Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose:
The management of women with musculoskeletal disorders during pregnancy and lactation presents many challenges. Since the first EULAR points to consider for the use of antirheumatic drugs before and during pregnancy, and lactation published in 2016, new relevant data has emerged. To inform the EULAR task force on the safety of antirheumatic drugs during pregnancy and lactation by a systematic literature review (SLR). This analysis focusses on the impact of glucocorticoids (GC) during pregnancy and lactation.
Methods: We searched Medline, Embase, Cochrane and LactMed from April 2015 to April 2023. All studies relating to the effect of GC on adverse pregnancy, maternal and infant’s outcomes in pregnant or breastfeeding women with an indication for antirheumatic drugs were eligible. The risk of bias was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale. We used narrative synthesis in case of heterogeneity regarding population or outcome. If the quality and the statistical homogeneity of included studies was sufficient, we pooled the reported outcomes and conducted a meta-analysis, using effect estimates from studies with adjustments for confounding factors. This analysis employed a random effect model. Odds ratios (OR) and risks ratios (RR) with adjustment for disease activity were used to assess the associations.
Results: Within 307 eligible publications (including all drugs and outcomes considered in the SLR), 21 articles including 8777 pregnancies were included for pregnancy outcomes and 5 articles including 32 patients were included for lactation outcomes.
Regarding exposure during pregnancy, 20 studies concerned oral GC and 1 study intravenous methylprednisolone (MP) pulses. The rates of miscarriage, stillbirth, major congenital malformation, preterm birth, low birth weight, small for gestational age, maternal hypertension were 9.4%, 2.3%, 5.2%, 18.2%, 22.2%, 5.2% and 5.5%, respectively. For MP pulses, only a case series of 5 patients was found and provided little evidence.
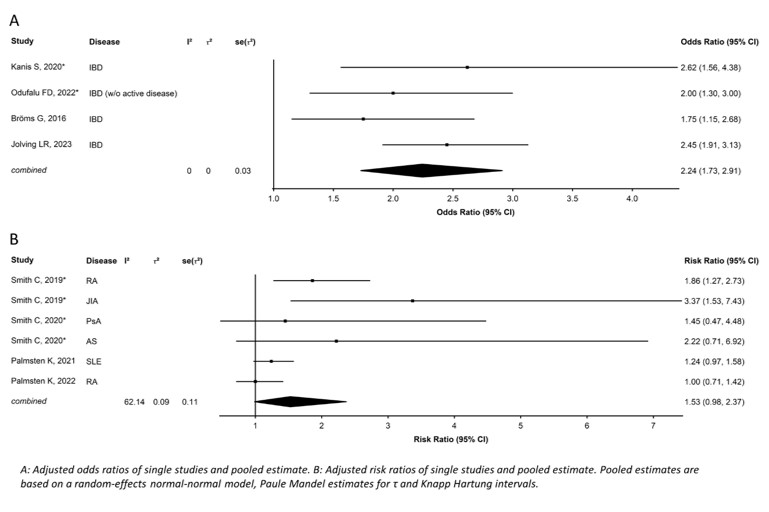
A meta-analysis was carried out on the risk of preterm birth with GC exposure during pregnancy: the pooled OR of the adjusted effect estimates was 2.24 [1.73-2.91] (I2=0%) and the pooled RR of the adjusted effect estimates was 1.53 [0.98-2.37] (I2=62%) (figure 1). In 3 studies reporting of dose of GC, a dose-dependent effect was observed, with more preterm births with higher GC doses.
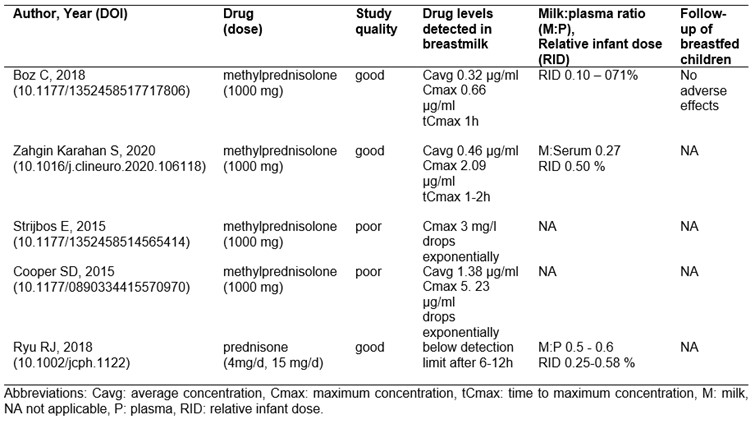
Regarding lactation, 1 study reported prednisone/prednisolone and 4 MP pulse exposures (table 1). The milk:plasma ratios ranged between 0.02 and 0.60. Drug levels after MP pulses were highest in the first hour post-dose, dropped exponentially within 4 hours and reached average levels between 0.32 and 1.40 µg/ml. All relative infant doses were very low. One study reported no adverse events in exposed infants during a 3-12 months follow-up phase.
Conclusion: An increased risk of preterm birth associated with GC exposure during pregnancy was found, which argues for a minimal maintenance dose and the use of a GC sparing agent with pregnancy-compatible cs/bDMARD. However, the amounts of oral and pulse GC in breastmilk are very low and no short-term adverse effects in breastfed infants were reported.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hamroun S, Pluma A, Rüegg L, Kramer M, Meissner Y, Finckh A, Foerger F. Glucocorticoids in Pregnancy and Lactation: Results of the Systematic Review Informing the EULAR Task Force on Antirheumatic Drugs in Reproduction, Pregnancy and Lactation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/glucocorticoids-in-pregnancy-and-lactation-results-of-the-systematic-review-informing-the-eular-task-force-on-antirheumatic-drugs-in-reproduction-pregnancy-and-lactation/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/glucocorticoids-in-pregnancy-and-lactation-results-of-the-systematic-review-informing-the-eular-task-force-on-antirheumatic-drugs-in-reproduction-pregnancy-and-lactation/