Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Higher inflammatory response in elderly patients during gout attack
Background/Purpose
Clinical experiences suggest that gout attacks in elderly patients are accompanied by stronger systemic inflammatory response including fever, higher C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sediment ratio (ESR) as compared those in younger patients. As such, it is often difficult to differentiate them from septic arthritis, leading to frequent use of empiric antibiotics and unnecessary diagnostic and therapeutic joint surgery. To define whether gout attacks are accompanied by stronger systemic inflammatory response with age.
Methods
In this retrospective study, medical records of patients who were evaluated for a possible gout attack between January 2000 and April 2014 were examined. The presence of fever (>37.8°Æ), levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sediment ratio (ESR) on attack were compared between young (<50 years), middle aged (50- 65 years) and elderly patients (>65 years).
Results
Gout attacks were observed in 188 patients with 34 young, 54 middle aged and 100 elderly patients. Baseline characteristics of three groups differed; elderly patients had more comorbidities including diabetes mellitus (p<0.001), hypertension (p<0.001), coronary artery disease (p=0.015), cerebrovascular accident (p<0.001), and cancer (p=0.031) as compared other groups. The elderly patients had a low body mass index (BMI) (24.60 ± 4.65, 24.55 ± 3.30, 23.27 ± 3.12, p=0.041 by ANOVA) and longer disease duration (2.76 ± 5.16, 4.20 ± 6.13, 6.58 ± 9.23 years, p=0.028 by ANOVA).
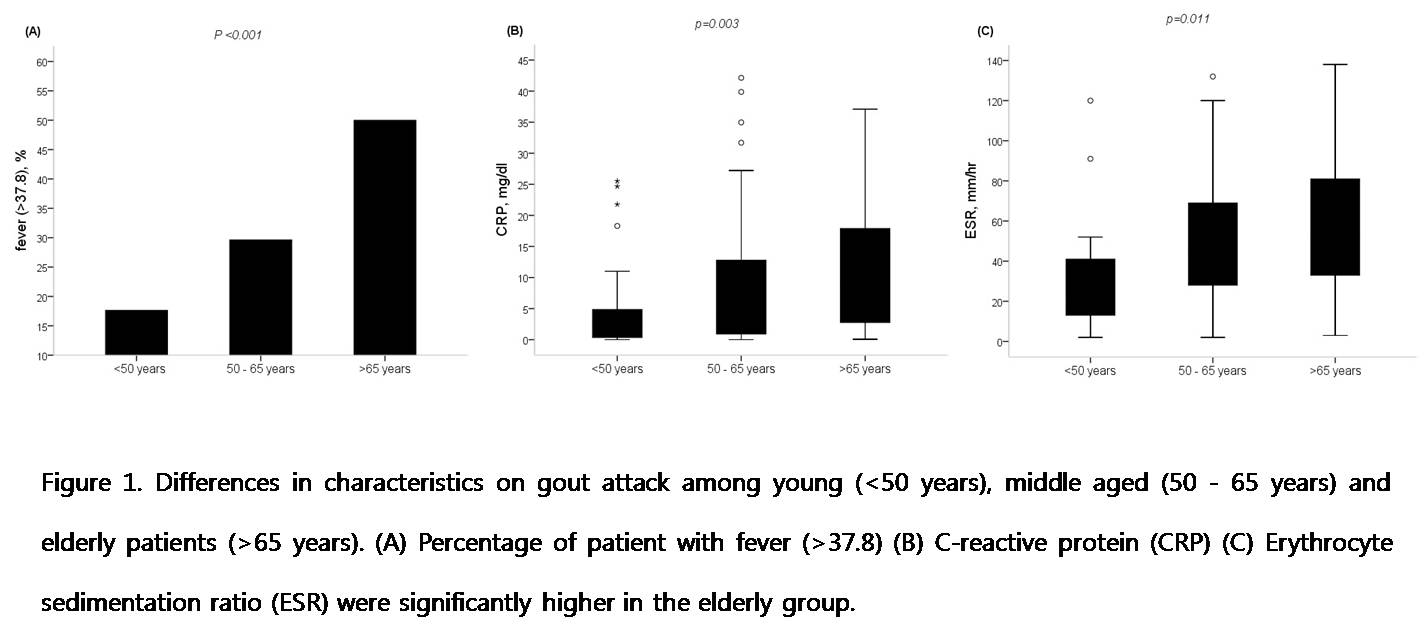
Fever was more often present in the elderly patients (17.6% in young vs. 29.6% in middle aged vs. 50.0% in elderly, p=0.001 by chi-square test). Although numbers of involved joints during attacks did not differ between groups (p=0.656), CRP and ESR levels during gout attack increased significantly with age (Figure 1).
Conclusion
Since gout attacks in elderly patients are accompanied by stronger systemic inflammatory response, often resembling sepsis or septic arthritis, it is crucial to correctly diagnose them as gout so that unnecessary invasive diagnostics including joint lavage and prolonged antibiotic treatment can be avoided.
Key words: gout, age, elderly, fever
Disclosure:
J. A. Yang,
None;
J. H. Lee,
None;
E. Y. Lee,
None;
E. B. Lee,
None;
Y. W. Song,
None;
J. K. Park,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/higher-inflammatory-response-in-elderly-patients-during-gout-attack/