Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a sensitive method for detection of sacroiliitis. However, recently, concerns have been raised about its specificity. In contrast to radiographic spondyloarthritis (SpA), non-radiographic SpA has a more equal sex distribution. Hence, in young women with back pain a broad differential diagnosis has to be considered. In clinical practice, women occasionally present with inflammatory(-like) low back pain, following pregnancy and childbirth. Up until now, little is known regarding the presence of SpA-like MRI lesions in postpartum women. We hypothesized that physical stress on the pelvis during pregnancy may lead to signs of bone marrow edema on MRI.
The objectives of this study are to explore (A) the association between pregnancy and giving birth on the one hand, and the occurrence of MRI lesions compatible with SpA on the other hand; and (B) if these lesions are transient.
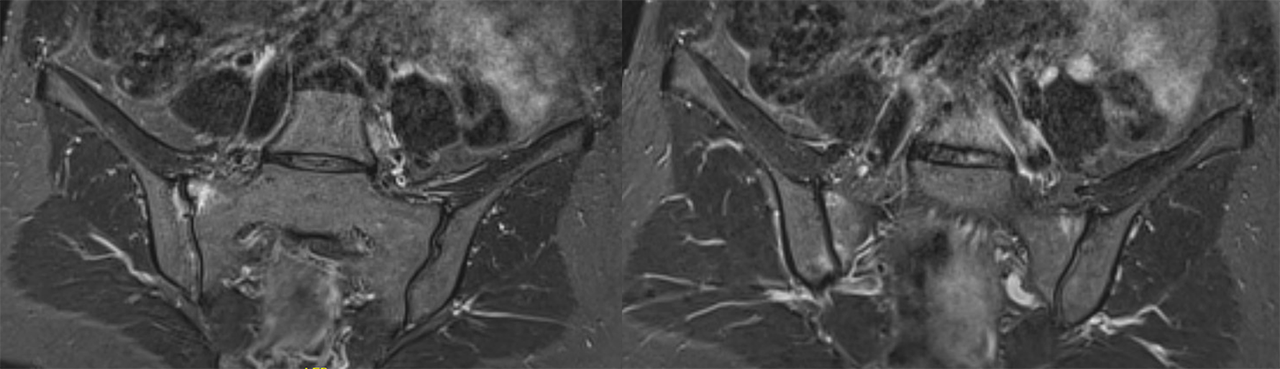
Methods: Twenty-five women underwent an MRI of the sacroiliac joints (SIJ) in the first 10 days after vaginal delivery. The scan was repeated after 6 months. Both time points were scored in pairs by 3 trained readers, blinded for time sequence and subject characteristics. MRI assessment was done on 6 consecutive slices for inflammatory and structural SpA-like lesions; bone marrow edema (BME), capsulitis, enthesitis, high signal intensity in joint space, erosions, fatty lesions, sclerosis and (partial) ankylosis. In addition, the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) definition of a positive MRI-SIJ was applied. MRI reader scores were reported as 2 out of 3 (median) scores.
Results: Twenty out of 25 (80.0%) subjects displayed BME; the median SPARCC score was 5 (IQR 1-11) (see table). One subject was lost to follow-up. After 6 months, 11 out of 24 (45.8%) subjects still showed BME; however, median SPARCC score dropped to 0 (IQR 0-1) (p = 0.002). At baseline, 16 out of 25 (64.0%) participants had a positive MRI-SIJ according to the ASAS definition, reducing to 4 out of 24 (16.7%) after 6 months (p = 0.002). 75.5% of the baseline lesions were located in the anterior part of the SIJ; 57.3% situated on the iliac side. Structural lesions were rarely detected in this study population (see table).
Conclusion: A very high prevalence of sacroiliac BME on MRI was seen in women immediately postpartum with 64.0% even having a positive MRI for sacroiliitis according to the ASAS definition. A significant decrease in BME was seen over 6 months time, yet a substantial fraction continued to display BME after follow up. History of a recent pregnancy is crucial to take into account when interpreting an MRI-SIJ. In case of a recent pregnancy and clinical suspicion of SpA, it may be wise to postpone MRI-SIJ imaging until at least 6 months after the delivery.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Renson T, De Craemer A, Deroo L, Depicker A, de Hooge M, Herregods N, Jans L, Roelens K, Dehaene I, Carron P, Van den Bosch F, Elewaut D. High Prevalence of Sacroiliac Bone Marrow Edema on MRI in Post Partum Women: A Temporary Phenomenom [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-prevalence-of-sacroiliac-bone-marrow-edema-on-mri-in-post-partum-women-a-temporary-phenomenom/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-prevalence-of-sacroiliac-bone-marrow-edema-on-mri-in-post-partum-women-a-temporary-phenomenom/