Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
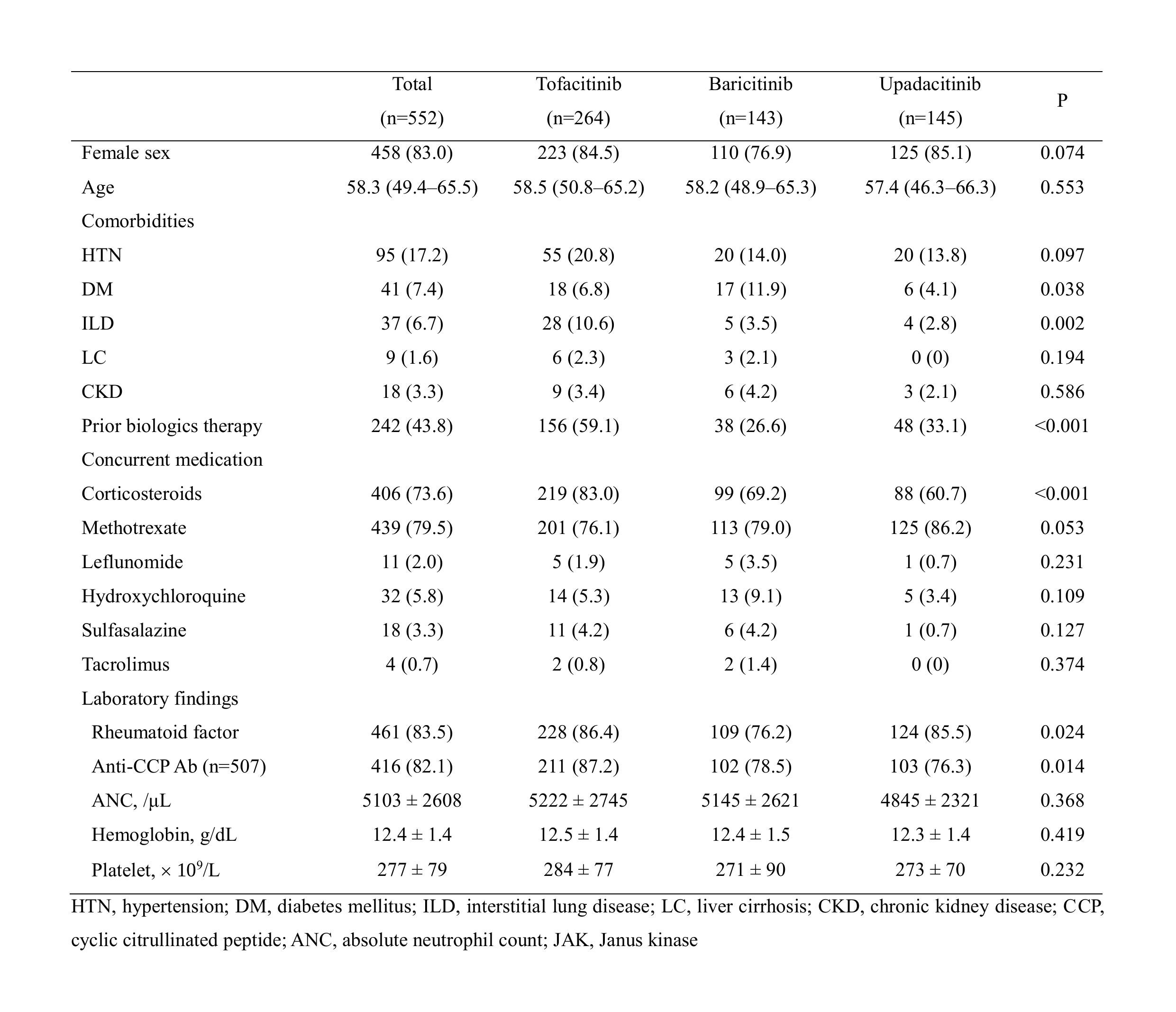
Background/Purpose: Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors’ introduction has significantly revolutionized the therapeutic landscape, notably influencing the management strategies for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). To compare the effects of different JAK inhibitors (tofacitinib, baricitinib, and upadacitinib) on hematological parameters in patients with RA.
