Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster IV
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Substantial numbers of patients with RA receiving advanced therapies including biologics, biosimilars, and Janus kinase inhibitors do not achieve ACR50 responses and lack of response has been associated with higher healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) and economic burden; however, such data for patients with RA in Japan are limited. This study compared HCRU and direct cost burden between patients with RA who responded (responders) or did not respond (non-responders) to advanced therapies.
Methods: This retrospective study included data from the Medical Data Vision claims database between April 2018 and September 2020. Patients who initiated ≥1 advanced therapy between October 2018 and September 2019 (index date was the date of initiation) and had ≥1 RA diagnosis claim during the 6-month pre-index period, ≥2 RA diagnosis claims at any time, and 12 months of follow-up, were included. Non-responders and responders to advanced therapies were identified using a validated algorithm developed by Curtis et al.1 A sensitivity analysis allowing a lower cutoff for adherence (Medical Possession Ratio ≥50%) was also carried out. HCRU and all-cause and RA-related direct medical, emergency department (ED), laboratory, and pharmacy costs, were compared between the groups. Costs were converted to 2019 ¥ and compared between groups. Multivariable analyses using negative binomial regression or generalized linear models were used to determine the risks of HCRU or cost; adjusted incidence rate ratios (IRR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) are reported.
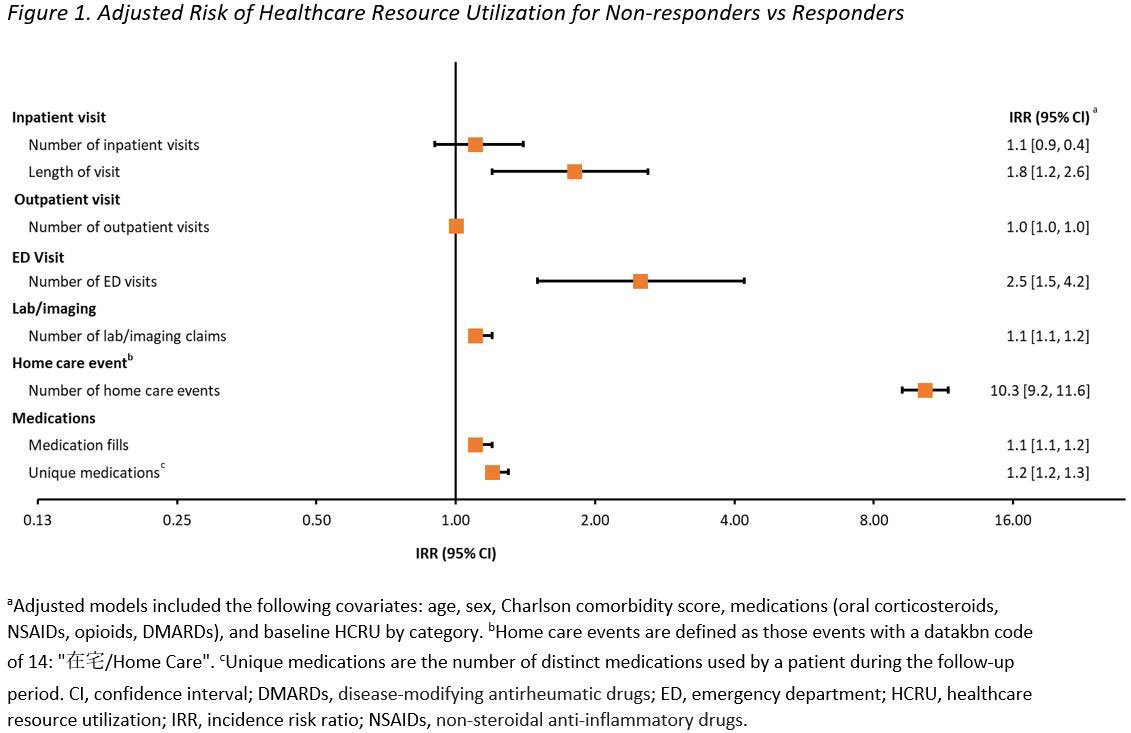
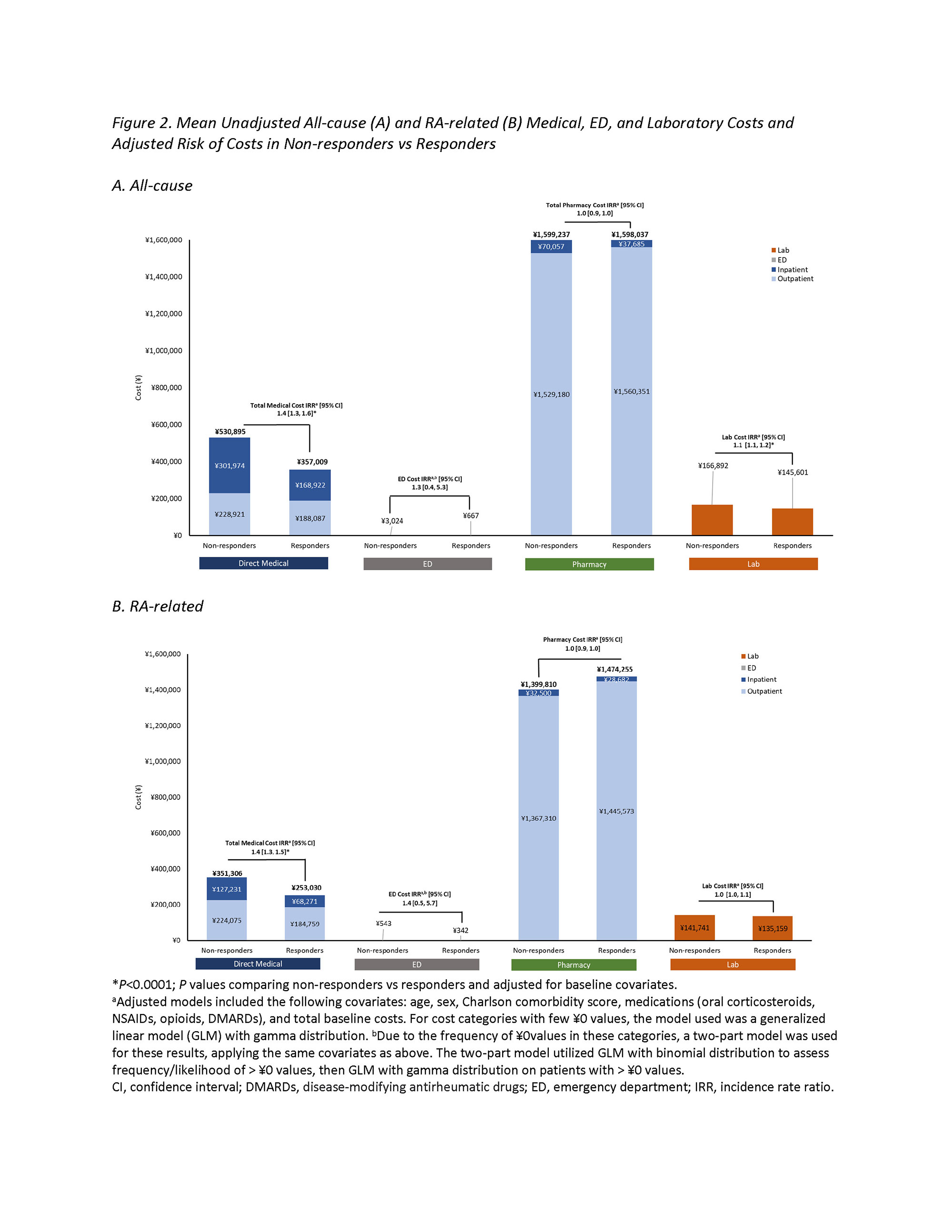
