Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Marketing of biosimilar biological drugs may significantly reduce drug costs if comparable safety and efficacy of originator and the biosimilar can be documented. In a phase 3 randomized clinical trial, biosimilar SB4 treatment had a slightly higher occurrence of hepatobiliary adverse events compared with the originator etanercept (ETN) treatment (ref 1) – potentially explained by differences in patients’ comorbid diseases and co-medication use (ref 2). In Denmark, biosimilars have high penetration due to a tender-based system with tax-paid biologics. Therefore, in April 2016, Danish patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases were mandatorily switched from ETN to SB4 (=non-medical switch) (ref 3) and SB4 became the first choice for bio-naïve patients.
We aimed to explore the incidence rates (IRs) of hepatobiliary events during the first 6 months of routine care treatment with either ETN or SB4 among Danish adult patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
Methods: Observational cohort study. Patients initiating treatment with ETN (Jan 2010-April 2016) or SB4 (April 2016-Feb 2018) were identified in the nationwide DANBIO registry. Among SB4 treated patients, the subgroup of non-medical switchers (i.e. had switched from ETN 0-90 days previously) was identified. Furthermore, patients could be either bDMARD-naïve or switchers from previous bDMARD treatment (other than ETN). Incident hospital contacts (hospitalizations or out-patient care) due to hepatobiliary events were identified through linkage to the national patient registry and included diseases of the liver, gallbladder and bile duct system. Age and gender standardized IRs per 100 person-years (PY) during 0-6 months since treatment start were assessed.
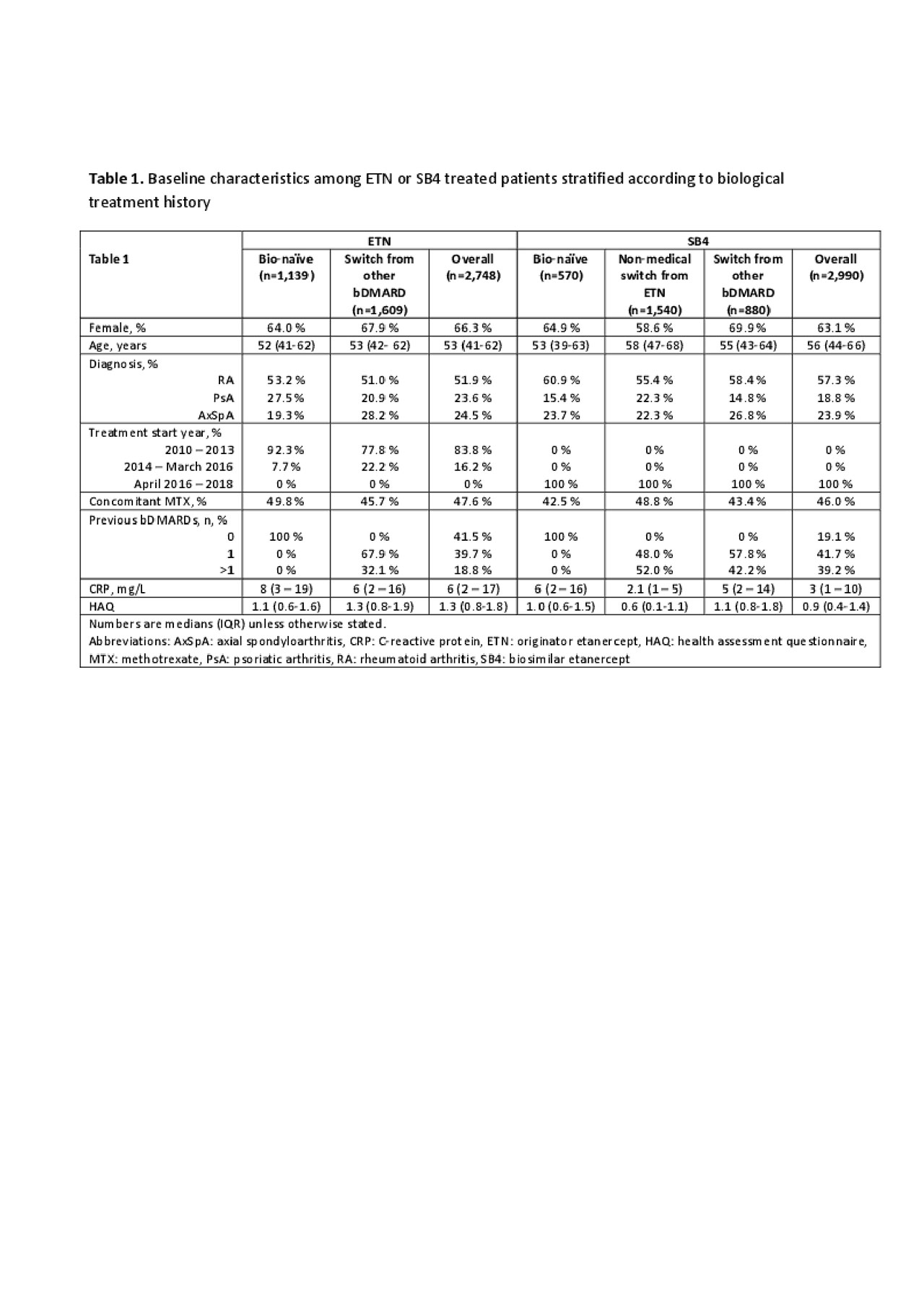
Results: A total of 5,738 patients (2,748 ETN/2,990 SB4) were included (Table 1). Among SB4-treated patients, 52% were non-medical switchers. Baseline characteristics were similar for bio-naïve patients who started SB4 or ETN and similarly for patients who had switched from other bDMARD. Non-medical switchers tended to have lower disease activity (Table 1).
