Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (1855–1876) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) is crucial for diagnosing and managing interstitial lung disease associated with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARD-ILD), as it reveals characteristic patterns that inform treatment and prognosis in clinical practice. However, molecular expression patterns linked to HRCT findings remain underexplored. Since lung sampling is invasive and rare clinically, identifying alternative biological materials that reflect lung processes is essential. The united airway disease hypothesis posits that similar molecular pathways exist between the upper and lower respiratory tracts. Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate the association between HRCT patterns and molecular expression profiles in SARD-ILD using transcriptomics.
Methods: Nasal mucosa samples were collected via Copan Flocked Swab (Copan Diagnostics 56380CS01) from SARD-ILD patients at Oslo University Hospital and healthy controls from UCLA and Oslo. HRCT patterns and clinical data were collected simultaneously. We assessed nasal mucosa transcriptomes to identify molecular expression profiles of SARD-ILD with lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia (LIP), nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis (NSIP) and usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) compared to healthy controls. Transcriptomes were determined by NanoString technology, using the Autoimmune Profiling panel. Gene expression and pathway analyses were conducted using ROSALIND software (https://www.rosalind.bio/). To confirm lung-level findings, lung tissue samples were collected at the University Hospital Zurich from eight SARD-ILD and two healthy controls. Gene expression patterns were assayed using the 10x VisiumHD spatial transcriptomics platform.
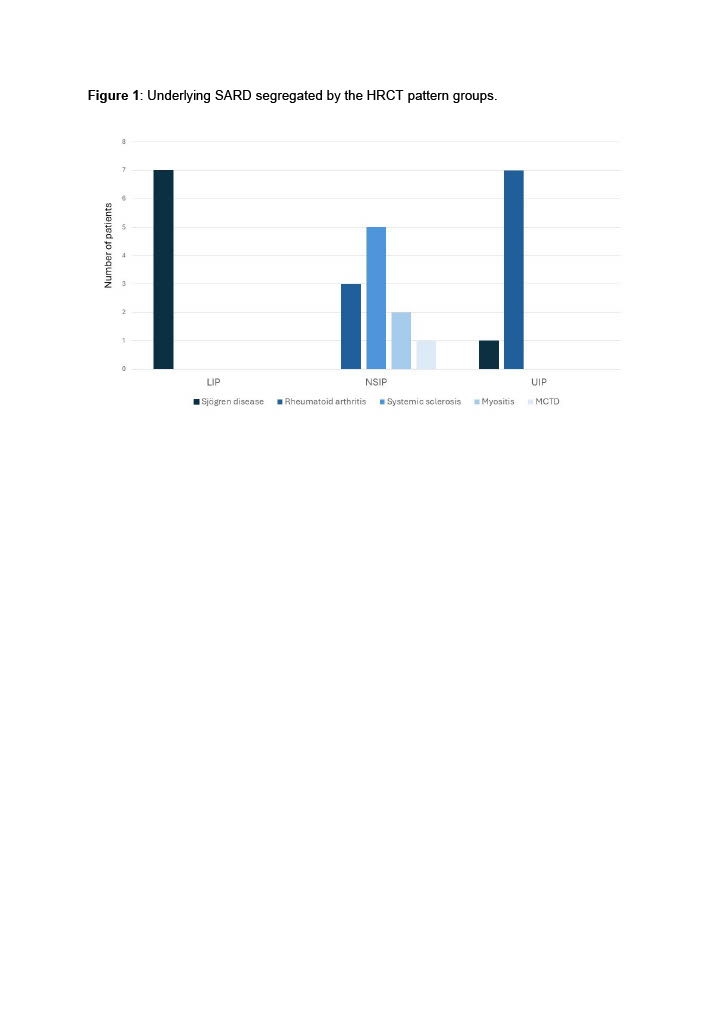
Results: We included nasal mucosa samples from 7 LIP, 11 NSIP, 8 UIP patients, and 10 healthy controls (Fig. 1). We identified 55, 236, and 79 significant differentially expressed genes for LIP, NSIP, and UIP, respectively, compared to controls (Fig. 2). LIP was enriched mainly for IFN-type I, MHC class I antigen presentation, epigenetic and transcriptional regulation, and IFN-type II; NSIP for IFN-type I, Treg and TH2 differentiation, and IFN-type II; UIP for TH2 differentiation, complement system, IL activation, inflammasomes, Treg, and TH17 differentiation (Fig. 3). Visium HD data from lung biopsies are being processed to spatially resolve whole transcriptomes and further examine these pathways in the lung.
Conclusion: The molecular fingerprints of LIP, NSIP, and UIP provide critical insights into their distinct pathophysiological mechanisms. While LIP is characterized by significant inflammation driven by lymphocytes, NSIP shows a mixed inflammatory response with some regulatory T cell involvement. In contrast, UIP is associated with a complex interplay of immune pathways that drive chronic inflammation and tissue remodeling. Understanding these molecular profiles is essential for tailoring treatment strategies and improving outcomes in patients with SARD-ILD. Our Visium HD results will further validate and characterize this preliminary molecular fingerprint by generating spatially resolved and unbiased lung transcriptome data.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Stauffer P, Palchevskiy V, Much L, Diep P, Abel M, Moe N, Gaisl T, Steinack C, Lari S, Pachera E, Molberg Ø, Distler O, Weigt S, Belperio J, Hoffmann-Vold A. High-throughput Screening Uncovers Distinct Molecular Signatures Linked with HRCT Patterns in SARD-ILD [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-throughput-screening-uncovers-distinct-molecular-signatures-linked-with-hrct-patterns-in-sard-ild/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-throughput-screening-uncovers-distinct-molecular-signatures-linked-with-hrct-patterns-in-sard-ild/

.jpg)
.jpg)