Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
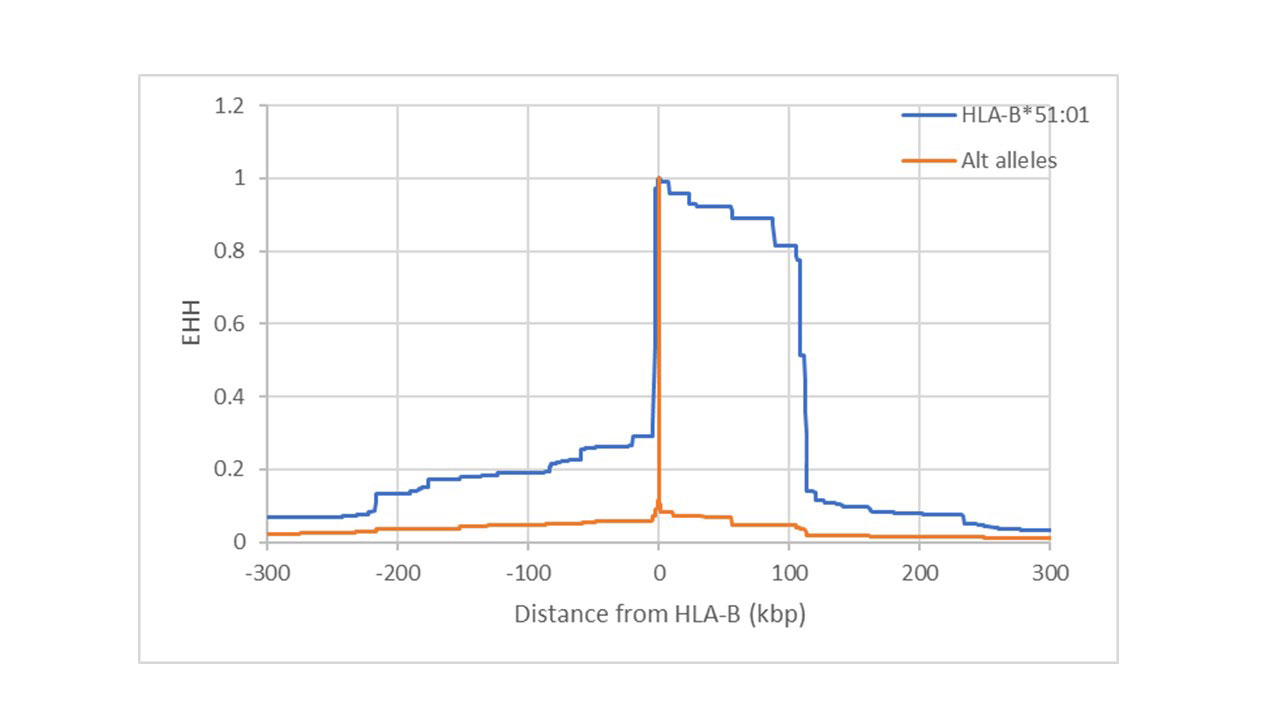
Background/Purpose: The Turkish population has one of the highest world-wide prevalence’s of the genetically complex inflammatory Behçet’s disease (BD), estimated as 4 affected per 1000 and also has one of the highest world-wide prevalence’s of HLA-B*51, the strongest identified BD genetic risk factor, with the prevalence of HLA-B*51:01 in healthy controls estimated as 25.6% and the prevalence in BD patients estimated as 55.6%. It has been proposed that the high frequency of HLA-B*51 in this population is a result of a selective advantage that was provided to carriers of this HLA allele, for example, in response to some life-threatening infection. If recent positive selection occurred, haplotypes bearing the HLA-B*51:01 allele should display unusually long-range linkage disequilibrium for their frequency, because selection would cause a rapid rise in the allele frequency over a short enough time that recombination does not substantially break down the selected haplotype. We looked for this genetic imprint of natural selection on HLA-B*51:01 carrier chromosomes from the Turkish population.
Methods: Genome-wide SNP genotypes from 1,779 healthy Turkish subjects were obtained from a prior genome-wide association study. HLA alleles and MHC region SNP genotypes were imputed with the SNP2HLA application. Haplotypes were derived from genotypes with Eagle. Extended haplotype homozygosity (EHH) and frequency normalized iHS statistic values were computed for each marker in the combined marker set with the Selscan application.
Results: The chromosome 6 region flanking HLA-B*51:01 exhibited extended haplotype homozygosity compared with other HLA-B alleles in the Turkish healthy control population (Figure 1). Of all the HLA-B alleles, HLA-B*51:01 had the strongest evidence for recent positive selection with a frequency normalized iHS statistic = 3.87 (values greater than 2.00 are suggestive of recent positive selection).
Conclusion: HLA-B*51:01 exhibits strong genetic evidence of recent positive selection in the Turkish population. An historical survival advantage provided by this allele could explain its current high frequency in the Turkish population, and as a strong BD risk factor, its high frequency could account for the high prevalence of BD in the Turkish population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Remmers E, Gül A, Kastner D. Genetic Evidence for Recent Positive Selection of the HLA-B*51:01 Allele in the Turkish Population, a Population with a High Prevalence of HLA-B*51-Associated Behçet’s Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genetic-evidence-for-recent-positive-selection-of-the-hla-b5101-allele-in-the-turkish-population-a-population-with-a-high-prevalence-of-hla-b51-associated-behcets-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genetic-evidence-for-recent-positive-selection-of-the-hla-b5101-allele-in-the-turkish-population-a-population-with-a-high-prevalence-of-hla-b51-associated-behcets-disease/