Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster II: Spondyloarthritis & Connective Tissue Disease
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Golimumab (GLM) has shown its efficacy and tolerability in various randomized clinical trials. Systemic data for GLM regarding health-economic parameters in daily clinical practice are essential not only for pharmaceutical companies but also for cost-benefit analyses in Germany.
This prospective NIS was designed to evaluate the impact of GLM therapy on work productivity and activity as well as Quality of Life (QoL) in patients with RA, AS or PsA in Germany under routine settings over an observation period of 12 months, plus an additional voluntary extension period of 12 months (total 24 months) to collect long-term data on health economic parameters.
Methods: GO-ART was an observational prospective study on patients with RA, AS or PsA (biologic-naïve and biologic-experienced) who started treatment with GLM at 63 sites of Germany.
The primary endpoint was the change in work productivity/activity impairment as measured by Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) questionnaire from baseline, measured primarily at month 3 and secondarily at months 6, 12 and 24.
As secondary endpoint the change in quality of life (RAQoL for RA patients, ASQoL for AS patients and NAPPA-QoL for PsA patients) was assessed.
Results: 748 patients (RA=250, PsA=249, AS=249) started GLM therapy. The primary efficacy endpoint was analyzed in the modified intention-to-treat (mITT) subset of 493 patients (RA=158, PsA=157, AS=178) with full-time or part-time employment at baseline (mITTe). A total of 348 patients entered the additional 12-month observation period, of which 303 completed the 24-month assessment.
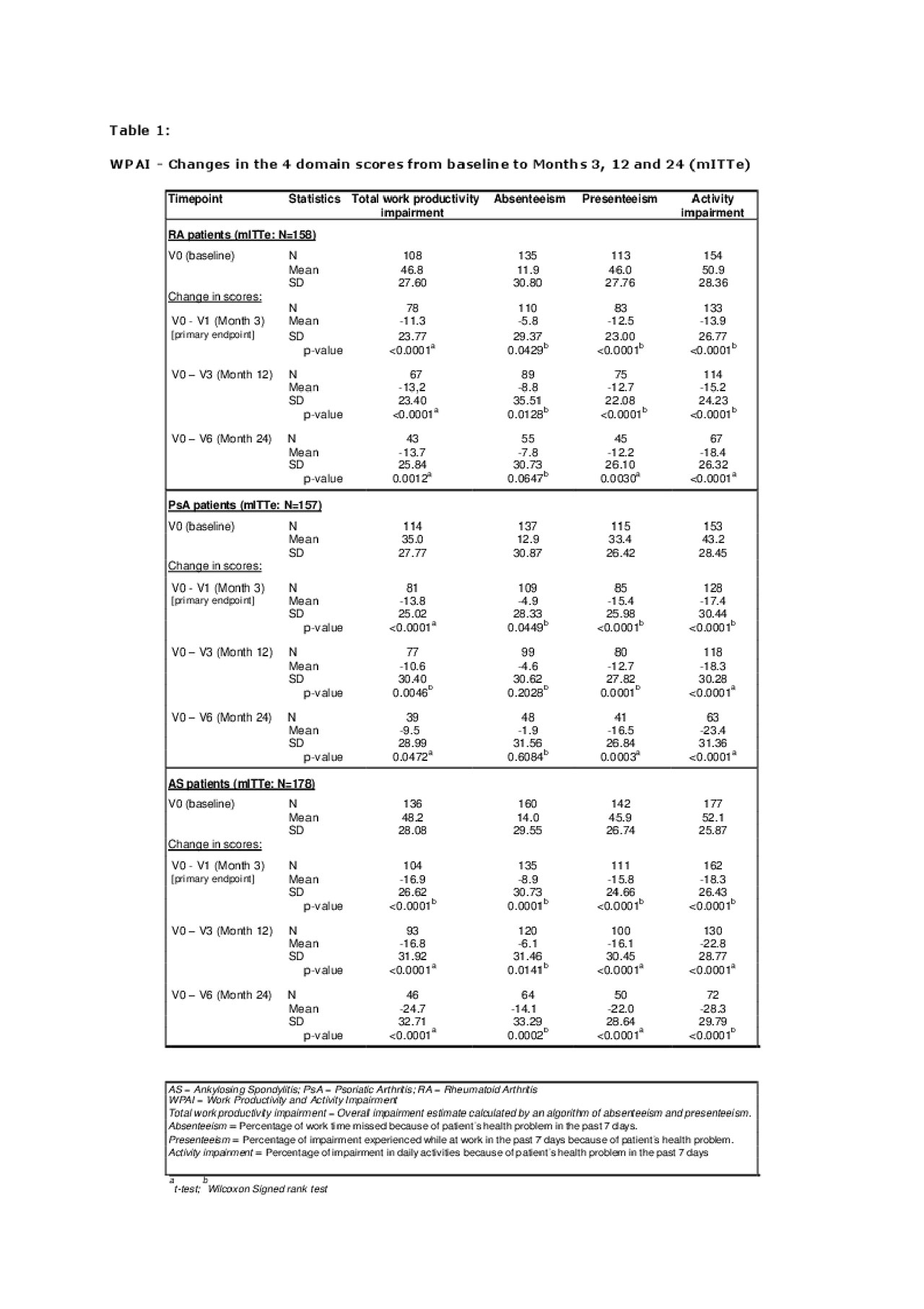
By 3 months after initiation of Golimumab treatment, a marked improvement was seen in all 4 WPAI domain scores (“absenteeism” (time off work), “presenteeism” (on-the-job productivity), “total work productivity impairment” (TWPI), and “activity impairment”) in daily living because of patient’s health problems related to RA, PsA or AS, as shown in Table 1 (all p-values < 0.05).
The statistically significant improvements in the mean WPAI domain scores were maintained over the 24-month observation period in all 3 indications with a higher treatment effect regarding “activity impairment” and “presenteeism” compared to “absenteeism” (Table 1).
Quality of life improved significantly (p< 0.0001) from baseline at month 3, 6, 12 and 24 in patients with RA (RAQoL), AS (ASQoL) and PsA (NAPPA-QoL) based on questionnaire data of 237 RA patients (RA-miTT), 228 AS patients (AS-mITT) and 235 PsA patients (PsA-mITT) indicating a clinically relevant improvement.
Conclusion: Treatment with GLM provided sustained improvement in WPAI and QoL in patients with RA, PsA and AS over the observational period of 24 months.
All scores of the WPAI showed a significant (p< 0.05) reduction in mean score values in each indication.
GLM leads to an improvement of work productivity and daily activities in patients already within the first 3 months of treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Krüger K, Remstedt S, Thiele A, Klaudius I. Golimumab Improves Work Productivity and Activity and Quality of Life in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) and Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): Final Results from a Non-Interventional Study in Germany (GO-ART) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/golimumab-improves-work-productivity-and-activity-and-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-ankylosing-spondylitis-as-and-psoriatic-arthritis-psa-final-results-from-a-non-in/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/golimumab-improves-work-productivity-and-activity-and-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-ankylosing-spondylitis-as-and-psoriatic-arthritis-psa-final-results-from-a-non-in/