Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) to intranuclear particles are found in the blood of people with and without autoimmune diseases. To our knowledge, only 1 past genome-wide association study (GWAS) has sought to identify genetic factors related to ANA positivity, reporting association with HLA-DR in a Japanese population (Terao C. et al Arthritis Rheum 2014). Dissecting the genetic basis for ANA positivity would allow new insights into susceptibility to autoimmunity.
Methods: We employed data from the Mass General Brigham Biobank, containing linked electronic health records and genotyping (Illumina’s Multi-Ethnic Genotyping Array or Global Screening Array chips) for >65,000 consented patients. We identified subjects with genotyping and results for either hep2 or ML immunofluorescence ANA assays (1989-2022). ANA+, those with ≥1 result of ≥ 1:80 titer, were compared to ANA-, those with no positive ANA results. After quality control, we imputed using the Haplotype Reference Consortium, excluding variants with imputation score < 0.5. Classical HLA alleles and amino acids for HLA genes were imputed with SNP2HLA using TopMed HLA data as reference. We restricted analyses to those with predicted European ancestry (1000 Genomes EUR group; 82% of biobank subjects). Diagnostic codes identified 8 autoimmune diseases: systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), scleroderma (SSc), Sjogren’s syndrome, mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), multiple sclerosis (MS), primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), and autoimmune thyroid disease (ATD). GWAS for ANA + vs – was done in PLINK2, with logistic regression adjusted for age, sex and 4 genetic principal components. We also tested for associations with HLA alleles and amino acids, adjusting for these variables.
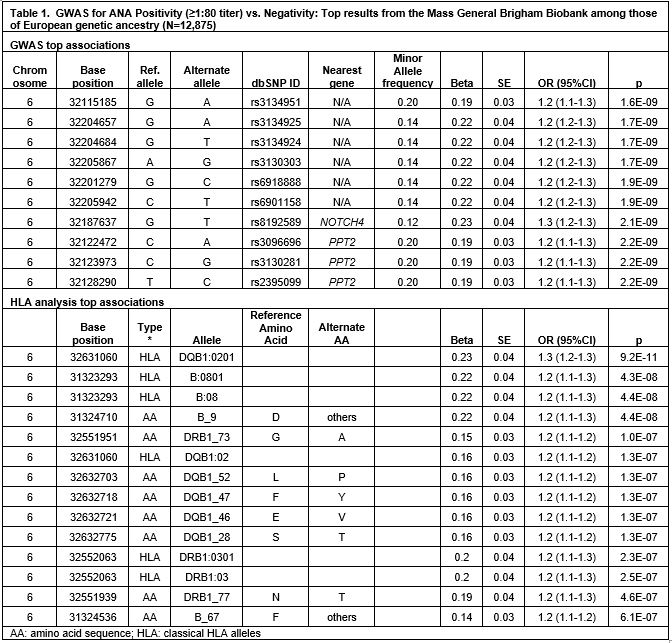
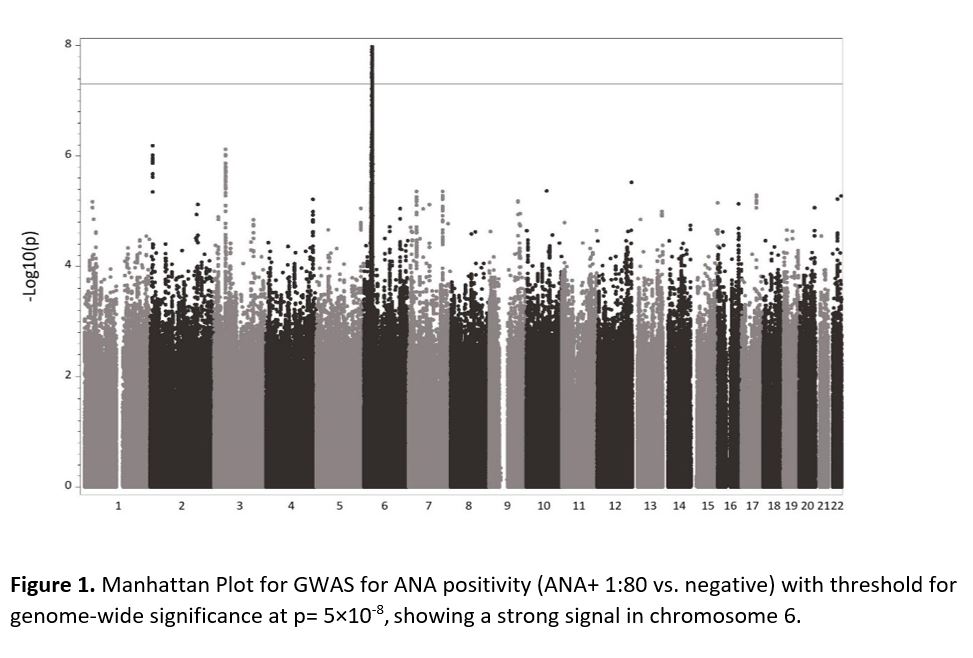
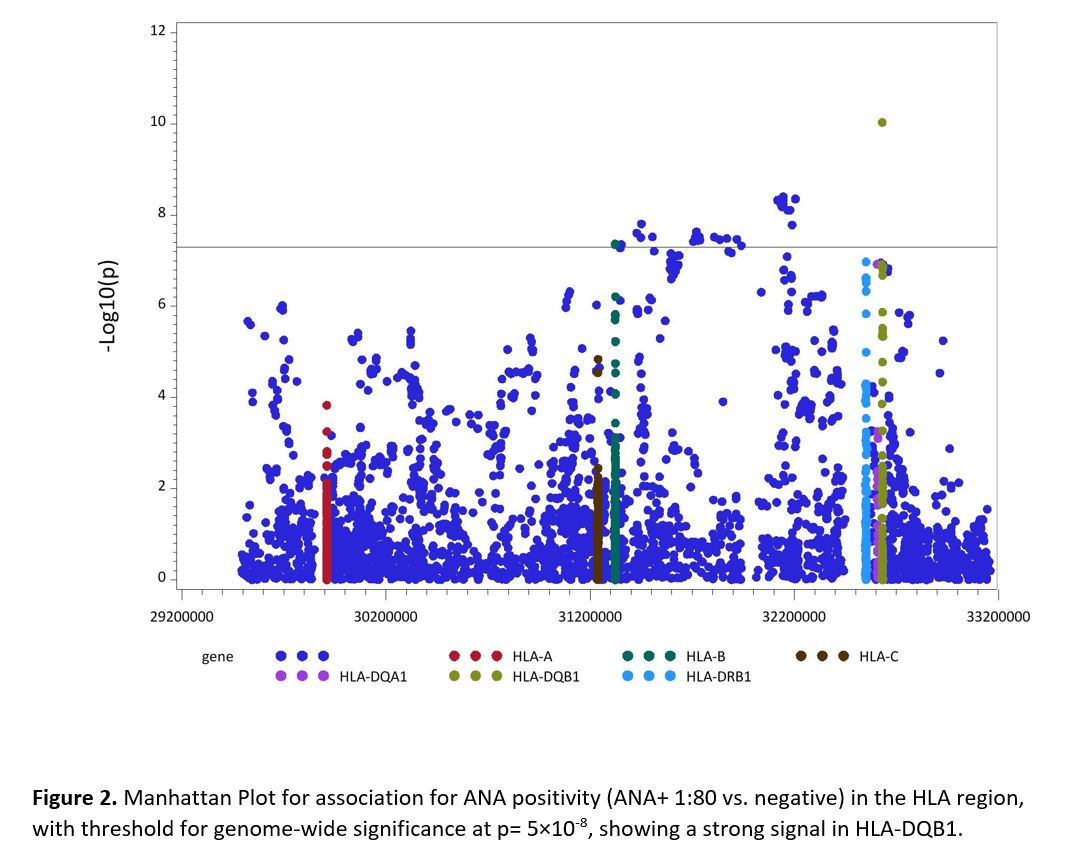
