Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Although hand osteoarthritis (OA) is a worldwide burden, there is no treatment able to cure it. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are considered ideal sources for exploring cell therapies and they have emerged as promising tools for modelling diseases. The advantages of using iPSC lines are unlimited cell source and chondrogenic differentiation potential. However, there are no studies generating iPSCs from patients with hand OA. Therefore, the aim of this study has been to generate iPSC-lines from patients with hand OA and healthy donors, which can be useful for studying the pathogenesis of the disease in vitro and for testing new drugs.
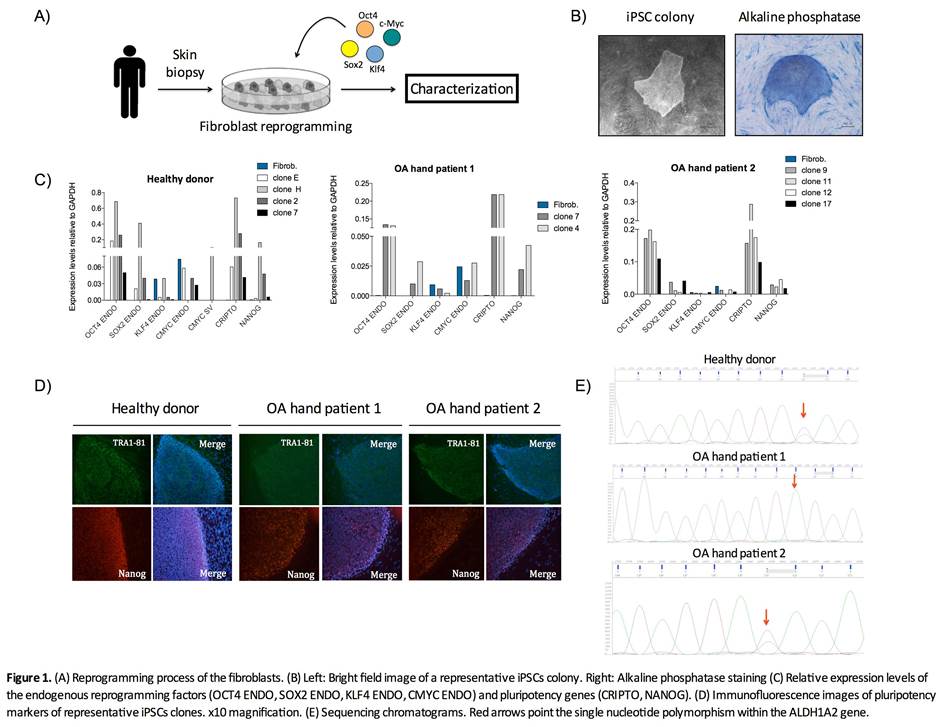
Methods: Patients with hand OA (rhizarthrosis) and a healthy control were selected for the study. Fibroblasts from 3mm skin biopsies of these patients were isolated. The transcriptional factors Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc were used for the reprogramming process; which was performed by using the non-integrating method Sendai virus (Fig 1A). Cell lines obtained were morphological, phenotypical and functionally characterized. Furthermore, to evaluate weather these iPSC lines could be used as cellular model of hand OA, presence of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the gene encoding the retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH1A2) was studied by Sanger sequencing, before and after reprogramming. The variant rs3204689 within the ALDH1A2 gene has been associated with severe OA of the hand (OR=1.46, p=1.1 x 10-11) (Styrkarsdottir et al., 2014).
Results: Fibroblasts were isolated from skin biopsies of two patients with radiographic hand OA and one healthy donor, which presented a normal karyotype: 46,XX. Three weeks after reprogramming, embryonic stem cell-like colonies emerged in culture (Fig 1B). These cells showed positivity for alkaline phosphatase activity (Fig 1B) and the pluripotency markers Tra1-81 and Nanog (Fig 1D). Molecular analyses showed high relative expression levels of the pluripotency-related genes OCT4, SOX2, NANOG and CRIPTO in the iPSCs (Fig 1C). These cells were also able to give rise to cells from the three germ layers. Indeed, during mesodermal differentiation, spontaneously beating cardiomyocytes were seen in culture. Regarding SNPs studies, cells from one of the patients with hand OA were homozygous for the at-risk C allele, both before and after reprogramming. Cells obtained from the healthy donor and the second OA hand patient were heterozygous for this variant (Fig 1E).
Conclusion: The reprogramming process using Sendai virus enabled us to generate iPSC lines from patients with hand OA. The presence of the at-risk C allele within the ALDH1A2 gene was maintained after fibroblast reprogramming. The iPSC lines obtained will enable us to model hand OA in vitro and to deeper study the role of this genetic variant in the pathogenesis of hand OA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Castro-Viñuelas R, Sanjurjo-Rodríguez C, Piñeiro-Ramil M, Hermida-Gómez T, De Toro Santos FJ, Blanco FJ, Fuentes-Boquete I, Díaz-Prado SM. Generation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Lines from Patients with Hand Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/generation-of-human-induced-pluripotent-stem-cell-lines-from-patients-with-hand-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/generation-of-human-induced-pluripotent-stem-cell-lines-from-patients-with-hand-osteoarthritis/