Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Gout is associated with decreased health-related quality of life (HRQoL). The ACR endorses treat-to-target (TtT) urate-lowering therapy (ULT) for gout with a serum urate (sUA) goal of < 6mg/dL. However, there is limited data examining whether recommended TtT ULT impacts HRQoL in gout. We sought to quantify the impact of TtT ULT on HRQoL among gout participants in a trial utilizing TtT and to identify participant characteristics associated with HRQoL.
Methods: This was a post-hoc analysis of a 72-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, non-inferiority trial comparing the efficacy of allopurinol and febuxostat (O’Dell JR et al. NEJM Evid, 2022). ULT was initiated/titrated in all participants to achieve sUA < 6mg/dl during weeks 0-24 and maintained between weeks 25-48. Participants were observed on stable ULT from weeks 49-72. Two HRQoL measures, the VR-12 (modified SF-12) and EQ-5D-3L, were administered at baseline, 24-, 48-, and 72-weeks. Changes in VR-12, EQ-5D-3L index, and component scores between baseline and 72-week values were examined using paired t-tests. Factors associated with baseline HRQoL for each measure were evaluated using multivariable linear regression. General estimating equations (GEE) were used to identify determinants of change in HRQoL from baseline to 24-, 48-, and 72 weeks. Covariates assessed in both models included demographics, urban/rural residence, ULT type, gout duration, tophi, prior allopurinol receipt, flare count, CRP, sUA, chronic kidney disease, comorbidity, diuretic use, BMI, and alcohol use. Time-varying factors from each time point included in GEE models were CRP, sUA < 6mg/dl, and flare burden during the prior phase.
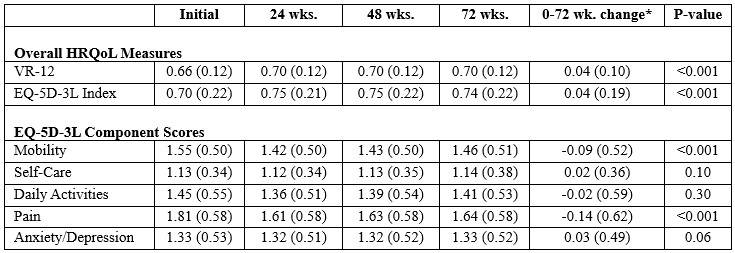
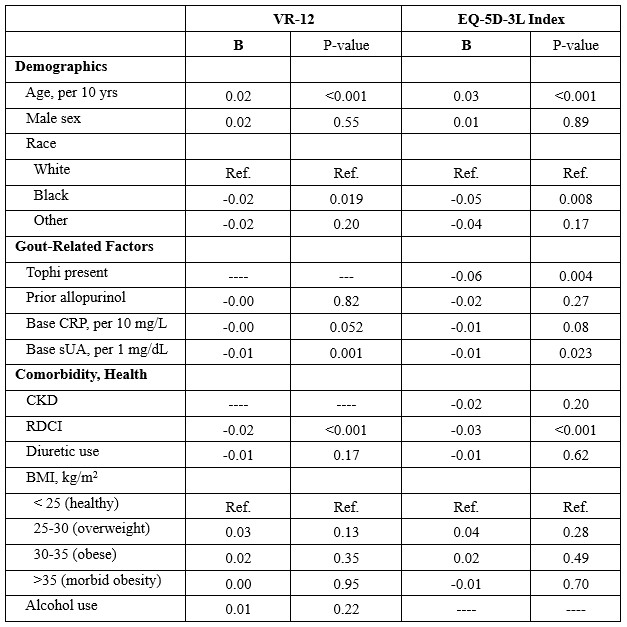
Results: Of 940 study participants, 877 (93.3%) with baseline HRQoL data available were included in this analysis (98.9% male, mean age 62.4, 67.4% reported white race). Baseline and follow-up HRQoL scores are shown in Table 1. VR-12 and EQ-5D-3L index scores and components assessing mobility and pain improved significantly over 72 weeks. Factors independently associated with reduced HRQoL scores at enrollment included younger age, Black race (vs. White), tophi (EQ-5D-3L), higher sUA, and comorbidity score (Table 2). Higher CRP trended towards associations with lower baseline VR-12 and EQ-5D-3L though neither achieved significance. In GEE models, factors associated with HRQoL improvement over 72 weeks included younger age, lower CRP, abstinence from alcohol (VR-12 only), and lower comorbidity burden (VR-12 only) (not shown).
Conclusion: Guideline concordant treat-to-target ULT leads to significant improvements in HRQoL. Demographic factors, measures of gout severity, and comorbidity burden are most strongly associated with reduced HRQoL in gout. Improvement in HRQoL observed with ULT appears to be attributable to treatment-related gains primarily in the domains of mobility and pain with the greatest improvement observed in younger patients and in participants with reductions in systemic inflammation. These observations could inform management strategies in gout with the aim of optimizing patient quality of life.
Values mean (SD). Change in scores examined using paired t-test limited to participants with data available at baseline and 72 weeks. (n=691).
*Positive changes in VR_12 and EQ-5D_3L index scores and negative changes in component scores equate to improved HRQoL.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Barry A, Sayles H, Helget L, Androsenko M, Wu H, Michaud K, Kramer B, Newcomb J, Brophy M, Davis-Karim A, England B, Ferguson R, Pillinger M, Neogi T, Palevsky P, O'Dell J, Mikuls T. Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Gout Receiving Treat-to-Target Urate-Lowering Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-gout-receiving-treat-to-target-urate-lowering-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-gout-receiving-treat-to-target-urate-lowering-therapy/