Results: We studied 12,875 subjects with ANA and genotyping results: 7,035 ANA + vs. 5,840 ANA -. The female/male ratio was similar in both groups: 62.9% female in ANA+ vs. 62.1% in ANA- (p 0.39). Patients who were ANA+ were older than the ANA- (56.1 ± 15.8 vs. 52.1 ± 15.2 years, p< 0.0001). Overall, by billing codes, SLE, RA, SSc, Sjogren’s syndrome, MCTD, MS, PBC and ATD were present in 538, 1425, 159, 370, 65, 354, 63 and 408 subjects (with ANA+ proportions 71%, 55%, 78%, 74%, 82%, 55%, 63%, and 62% respectively).Of ANA+ patients, 33% had ≥1 of the 8 autoimmune diseases, as did 19% of ANA- patients. 8,073,314 SNPs with MAF >=0.01 were included. The strongest GWAS association with ANA+ was for rs3134951 on chromosome 6 in the HLA region with OR 1.2 (95% CI 1.1-1.3, p 1.6×10-9) (Table 1, Figure 1). HLA region association analysis revealed HLA-DQB1:0201 allele had strong association with OR 1.3 (95% CI 1.2-1.3, p 9.2×10-11). HLA-DRB1:03 and HLA-B:08 alleles also had significant associations (Figure 2). We identified 2 suggestive novel loci for ANA +, one in LOC105373419 gene (rs60343674) and the other in ABHD5 gene (rs12489159). (Figure 1)
Conclusion: These results confirm that HLA-DRB, as well as newly identified HLA-DQB1 and HLA-B, are strong genetic factors predisposing to ANA positivity in this European ancestry population. We are pursuing stratified analyses by ANA pattern and titer, sex, and autoimmune disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cui J, Yee J, Liang L, Ellrodt J, Oakes E, Guan H, Costenbader K. Genome-Wide Association Study for Loci Associated with Positive Antinuclear Antibodies in a Large Hospital Biobank [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genome-wide-association-study-for-loci-associated-with-positive-antinuclear-antibodies-in-a-large-hospital-biobank/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genome-wide-association-study-for-loci-associated-with-positive-antinuclear-antibodies-in-a-large-hospital-biobank/