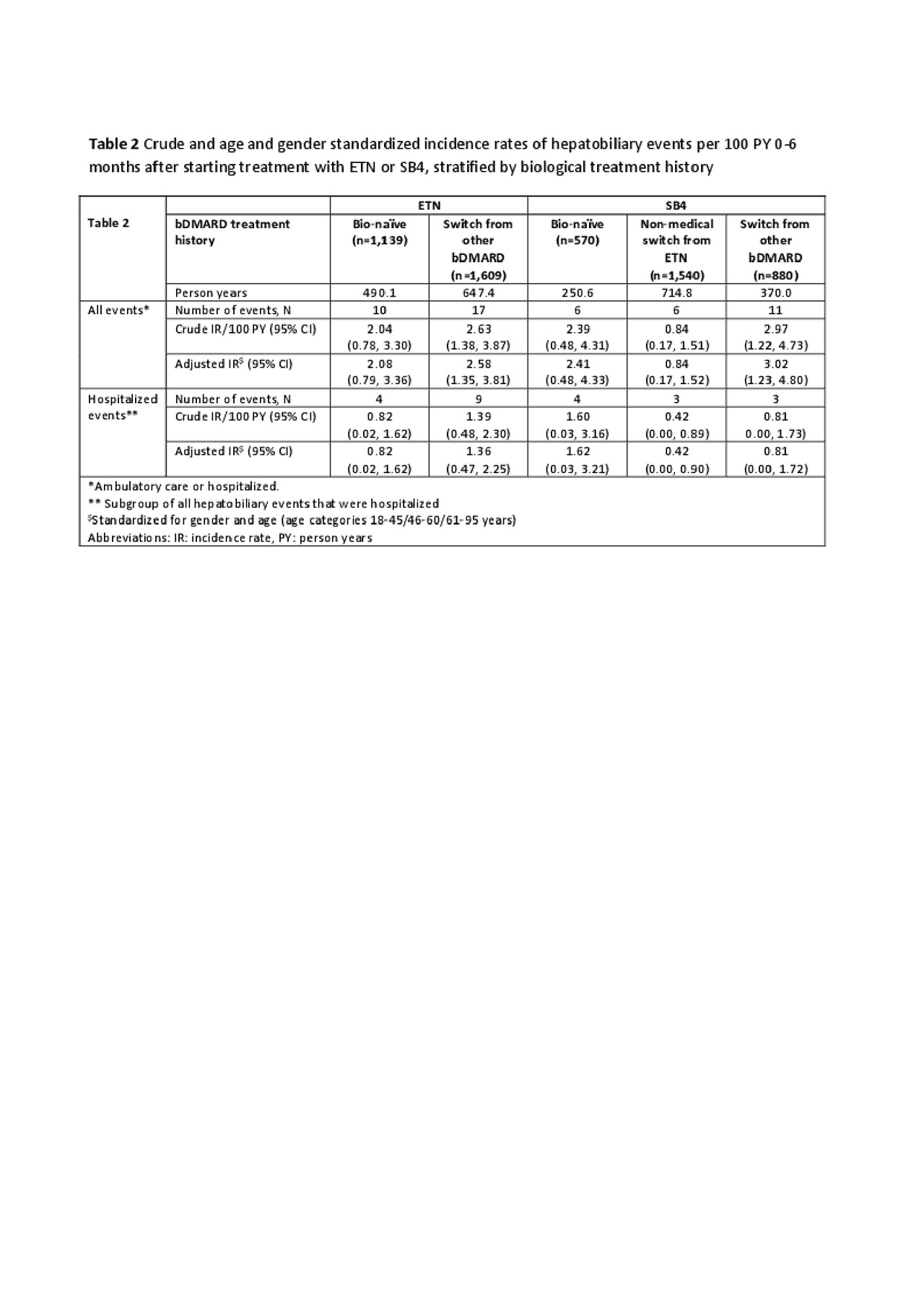
During the first 6 months of treatment, 50 hepatobiliary events were identified, of which 23 were hospitalized (Table 2). IRs in all treatment groups were low with wide and overlapping confidence intervals. There was a tendency towards lover IR of hepatobiliary events among SB4 non-medical switchers.
Among the 50 patients with hepatobiliary events, 14 (28%) received concomitant methotrexate. Main events were gall-bladder stones (8 events), elevated transaminases (5 events), liver-cirrhosis (3 events) and pancreatitis (3 events).
Conclusion: In this observational cohort study of >5,000 patients with inflammatory arthritis treated with originator or biosimilar etanercept in routine care, IRs of hepatobiliary events occurring during the first 6 months of treatment showed no apparent differences between the treatment groups.
References
- Emery P, et al. ARD 2017; 76(1):51-57.
- Emery P, et al. ARD 2016;75(10):e65.
- Glintborg B, et al. ARD 2019;78(2):192-200.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Glintborg B, Georgiadis S, Nørgaard M, Mehnert F, Lederballe Grøn K, Krogh N, Lund Hetland M. Hepatobiliary Events in >5000 Patients with Inflammatory Arthritis Treated with Biosimilar or Originator Etanercept in Routine Care, Results from the Danish Nationwide DANBIO Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hepatobiliary-events-in-5000-patients-with-inflammatory-arthritis-treated-with-biosimilar-or-originator-etanercept-in-routine-care-results-from-the-danish-nationwide-danbio-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hepatobiliary-events-in-5000-patients-with-inflammatory-arthritis-treated-with-biosimilar-or-originator-etanercept-in-routine-care-results-from-the-danish-nationwide-danbio-registry/