Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster II: Measurements (0739–0763)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
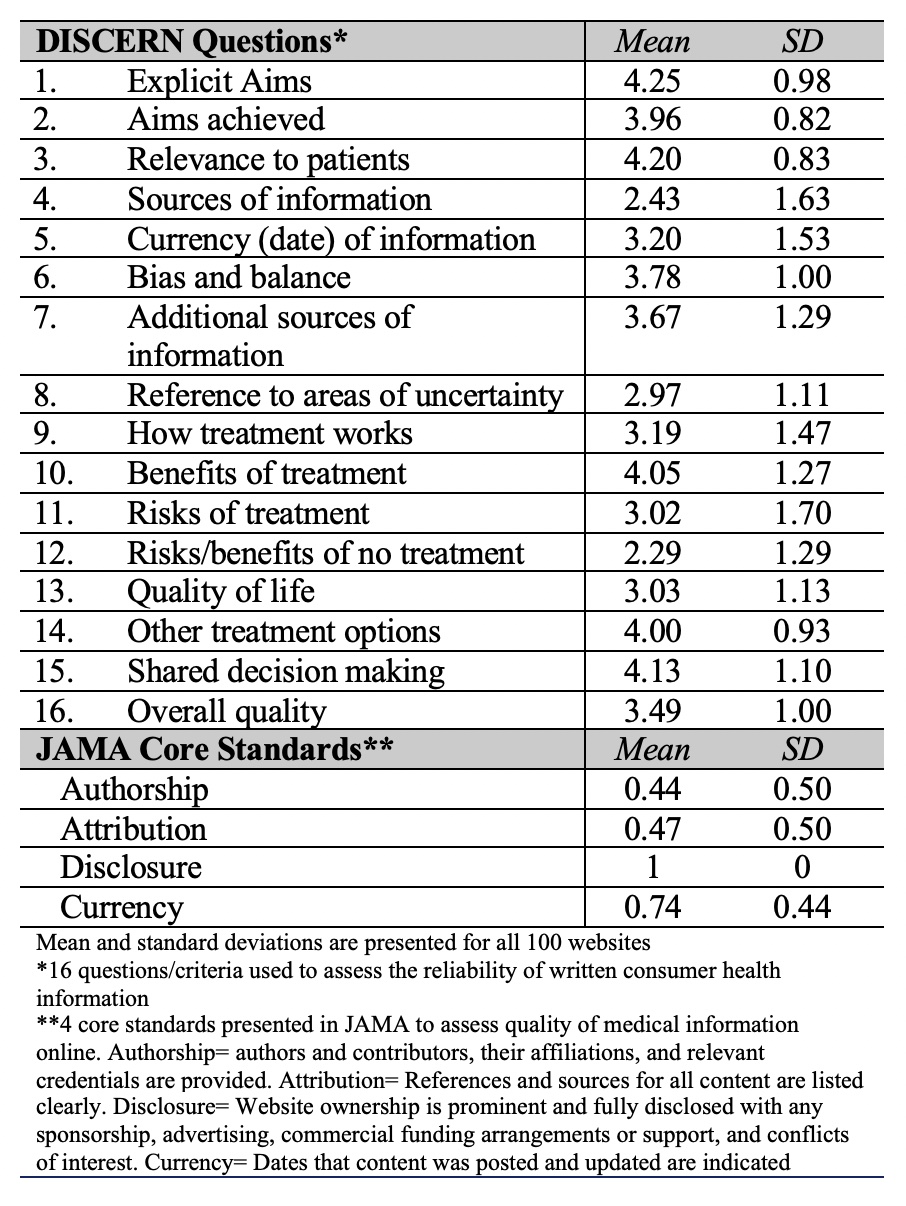
Background/Purpose: The internet is a significant source of information for health-related topics. Given the complexity of rheumatic diseases, rheumatologists may find their patients searching online for information related to their diagnosis, including treatment options and complications. Often, what patients find on the internet can steer their decisions on treatments and issues they discuss with their provider, regardless of how varied the quality and reliability of this information may be. This study was thus designed to critically evaluate the information found on common rheumatic diseases through Google search using two instruments (Table 1): Four core standards presented by the Journal of American Medical Association (JAMA) to promote accountability for information written on the internet and the DISCERN instrument which is the first standardized quality index developed to judge the quality of written consumer health information.
