Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic and Clinical Science Poster
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Wrist fractures are the most common fracture of the upper extremity and increase subsequent fracture risk in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Most wrist fractures occur at the ultradistal (UD) radius. Abaloparatide (ABL) is a selective activator of the PTH1 receptor signaling pathway that stimulates bone formation. In the ACTIVE phase 3 study, 18 months of ABL significantly increased bone mineral density (BMD) at the UD radius and maintained BMD at the 1/3 distal radius vs placebo (PBO) and teriparatide (TPTD). BMD effects were associated with a trend for numerically lower wrist fracture incidence for ABL vs TPTD (P=0.052). Women receiving ABL or PBO in ACTIVE were offered enrollment in the ACTIVExtend extension study in which both groups received 24 months of open-label alendronate (ALN) 70 mg/wk for a total of 43 months (18 months ABL or PBO, 1 month for reconsent, 24 months ALN). Our objective was to determine the efficacy of ABL followed by ALN (ABL/ALN) vs PBO/ALN on BMD at the UD radius over 43 months.
Methods: Forearm BMD data (ACTIVE baseline and month 43) were measured for 213 and 233 women in ABL/ALN and PBO/ALN groups, respectively. BMD was centrally analyzed and adjusted for machine differences. DXA scanner and baseline BMD were included as covariates. Wrist fracture event rates were estimated for the ACTIVExtend ITT population (558 ABL/ALN; 581 PBO/ALN) by KM method.
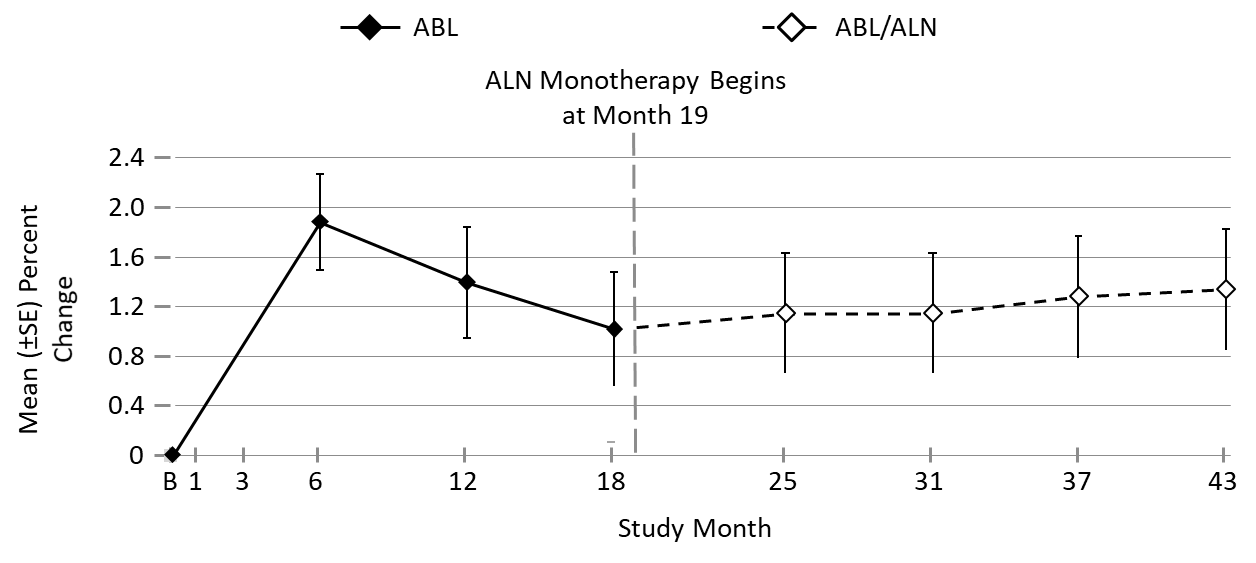
Results: Over the 18 months of the ACTIVE trial, BMD of the UD radius decreased in the placebo group but increased with ABL; these increases were maintained over the ALN extension (Figure). There were 15 women with wrist fractures in the ABL/ALN group (KM estimate: 2.8%) and 20 in the PBO/ALN group (3.6%). Although the number of wrist fractures was low, these fractures were numerically lower with ABL/ALN vs PBO/ALN (HR=0.77, 95% CI [0.39, 1.50], P=NS).
Conclusion: The BMD gains at the UD radius following treatment with ABL were maintained over the subsequent 24 months of treatment with ALN. Wrist fracture risk was numerically lower with ABL/ALN vs PBO/ALN. These results, together with previous ACTIVE analyses, suggest that BMD of the UD radius, which is rich in trabecular bone, may be a better predictor of wrist fracture than the 1/3 distal radius.
Figure. Mean (± SE) Percent Change in Ultradistal Radius BMD from Baseline Through Month 43
Missing BMD data imputed using the method of last observation carried forward. ABL, abaloparatide; ALN, alendronate; SE, standard error.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Watts NB, Dore RK, Baim S, Hattersley G, Williams G, Wang Y, Rozental TD, LeBoff MS. Forearm Bone Mineral Density and Fracture Incidence in Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/forearm-bone-mineral-density-and-fracture-incidence-in-postmenopausal-women-with-osteoporosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/forearm-bone-mineral-density-and-fracture-incidence-in-postmenopausal-women-with-osteoporosis/