Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: 3S078: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes I: Pulmonary & Other Comorbidities (839–844)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD), a significant cause of morbidity and mortality, are poorly understood. RA-ILD detection is limited by the poor inter- and intra- observer variability on computed tomography (CT) scans, especially in early disease or when quantification of lung parenchyma involvement is attempted. Quantitative densitometry uses a computerized algorithm to measure the density of lung parenchyma, expressed as the proportion of the volume of high attenuation [percent high attenuation areas (%HAA)]. We sought to identify demographic and RA disease-specific risk factors for %HAA progression (increased by ≥ 10% from baseline %HAA).
Methods: RA patients enrolled in a prospective cohort study of cardiovascular disease underwent cardiac CT scans at baseline, pulmonary function testing and pulmonary symptom questionnaire at visit 2 (an average of 18 months post-baseline). A subset of patients underwent repeat cardiac CT scans at visit 3 (an average of 38 months post-baseline). Baseline scans were read by an expert pulmonary radiologist for ILD features. Baseline and V3 scans were assessed with quantitative densitometry, with %HAA calculated. Logistic regression was used to model the association of RA characteristics with strata of %HAA.
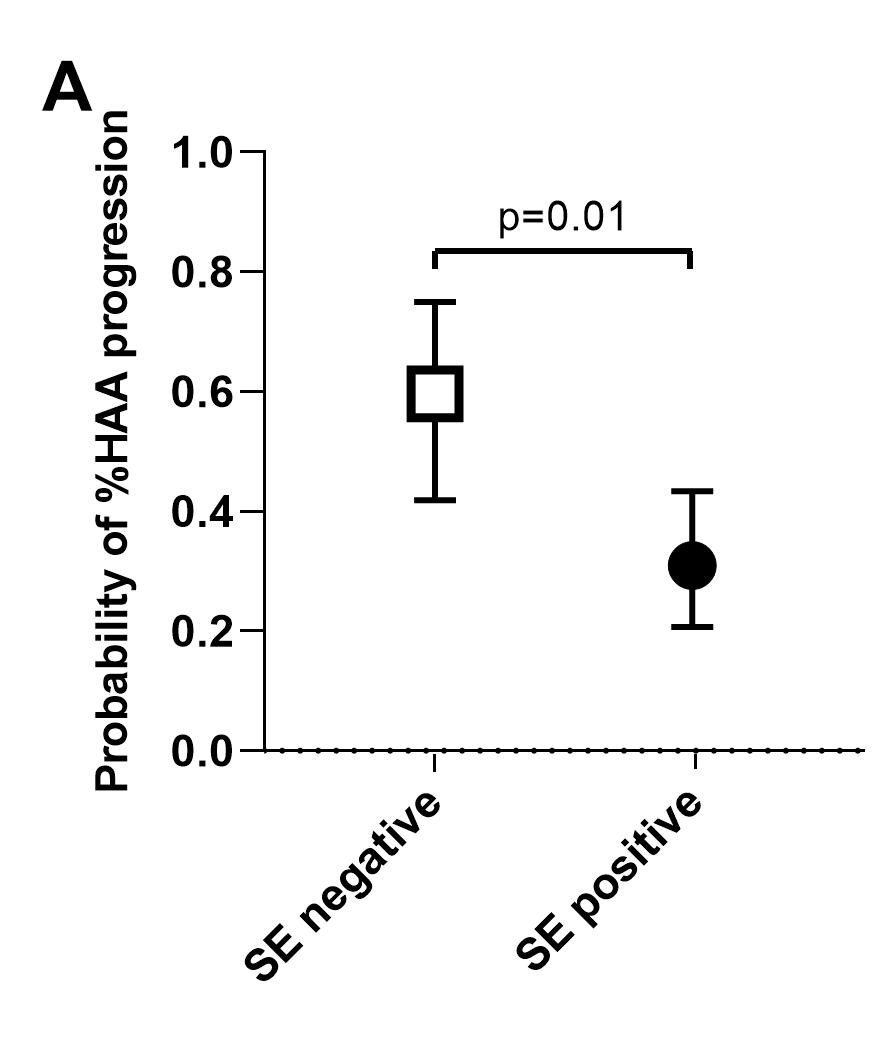
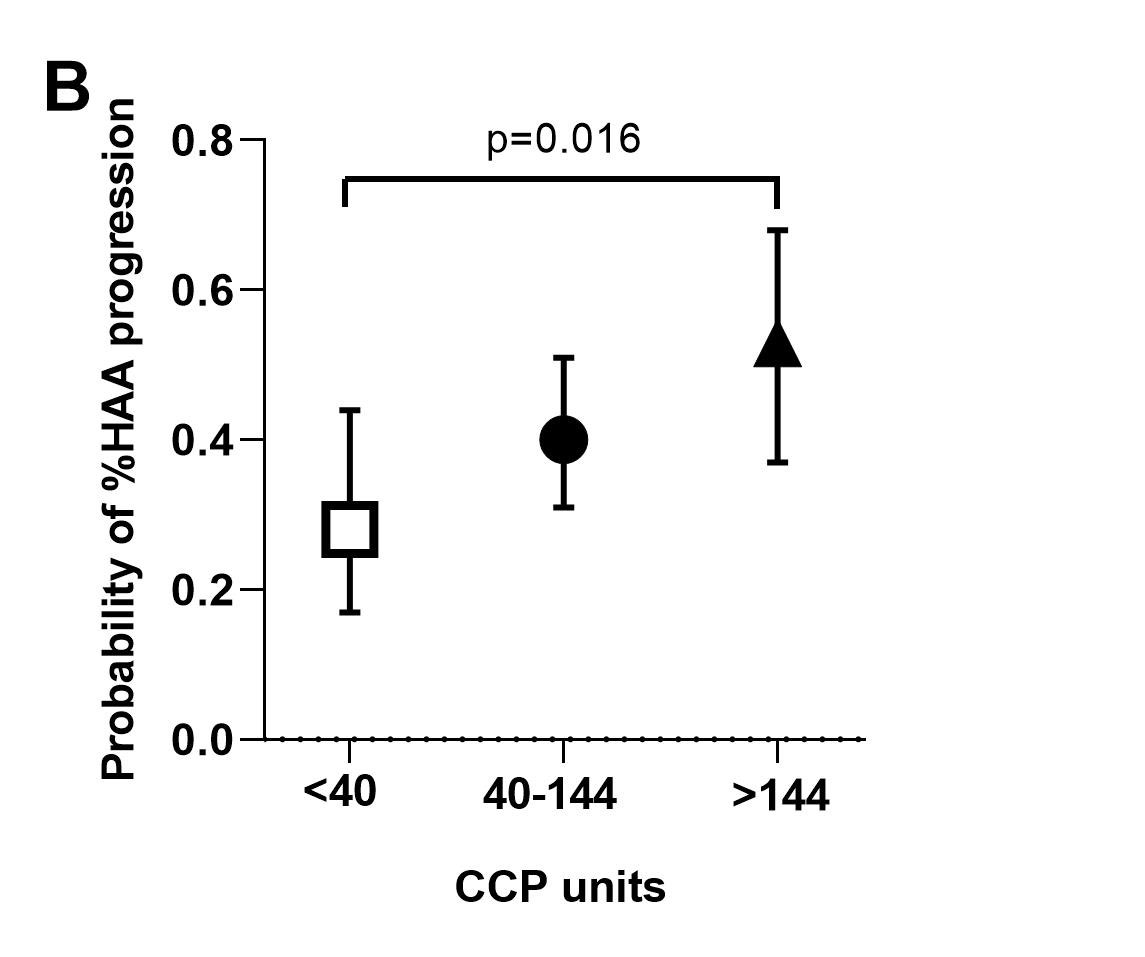
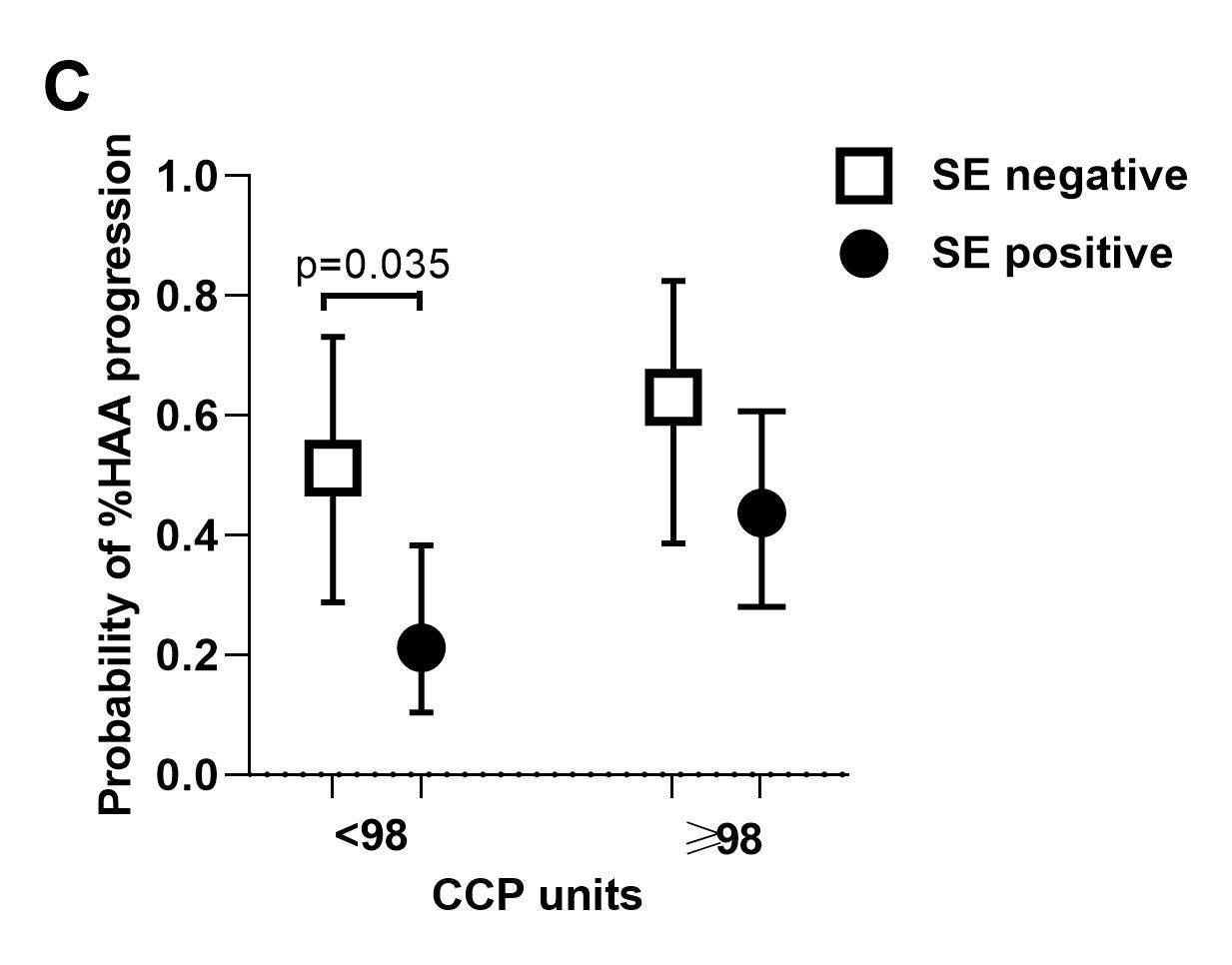
Results: A total of 193 patients had CT densitometry assessed at V1 [mean age=59 years; 61% female; median RA duration=8 years; %HAA=2.3-18.8 % of the lung parenchyma; 36% had evidence of ILD (predominantly mild) on expert read, 60% of whom were symptomatic]. Compared with subjects in the low %HAA stratum, subjects in the high %HAA stratum had a greater number of pack-years of smoking, a higher BMI, and a higher fibrosis score based on expert evaluation. A greater proportion were ever smokers, had shortness of breath on exertion on visit 2, a restrictive pattern on pulmonary function tests on visit 2, and a lower FVC on visit 2. After adjustment, higher BMI, anti-CCP ≥ 200 units, and a greater number of pack-years of smoking were each significantly associated with increased %HAA (≥10 % of the lung) at baseline visit, while male sex had a protective role against %HAA. For the subgroup of n=107 patients with repeat CT densitometry at V3, %HAA remained stable in 26%, decreased in 35%, and progressed in 39% of subjects. After adjustment, shared epitope was inversely associated with %HAA progression in the follow-up period (Figure A). Higher anti-CCP was significantly associated with %HAA progression in the follow-up period (Figure B). The protective effect of shared epitope against HAA progression was statistically significant in patients in the low anti-CCP stratum (Figure C).
Conclusion: These prospective data provide evidence that anti-CCP, smoking, and absence of shared epitope are contributors to RA-ILD and could allow for early diagnosis and management of this serious complication of RA. Our findings on the negative effect of shared epitope are congruent with recently published data that have revealed strong association of a non-HLA gene (MUC5B promoter variant) with RA-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alevizos M, Danoff S, Pappas D, Lederer D, Johnson C, Bernstein E, Bathon J, Giles J. High Lung Attenuation Measured with Quantitative Densitometry as a Surrogate Marker for Interstitial Lung Disease in RA: Association with Anti-CCP, Smoking, and Absence of Shared Epitope [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-lung-attenuation-measured-with-quantitative-densitometry-as-a-surrogate-marker-for-interstitial-lung-disease-in-ra-association-with-anti-ccp-smoking-and-absence-of-shared-epitope/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-lung-attenuation-measured-with-quantitative-densitometry-as-a-surrogate-marker-for-interstitial-lung-disease-in-ra-association-with-anti-ccp-smoking-and-absence-of-shared-epitope/