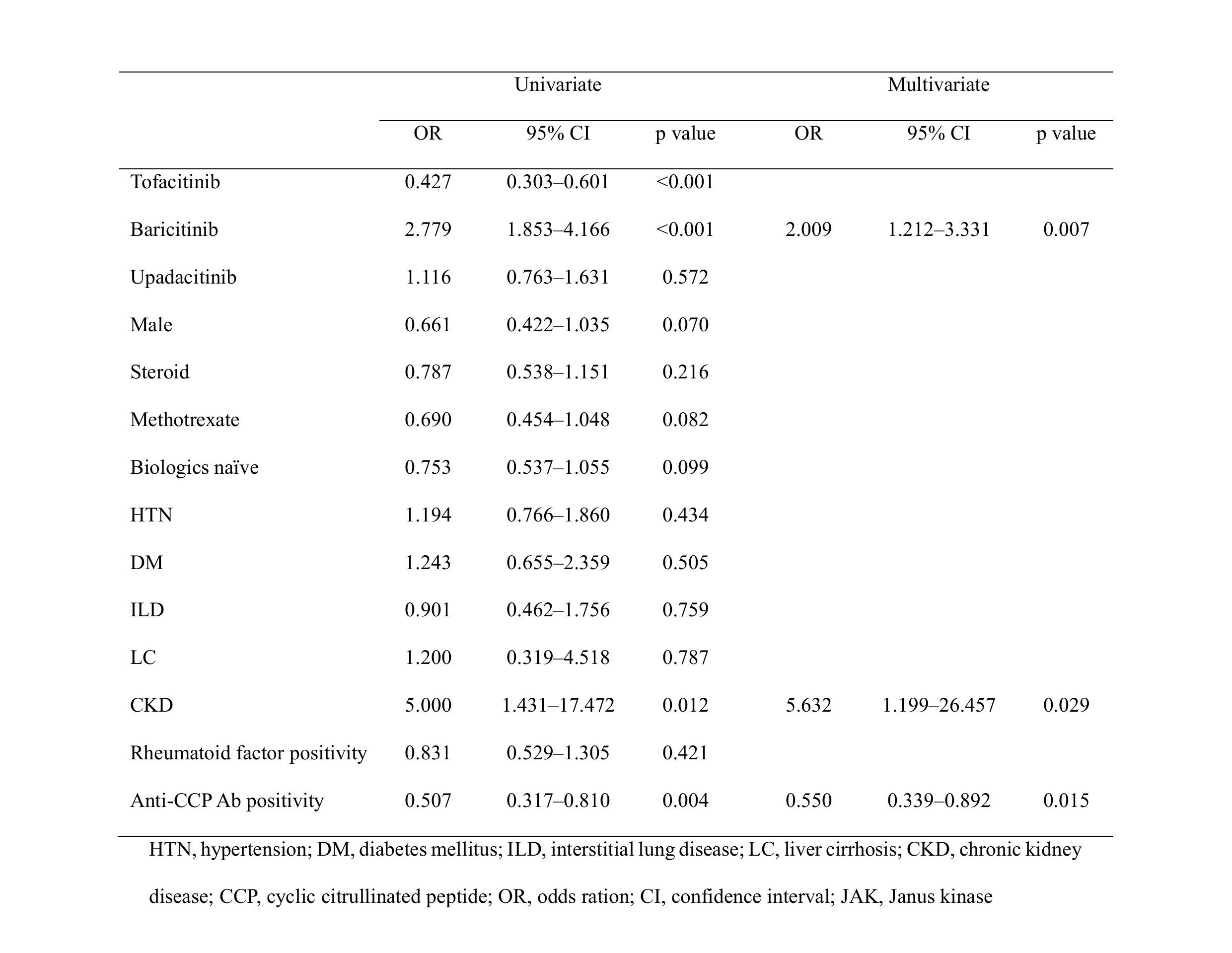
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on patients with RA treated with JAK inhibitors at a tertiary hospital between August 2015 and February 2024. Hematological parameters, including absolute neutrophil count (ANC), hemoglobin, and platelet count, were assessed at baseline and after 6 months of therapy with JAK inhibitors. Statistical analysis was performed to evaluate changes over time, and logistic regression analyses was conducted to identify factors associated with hematologic alterations.