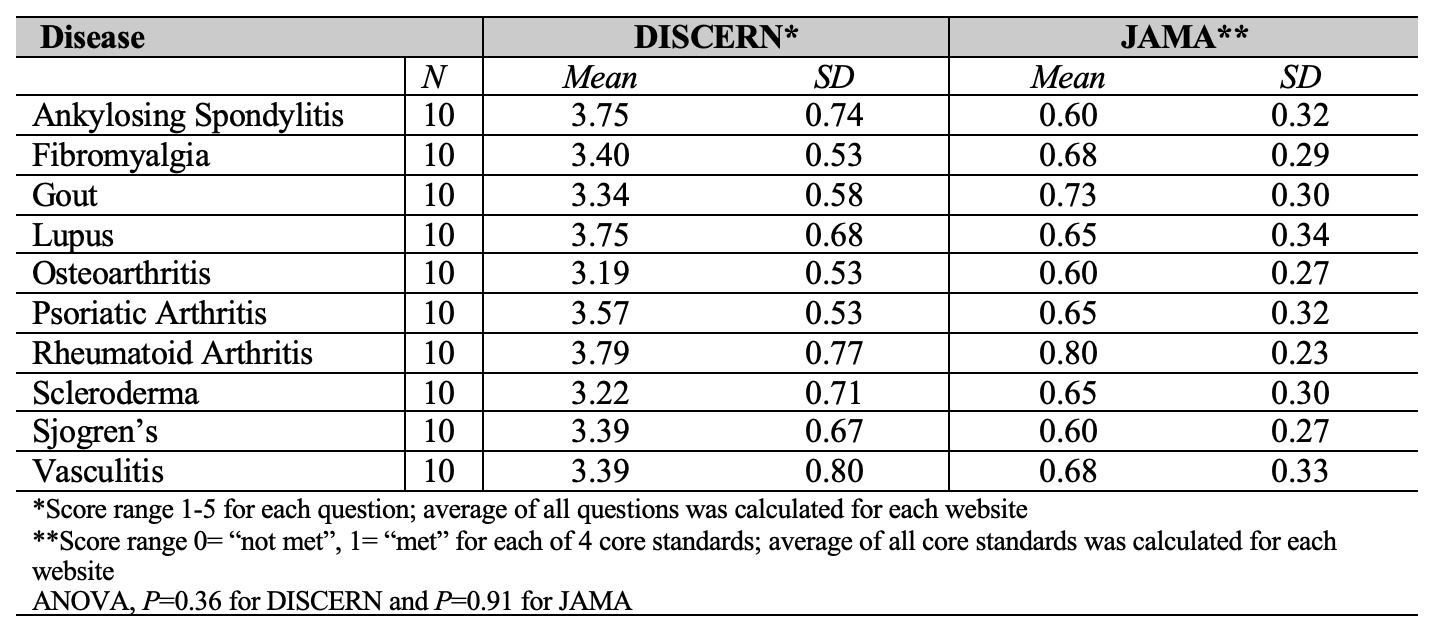
Methods: Google search was performed for 10 diseases commonly evaluated by rheumatologists: ankylosing spondylitis, fibromyalgia, gout, lupus, osteoarthritis, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, Sjogren’s, and vasculitis. The first 10 website search results for each diagnosis were included in the study to yield a total of 100 websites. All websites were classified into major medical information websites (websites that disseminate information on a wide variety of health topics) and non-major websites. Websites were then assessed using JAMA and DISCERN. Primarily descriptive statistics were utilized. One-way analysis of variance and two tailed t-tests were performed to assess differences in scores.