Results: Of the 2446 patients meeting eligibility criteria, 74% (1817) vs 26% (629) were categorized as non-responders and responders, respectively. The risk (IRR [95% CI]) of a greater number of days of hospitalization (1.8 [1.2, 2.6]), ED visits (2.5 [1.5, 4.2]), and prescription fills (1.1 [1.1, 1.2]) was 80%, 150%, and 10% higher, respectively, among non-responders vs responders (Figure 1). Mean all-cause inpatient (¥301,974 vs ¥168,922) and outpatient (¥228,921 vs ¥188,087) medical costs were higher for non-responders vs responders, contributing to 40% higher all-cause total medical costs (1.4 [1.3, 1.6]); a similar trend was observed for RA-related medical costs. Mean all-cause laboratory costs (¥166,892 vs ¥145,601) were lower among non-responders vs responders (1.1 [1.1, 1.2]); RA-related laboratory costs were similar between groups (1.0 [1.0, 1.1]) All-cause pharmacy costs were similar between groups (1.0 [0.9, 1.0]), while RA-related pharmacy costs were numerically higher in responders vs non-responders (1.0 [0.9, 1.0])) (Figure 2). Results from the sensitivity analysis allowing for lower adherence were similar to the results of the main analysis.
Conclusion: Non-responders to advanced therapies in Japan, had greater HCRU and economic burden vs responders, including higher all-cause and RA-related direct medical costs over 12 months, suggesting a need for more effective therapies for patients with RA.
1. Curtis JR, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(5):R155. doi:10.1186/ar3471
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ikeda K, Kaneko Y, Patel J, Yamazaki T, Fang S, Yuki T, Kawahito Y. Healthcare Resource Utilization and Economic Burden of Patients with Adequate and Inadequate Responses to Advanced Therapies for Rheumatoid Arthritis in Japan [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/healthcare-resource-utilization-and-economic-burden-of-patients-with-adequate-and-inadequate-responses-to-advanced-therapies-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-japan/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/healthcare-resource-utilization-and-economic-burden-of-patients-with-adequate-and-inadequate-responses-to-advanced-therapies-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-japan/