Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The primary objective was to evaluate the effect of body mass index (BMI) on tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) blockers (including etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab and golimumab) retention in patients with RA.
Methods: This prospective cohort study contains data from the Israeli registry of inflammatory diseases, status May 2019. Patients were grouped by BMI: normal (BMI < 24.9 kg/m2), overweight (BMI 25-29.9 kg/m2), obese (BMI 30-34.9 kg/m2) and morbid obese (BMI ≥35 kg/m2). Event-free survival was calculated using Cox regression with a Hazard Ratio and Confidence Interval of 95%. Kaplan-Meier Analysis was used to describe drug survival. Statistical significance was defined as p< 0.05.
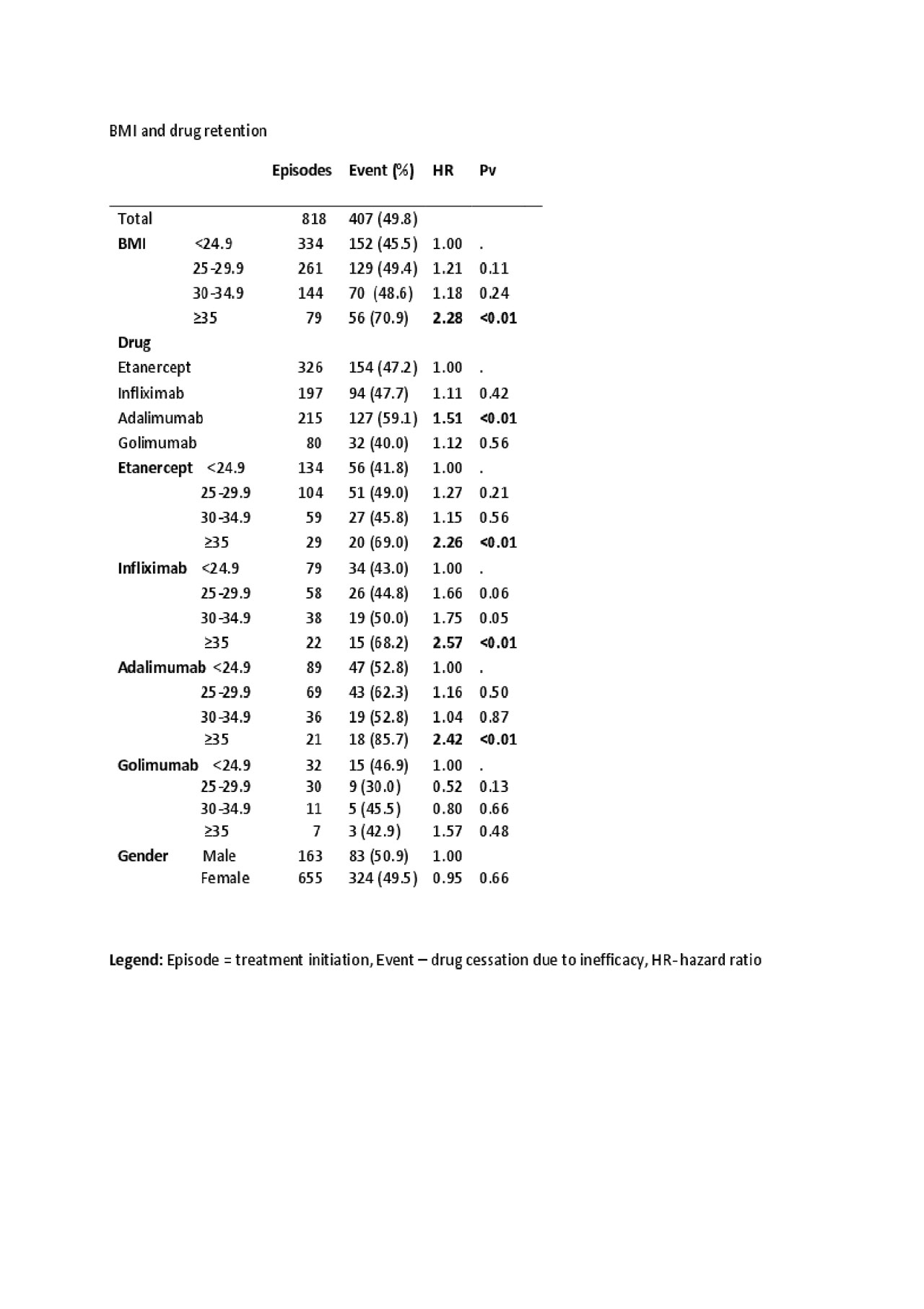
Results: The registry included 521 RA patients (80% females) treated with etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab or golimumab. 818 treatment initiations were included in the final analysis, 334 in the normal weight group, 261 in the overweight, 144 in the obese and 79 in the morbid obesity group. 326 treatment episodes were with etanercept, 215 with adalimumab 197 with infliximab, and 80 with golimumab. Negative correlation of elevated BMI with lower drug survival was significant when comparing the morbid obese group to the other patients HR 2.06 (95% CI 1.55-2.73, p< 0.01), indicating a higher rate of treatment switches with BMI >35, the difference was significant in all the drugs, except golimumab that showed insignificant trend. Adalimumab switch rate was higher compared to etanercept with HR =1.51 (95% CI 1.20-1.91, p< 0.01), no other significant differences were noted between the other drugs.
Conclusion: Morbid obese RA patients have lower TNF-α blocker retention compared to normal weight patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Elkayam O, Lidar M, Reitblat T, Zisman D, Balbir-Gurman A, Kakakian O, Meshiach T, Almog R, Elalouf O. High Body Mass Index Shortens Retention of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Blocker Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-body-mass-index-shortens-retention-of-tumor-necrosis-factor-%ce%b1-blocker-treatment-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-body-mass-index-shortens-retention-of-tumor-necrosis-factor-%ce%b1-blocker-treatment-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/