Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: IL-6 is a key cytokine in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and is elevated in serum and synovial fluid of RA patients. However, the impact of baseline IL-6 levels on patient-reported RA symptoms and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) has not been explored in clinical trials evaluating IL-6 blockade. Sarilumab, a human monoclonal antibody targeting IL-6 receptor alpha, plus methotrexate (MTX) significantly improved clinical and patient reported outcomes vs MTX alone among inadequate responders (IR) to MTX in the MOBILITY randomized controlled trial (NCT01061736). This post-hoc analysis evaluated if baseline IL-6 levels can predict greater improvements in symptoms and HRQoL with sarilumab + MTX vs MTX.
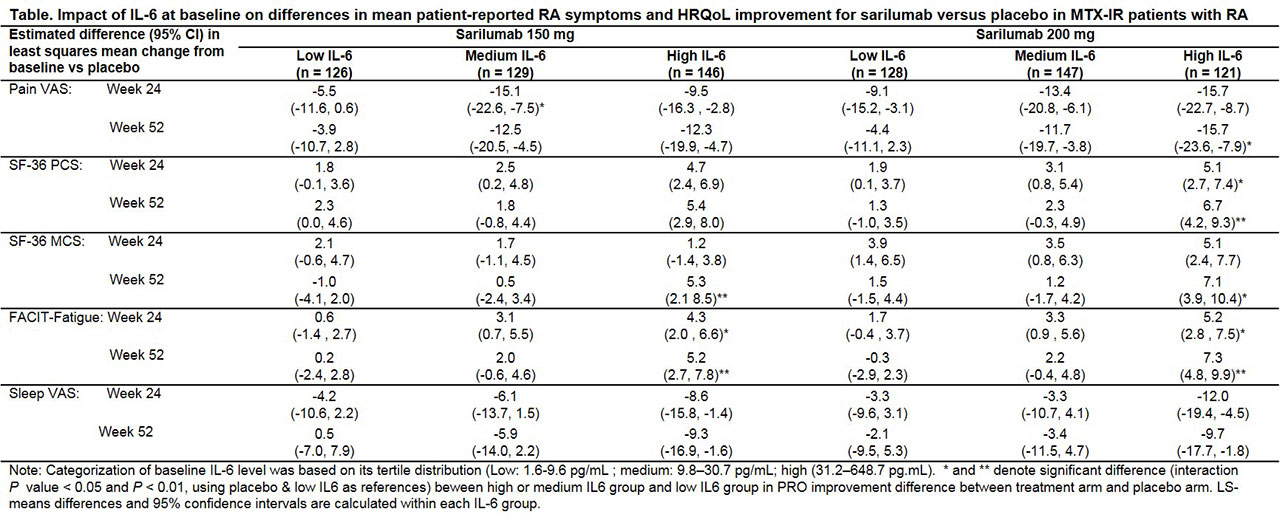
Methods: 1193 of 1197 patients in the intent-to-treat population with moderate-to-severely active RA receiving MTX or sarilumab (150 mg or 200 mg subcutaneous every 2 weeks) + MTX, with baseline IL-6 values were included. Serum IL-6 was measured by immunoassay (Quantikine IL-6). Patients were grouped into tertiles according to baseline IL-6 levels (high, medium and low, see Table). Patient-reported RA symptoms and HRQoL were measured at baseline and post-treatment (Weeks [W] 24 and 52): pain visual analog scale (VAS), SF-36 physical (PCS) and mental component scores (MCS), FACIT-Fatigue (FACIT-F) and sleep VAS. Linear regression on changes from baseline in symptoms and HRQoL were performed with IL-6 tertile, treatment, prior biologic use, and region as stratification factors, and baseline IL-6 tertile-by-treatment interactions (with placebo and low IL-6 tertile as references) as fixed effects, to assess the predictivity of IL-6 levels. P-values of the interaction for each sarilumab group were provided using placebo and low tertile as references. Pairwise comparisons of symptoms and HRQoL improvements between treatment groups were also performed in each tertile; differences in least squares mean vs placebo, and 95% CIs were calculated.
Results: At baseline, patients in the high IL-6 tertile had greater disease activity, more radiographic structural damage, elevated levels of CRP levels, and poorer symptoms and HRQoL (pain VAS, SF36-PCS, and sleep VAS; data not shown) vs those in lower IL-6 levels (P < 0.05) and generally reported greater RA symptoms and HRQoL improvements with sarilumab vs placebo (Table). Significant differences (interaction P-value < 0.005) between high and low tertiles were evident in pain VAS (W52) and SF-36 PCS (W24 and W52) with 200 mg; SF-36 MCS with both 150 mg and 200 mg (W52) and FACIT-F scores with both 150 mg and 200 mg (W24 and W52). The incidence of treatment emergent adverse events was similar across IL-6 groups.
Conclusion: Among MTX-IR RA patients, high baseline IL-6 levels may predict better improvements in patient-reported RA symptoms and HRQoL with sarilumab treatment vs placebo than those with low levels. This findings support previous analyses, which showed that across clinical and radiographic endpoints, patients with elevated baseline IL-6 levels had greater responses to sarilumab compared with MTX or adalimumab than those without IL-6 elevations. Prospective validation is warranted to confirm these data.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Msihid J, Kimura T, Boyapati A, St John G, Wei W. High Baseline Serum IL-6 Predicts Increased Sarilumab Treatment Response for Patient Reported Symptoms and Health-Related Quality of Life Among Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Inadequate Response to Methotrexate [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-baseline-serum-il-6-predicts-increased-sarilumab-treatment-response-for-patient-reported-symptoms-and-health-related-quality-of-life-among-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-inadequate-response-t/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-baseline-serum-il-6-predicts-increased-sarilumab-treatment-response-for-patient-reported-symptoms-and-health-related-quality-of-life-among-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-inadequate-response-t/