Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Safety and Comorbidity
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tolerability remains ill-defined in clinical trials and most commonly refers to non-serious adverse events (AEs) that may impact patient (pt) satisfaction and adherence to treatment. Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of RA. This update to a previously reported post hoc analysis1 describes the frequency and duration of the most commonly reported non‑serious AEs related to tolerability in pts with RA treated with tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID) as monotherapy or in combination with conventional synthetic (cs)DMARDs in Phase (P)3 and P3b/4 studies.
Methods: Data were pooled from the following studies of tofacitnib in pts with moderate to severe RA: ORAL Step (NCT00960440); ORAL Solo (NCT00814307); ORAL Scan (NCT00847613); ORAL Sync (NCT00856544); ORAL Standard (NCT00853385); and ORAL Strategy (NCT02187055). This analysis included data from pts receiving tofacitinib 5 mg BID monotherapy (ORAL Solo, ORAL Strategy), placebo (PBO; ORAL Solo), or tofacitinib 5 mg BID or PBO in combination with csDMARDs (all studies except ORAL Solo). Non-serious AEs with an incidence rate (IR, pts with events per 100 pt-years [PY]) ≥5 were evaluated up to Month 3. Non‑serious AEs were defined as AEs affecting pts’ day-to-day experience and ability to tolerate treatment. Infections, laboratory test abnormalities, general disorders, or events not reported directly by pts, and musculoskeletal events likely to be due to underlying RA, were excluded, to focus on AEs which could impact treatment adherence.
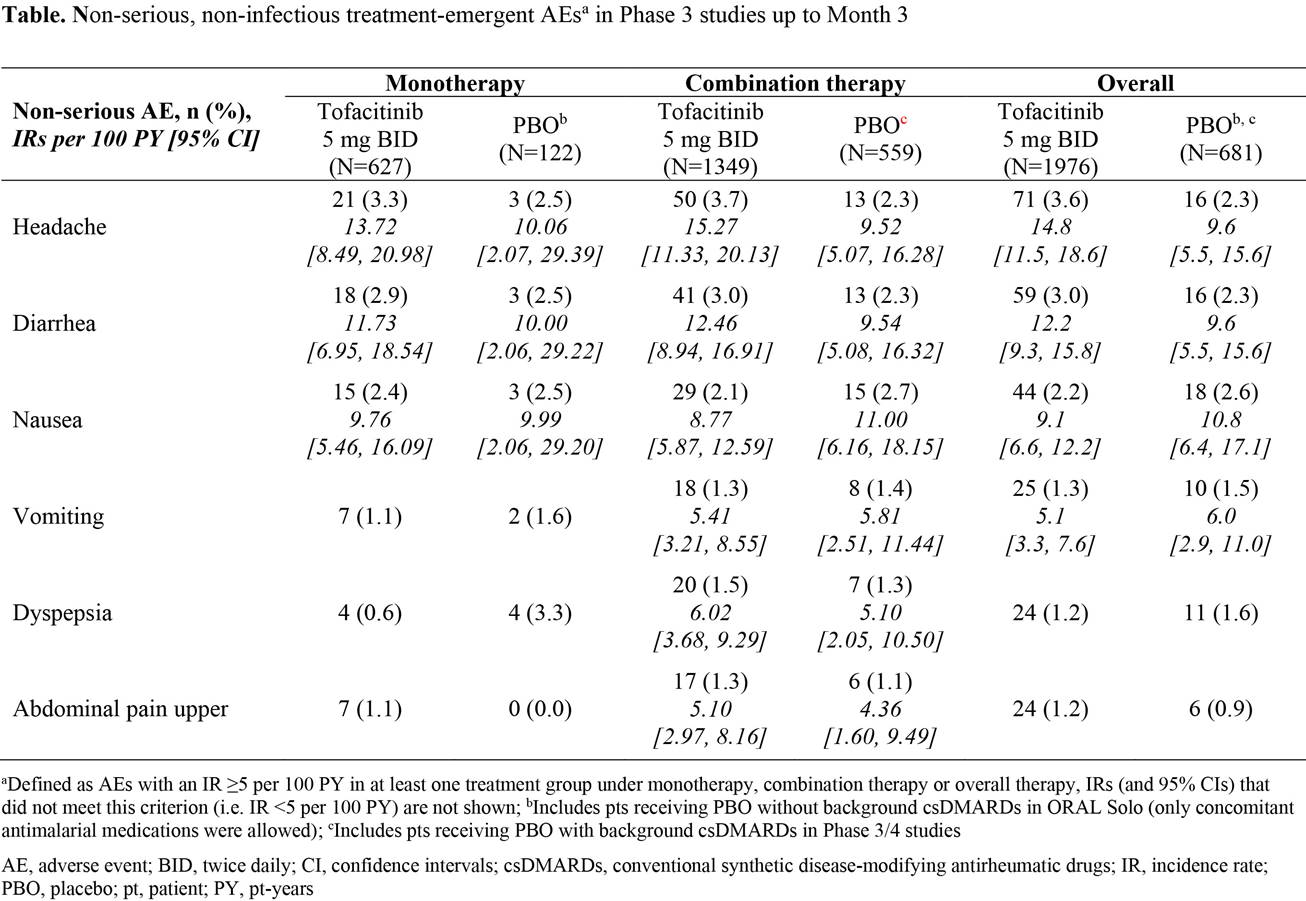
Results: In total, 2657 pts were included in the analysis; 1976 received tofacitinib 5 mg BID (monotherapy: N=627; combination therapy: N=1349); 681 received PBO (monotherapy: N=122; combination therapy: N=559). Up to Month 3, the most frequently reported non-serious AEs which met the search criteria for either tofacitinib or PBO groups were headache, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, and abdominal pain upper; an IR of ≥10 was observed for headache and diarrhea in pts receiving tofacitinib 5 mg BID, and for nausea in pts receiving PBO (Table). Duration of AEs was ≤4 weeks for the majority of pts experiencing headache, diarrhea, or gastric discomfort (defined as any gastrointestinal pain, dyspepsia, epigastric discomfort, or abdominal discomfort or pain). Overall, in pts receiving tofacitinib 5 mg BID and PBO, respectively, 43.2% and 64.7% experienced headache; 66.1% and 81.3% experienced diarrhea; and 36.2% and 58.6% experienced gastric discomfort, for ≤2 weeks. The majority of AEs were mild or moderate.
Conclusion: Overall, non-serious, non-infectious AEs were mild or moderate and self‑limiting. The frequency of non-serious AEs was comparable for pts receiving tofacitinib as monotherapy, or in combination with csDMARDs, and was generally similar for pts receiving tofacitinib compared with pts receiving PBO.
1. Dikranian A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2013; 65: S192.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dikranian A, Wollenhaupt J, Azevedo VF, Bessette L, Gold D, Rivas JL, Shi H, Wang L, Woolcott J, Shapiro A, Nash P. Frequency and Duration of Early Non-Serious Adverse Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated with Tofacitinib 5 Mg Twice Daily As Monotherapy and Combination Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/frequency-and-duration-of-early-non-serious-adverse-events-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-tofacitinib-5-mg-twice-daily-as-monotherapy-and-combination-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/frequency-and-duration-of-early-non-serious-adverse-events-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-tofacitinib-5-mg-twice-daily-as-monotherapy-and-combination-therapy/