Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Combination induction therapy with guselkumab (GUS), an interleukin (IL)-23p19 subunit antagonist, and golimumab (GOL), a tumor necrosis factor (TNFα) antagonist, induced higher rates of clinical remission, endoscopic, and histologic outcomes than either monotherapy at Week (WK)12 in patients with ulcerative colitis (VEGA NCT03662542). Data through WK38 suggested the continued benefit of combination induction even after a transition to GUS monotherapy at WK12. We explored early molecular changes in colon tissue in a subset of patients at WK4 to define mechanistic contributions of each monotherapy and combination; these parameters were evaluated again at WK38 to assess potential carry-over of efficacy.
Methods: Colon biopsies were obtained at baseline (n=195), WK4 (n=42 substudy), and WK38 (n=172). Transcriptional profiles were generated with RNA sequencing (RNAseq). Gene correlation network analysis was applied in conjunction with publicly available single cell RNAseq data to define biologically relevant bulk and cell type-specific transcriptional modules associated with molecular features of disease. Gene set variation analysis (GSVA) was used to quantitatively assess changes in biologic modules with treatment.
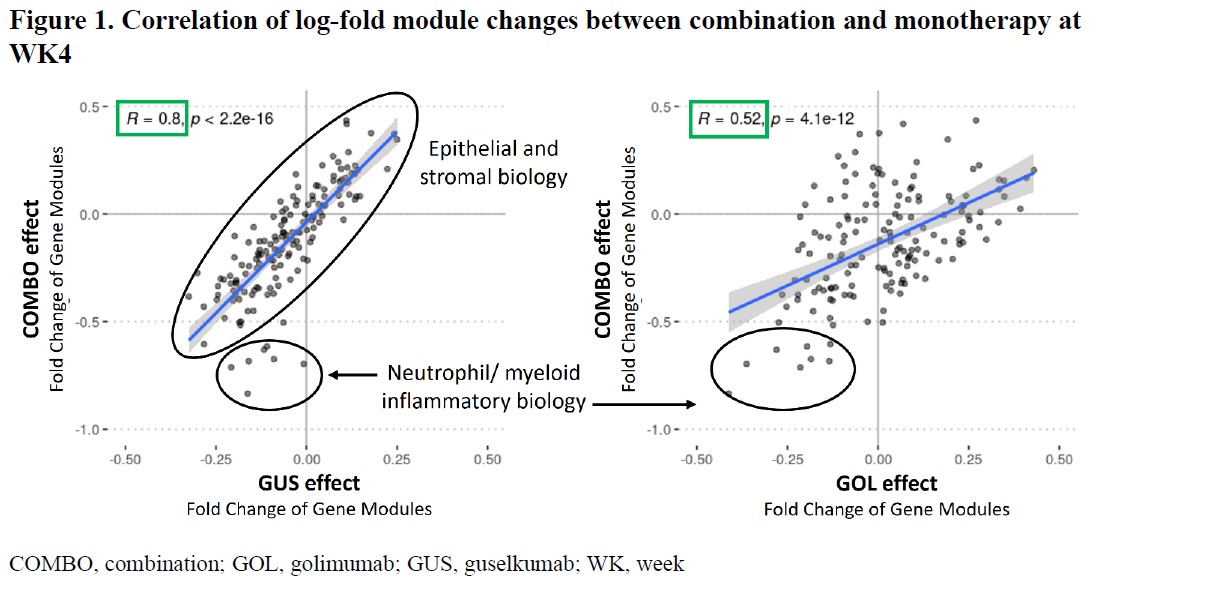
Results: At WK4, combination induction (n=10) showed significant (p< 0.05) decreases in molecular features compared to GUS (n=19) and GOL (n=13), including transcriptomic modules representing the IL-23 pathway, interferon response, and inflammatory epithelial and myeloid transcriptional states associated with endoscopic improvement at WK4 (Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1) (combination 5/11, GOL 1/13; GUS 2/19). Reduction (p< 0.05) in inflammatory modules persisted through WK38 with combination vs monotherapy induction. Module changes between treatments at WK4 indicated a stronger correlation between GUS and combination (R=0.8; p=2.2e-16) than GOL and combination (R=0.52; p=4.1e-12), with processes associated with epithelial and stromal biology, and mucosal inflammation. In contrast, the combination effect on specific neutrophil/myeloid biology at WK4 was more similar to GOL than GUS, supporting the early role of GOL in targeting innate inflammation.
Conclusion: Combination induction with GUS and GOL showed significant reductions in major inflammatory features of disease as early as WK4 which persisted through WK38 with GUS maintenance. Correlative analysis supports the role of GUS as the primary driver of tissue healing, with GOL further contributing to innate inflammatory activity, which demonstrate differential and complementary mechanisms of action of TNFα and IL-23p19 subunit blockade.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Richards D, Vetter M, Germinaro M, Verstockt B, Atreya R, Panés J, Sands B, Feagan B, McRae B, Cua D, Branigan P, Freeman T. Guselkumab and Golimumab Combination Induction Therapy in Ulcerative Colitis Results in Early Local Tissue Healing That Is Sustained Through Guselkumab Maintenance Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-and-golimumab-combination-induction-therapy-in-ulcerative-colitis-results-in-early-local-tissue-healing-that-is-sustained-through-guselkumab-maintenance-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-and-golimumab-combination-induction-therapy-in-ulcerative-colitis-results-in-early-local-tissue-healing-that-is-sustained-through-guselkumab-maintenance-therapy/