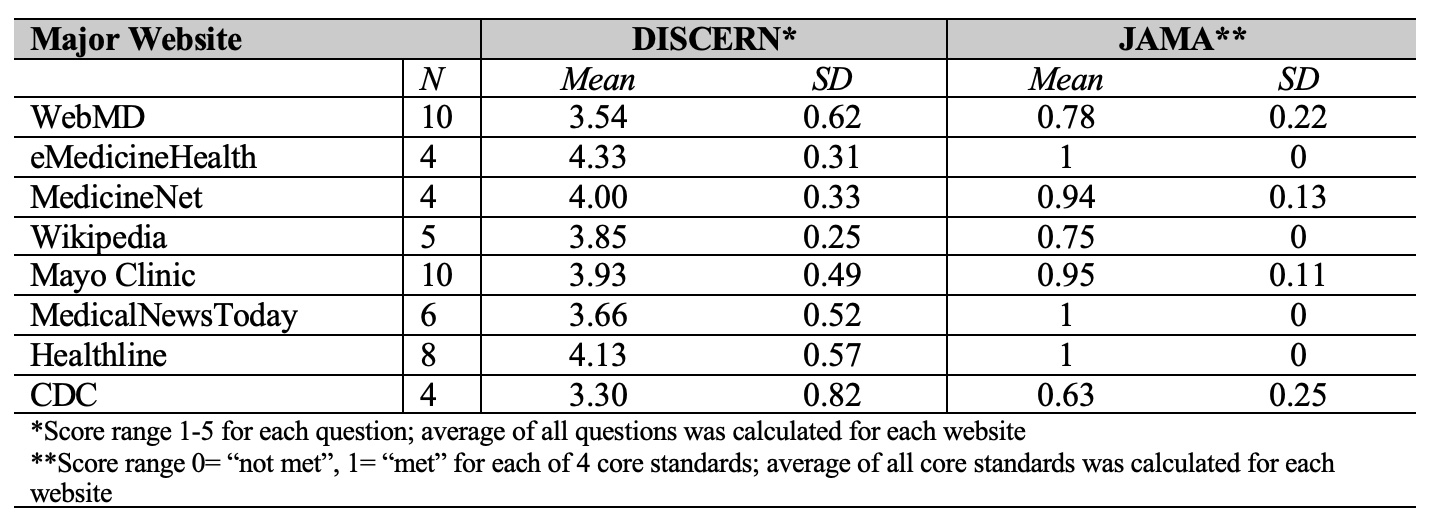
Results: Average DISCERN quality score and JAMA score for all 100 websites were 3.48 (SD 0.66) and 0.66 (SD 0.29), respectively. Only 24 websites scored ≥ 4 on the DISCERN instrument. Risks of no treatment was the most missed question on the DISCERN instrument and authorship was the most missed core standard on the JAMA instrument (Table 1). While there was no statistically significant difference in DISCERN scores and JAMA scores for the 10 different diagnoses (P =0.36 for DISCERN, P=0.91 for JAMA), websites on ankylosing spondylitis numerically scored highest on the DISCERN instrument and rheumatoid arthritis scored highest on the JAMA instrument (Table 2). We observed that the major medical information websites (n=49) scored higher than non-major websites (n=51, P < 0.0001) on both instruments with eMedicineHealth scoring highest on the DISCERN instrument (4.33, SD 0.31) (Table 3).
Conclusion: Information on common rheumatic conditions procured through Google searches is of moderate quality and lacks essential aspects such as authorship, sources, and thorough explanation of treatment options. Not surprisingly, major medical information websites present more reliable information than non-major websites. If patients are looking for information on the internet, rheumatologists should guide them towards more reliable resources for further reading.
References
Charnock D et al. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1999 Feb;53(2):105-11.
Silberg WM et al. JAMA. 1997 Apr 16;277(15):1244-5.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chiruvolu N, Karim M, Sandhu V. Googling Rheumatic Diseases: Evaluating the Reliability of Information Found on the Internet [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/googling-rheumatic-diseases-evaluating-the-reliability-of-information-found-on-the-internet/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/googling-rheumatic-diseases-evaluating-the-reliability-of-information-found-on-the-internet/