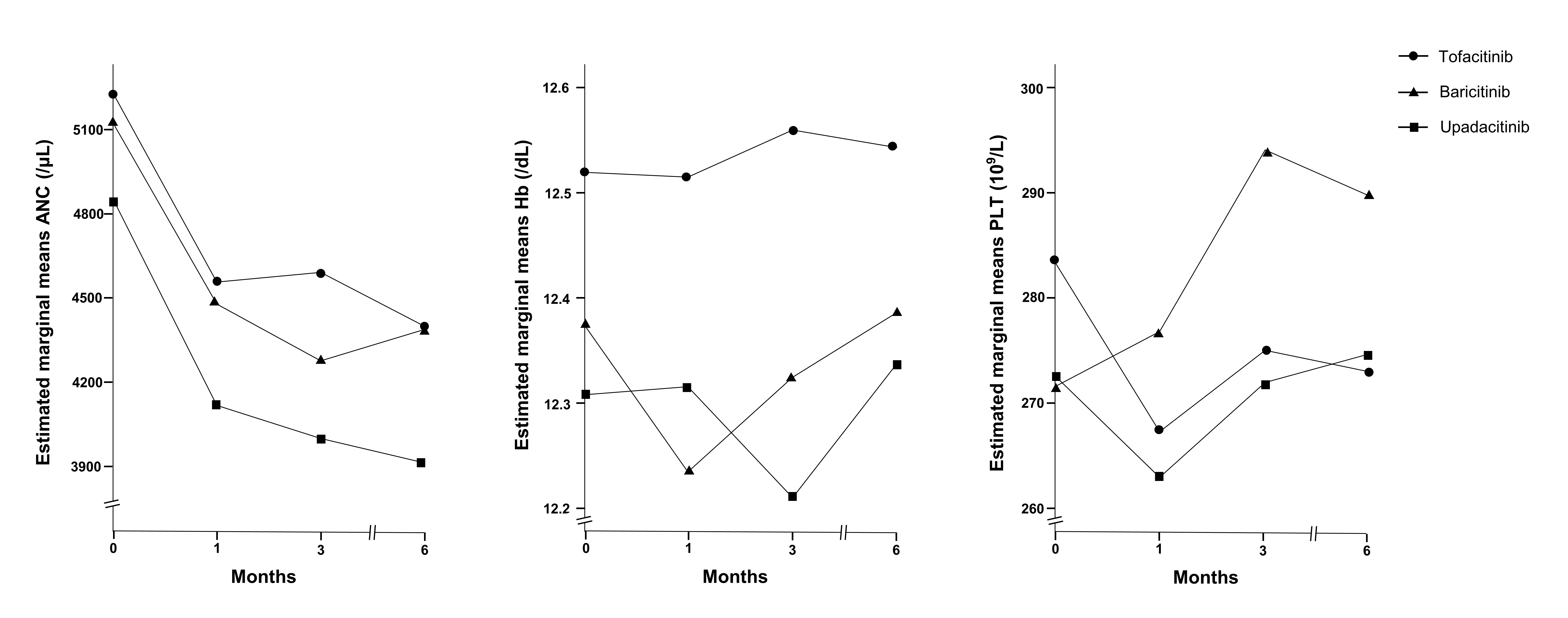
Results: The study included 552 patients in three groups: tofacitinib (n=264), baricitinib (n=143), and upadacitinib (n=145). There were no significant differences in baseline hematological parameters across the three groups. After 6 months, ANC decreased in all the groups, without a statistical significance difference between them (P=0.465). Platelet counts increased in patients treated with baricitinib compared to those in patients treated with tofacitinib (Pillai’s trace value, 0.063, P< 0.001) or upadacitinib (Pillai’s trace value, 0.029, P< 0.001). Multivariate analysis showed that baricitinib was significantly associated with increased platelet count (odds ratio, 2.009; 95% confidence interval, 1.212–3.331, P=0.007).
Conclusion: Although therapy with all the three JAK inhibitors showed a decrease in ANC, baricitinib treatment was notably associated with an increase in platelet counts. These findings suggest the potential differences among JAK inhibitors according to their subtypes, and the need for individualized monitoring. We highlighted the importance of understanding hematological changes for optimizing RA management with JAK inhibitors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ahn S, Cho M, Oh J, Kim Y, Lee C, Yoo B, Hong S. Hematological Impact Assessment of Tofacitinib, Baricitinib, and Upadacitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hematological-impact-assessment-of-tofacitinib-baricitinib-and-upadacitinib-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-treatment/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hematological-impact-assessment-of-tofacitinib-baricitinib-and-upadacitinib-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-treatment/