Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: 3S108: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes II: Cardiovascular Comorbidities (921–926)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: We recently reported that highly-sensitive cardiac troponin-I (hs-cTnI) associates with occult coronary atherosclerosis burden and cardiovascular event (CVE) risk in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We further showed that IgA antibodies against beta2-glycoprotein-1 (a-b2GPI-IgA) contribute to higher coronary artery calcium (CAC) and accelerated plaque and CAC progression in RA. It is unclear when to proceed with coronary atherosclerosis evaluation in asymptomatic RA patients and whether such an assessment should be repeated in the future. We here explored whether either biomarker alone or their combination best predicted plaque or CAC presence on an initial coronary CT angiogram (CCTA); we then interrogated whether either biomarker predicted progression to extensive or obstructive plaque on a follow-up evaluation.
Methods: One hundred fifty RA patients underwent a baseline CCTA; 101 had repeat evaluation within 83±3.6 months. Hs-cTnI and a-b2GPI IgAwere assessed at baseline; the latter were confirmed 12 weeks later, if positive. Extensive plaque was defined as >5 coronary segments withplaque, or stenosis score >5, or CAC >100.The diagnostic accuracy of Framingham D’Agostino cardiac risk score (FRSDA) alone vs. hs-cTnI or a-b2GPI-IgA sequentially or combined for plaque or CAC at baseline was evaluated as area under the curve (AUC). Improvement in prediction accuracy between constructs was further assessed as integrated discrimination improvement (IDI). Similar AUC and IDI constructs were evaluated for transition to obstructive or extensive atherosclerosis at follow-up in patients with baseline plaque.
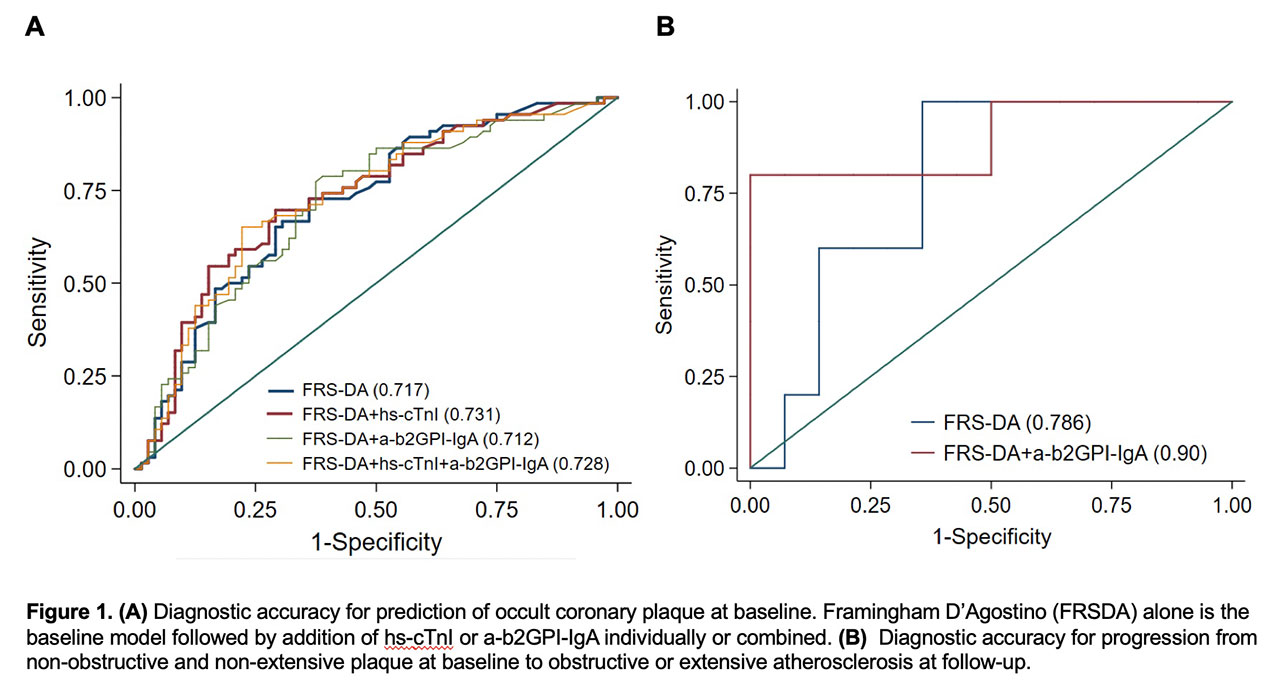
Results: High hs-cTnI added to FRSDA increased AUC from 0.717 to 0.731 (Figure 1A) and improved prediction for baseline plaque [IDI=0.041 (SE)=0.017, p=0.015]. In contrast, a-b2GPI-IgA did not [0.005 (0.006), p=0.47] and the combination offered no added benefit to the hs-cTnI model alone. Similar observations were made for baseline CAC. Hs-cTnI alone did not independently predict CAC change (β=0.084, p=0.215) whereas a-b2GPI-IgA presence did (β=0.235, p=0.001). High hs-cTnI predicted greater CAC change in a-b2GPI-IgA positive patients but not in negative ones [p-interaction= 0.034, estimated marginal mean difference (IQR)=0.36 (0.12-0.59), p=0.003]. Addition of a-b2GPI-IgA to FRSDA in patients with prevalent non-extensive non-obstructive plaque increased AUC from 0.785 to 0.900 (Figure 1B) and significantly improved the prediction for development of obstructive or extensive atherosclerosis at follow-up [0.387, (0.13), p=0.003].
Conclusion: High hs-cTnI significantly and independently improved the risk of baseline plaque presence and may trigger an initial non-invasive coronary atherosclerosis evaluation. A-b2GPI-IgA presence may justify a follow-up evaluation in patients with non-extensive, non-obstructive plaque at baseline.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Karpouzas G, Ormseth S, Hernandez E, Budoff M. Highly-sensitive Cardiac Troponin-I and Beta-2-Glycoprotein-I IgA Antibodies Inform the Utility of Screening and Follow-up Non-invasive Coronary Atherosclerosis Evaluation and Optimize Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/highly-sensitive-cardiac-troponin-i-and-beta-2-glycoprotein-i-iga-antibodies-inform-the-utility-of-screening-and-follow-up-non-invasive-coronary-atherosclerosis-evaluation-and-optimize-cardiovascular/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/highly-sensitive-cardiac-troponin-i-and-beta-2-glycoprotein-i-iga-antibodies-inform-the-utility-of-screening-and-follow-up-non-invasive-coronary-atherosclerosis-evaluation-and-optimize-cardiovascular/