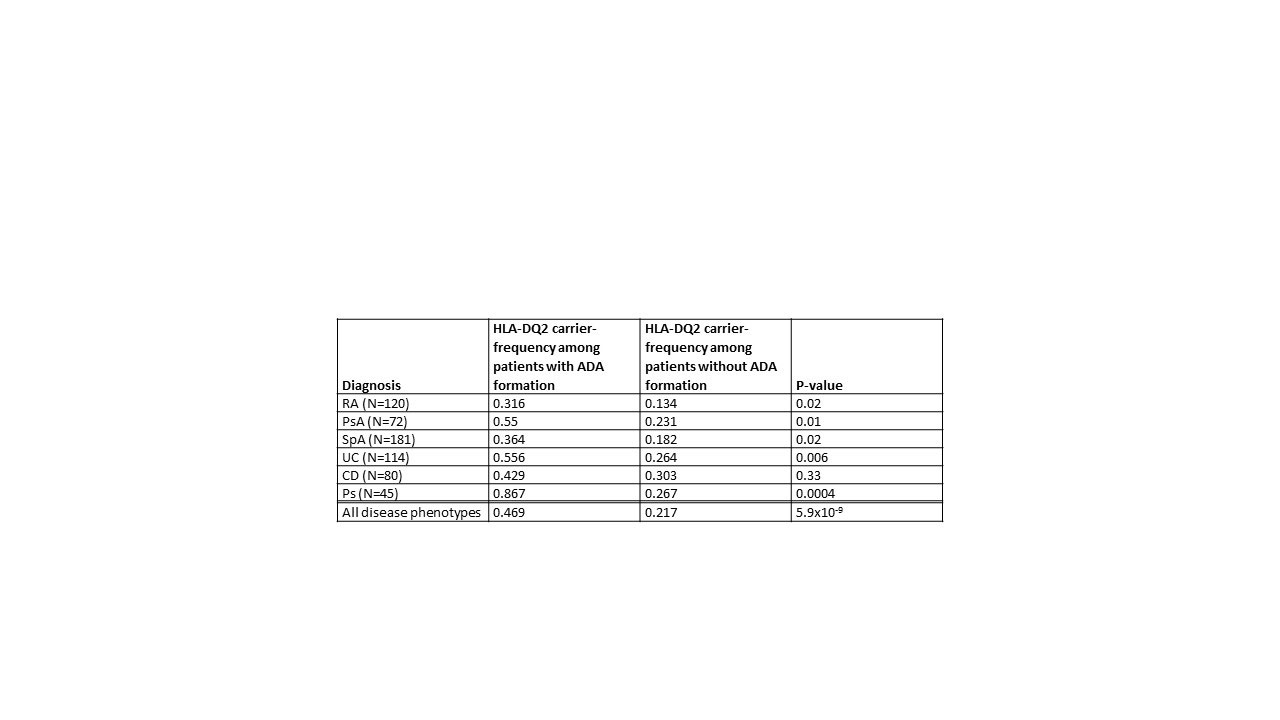
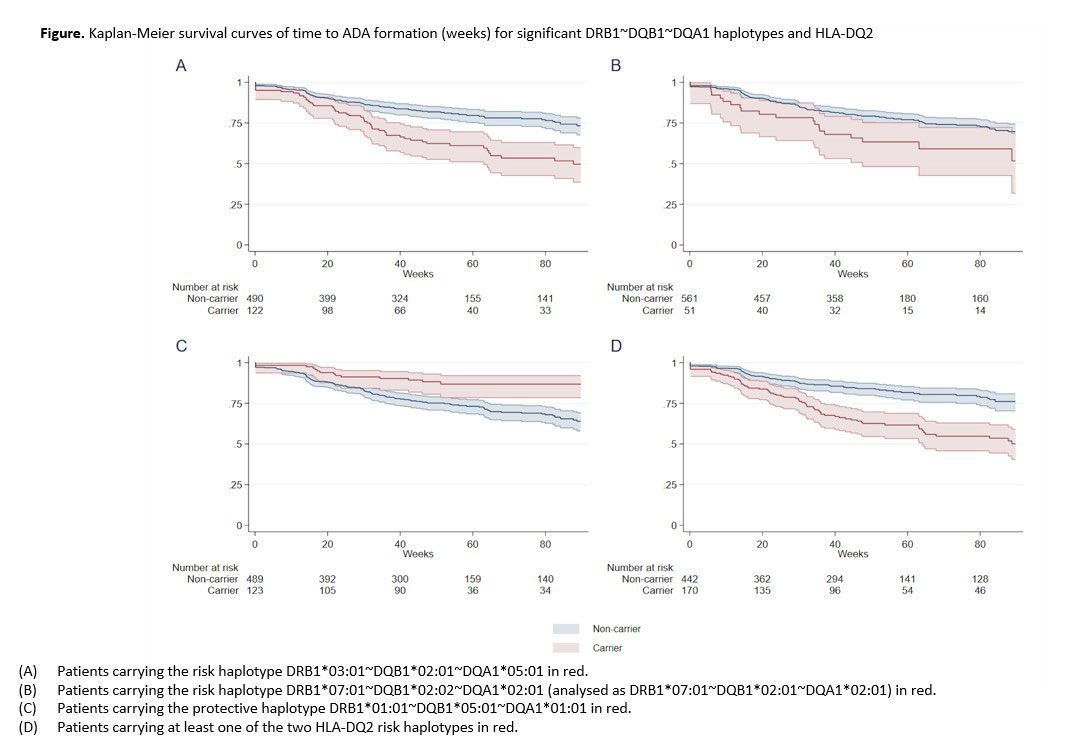
Results: ADA were detected in 147 patients (24%). Significant associations were shown between ADA and several HLA loci, whereas conditional analyses indicated HLA-DQB1 (p=1.4×10-6) as the primary risk locus. Highest risk of ADA formation was seen for patients carrying at least one of the HLA-DQ2 haplotypes; DQB1*02:01~DQA1*05:01 and DQB1*02:02~DQA1*02:01 (OR 3.18, 95% CI 2.15 to 4.69, p=5.9×10-9) (Figure). These findings were consistent across diagnoses (Table), and remained significant when adjusting for other possible predictors of ADA. Computational predictions indicated that both these HLA-DQ2 haplotypes could strongly bind two peptide motifs (INTVESEDI and VYACEVTHQ) in the infliximab heavy and light chain.
Conclusion: The risk of ADA to infliximab was three-fold higher in patients carrying the HLA-DQ2 risk haplotypes across diseases. A biological role for the HLA-DQ2 molecules encoded by the two different HLA-DQ2 risk haplotypes in the formation of ADA was further supported by peptide binding predictions. These novel findings provide promise for future incorporation of HLA-DQ2 testing to facilitate personalized treatment decisions.
1. Syversen SW et al. Jama. 2021;326(23):2375-84.
2. Syversen SW et al. Jama. 2021;325(17):1744-54.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brun M, Bjørlykke K, Viken M, Stenvik G, Klaasen R, Gehin J, Warren D, Sexton J, Haavardsholm E, Jahnsen J, Lie B, Bolstad N, Jørgensen K, Goll G, Syversen S. HLA-DQ2 Is Associated with Anti-drug Antibody Formation to Infliximab Across Immune-mediated Inflammatory Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hla-dq2-is-associated-with-anti-drug-antibody-formation-to-infliximab-across-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hla-dq2-is-associated-with-anti-drug-antibody-formation-to-infliximab-across-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases/