Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The optimal initial treatment for systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA) is unclear. To further study the initial treatment of sJIA, the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) developed Consensus Treatment Plans (CTPs) to formalize and standardize current treatment practices into 4 CTPs: initial systemic glucocorticoid (GC) only; initial methotrexate (MTX) +/- GC; initial IL-1 inhibition (IL-1i) +/- GC; and initial IL-6 inhibition (IL-6i) +/- GC. FiRst Line Options for sJIA Treatment (FROST) was a prospective observational study designed to assess the effectiveness and safety of each of the 4 CTPs.
Methods: Patients with recent onset sJIA who were initiating therapy were considered for enrollment in FROST. Key inclusion criteria were fever for ≥2 weeks, arthritis for ≥ 10 days, and at least 1 of the following: evanescent rash, generalized lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, or serositis. Treatment assignment was at the discretion of the treating physician and family. Actual medication usage was captured. The primary study outcome was clinical inactive disease (CID; Wallace ACR provisional criteria) and no current use of GC at 9 months. Selected secondary outcomes included CID irrespective of current GC use and cJADAS-10 without current fever. Because few patients were treated with the GC, MTX, and IL-6i arms, only results for biologic therapy (IL-1i/IL-6i) and non-biologic therapy (GC/MTX) are presented. Results were attributed to the intended CTP, irrespective of treatment actually received (intention to treat). No statistical comparisons were made between treatment arms. Imputation of missing data was not performed.
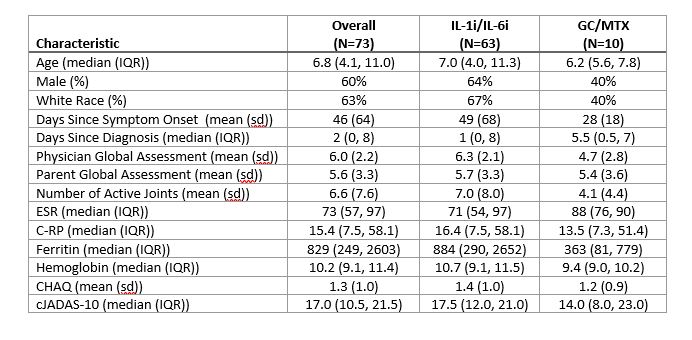
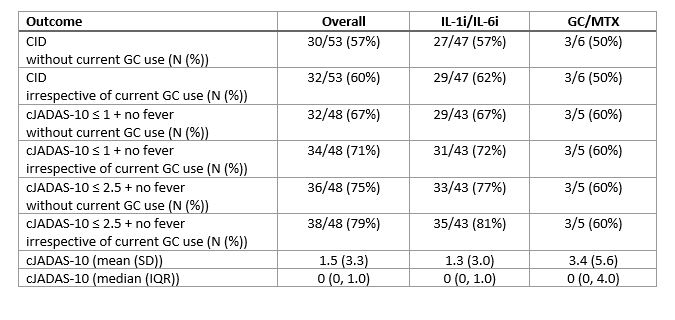
Results: Overall, 73 patients (characteristics in Table 1) were enrolled in FROST (63 IL-1i/IL-6i and 10 GC/MTX). As intended, all patients in the IL-1i/IL-6i arm started biologic therapy. Initiation of biologic therapy ranged from 7 days prior to enrollment to 61 days after with 75% initiating within 1 day after enrollment. 8/59 (14%) patients who initiated IL-1i subsequently switched to IL-6i, and 0/4 (0%) patients switched from IL-6i to IL-1i. Among patients in the GC/MTX arm, 5 (50%) eventually initiated biologic therapy during the study period (time to initiation 10 to 101 days). The 9-month outcomes are shown in Table 2. 16 patients did not have a 9-month visit recorded. Overall, 57% of patients met the primary outcome of CID without current GC use, and 75% had cJADAS-10 score ≤ 2.5 with no fever and no current GC use. Overall, there were 16 CTCAE grade 3 or higher safety events observed (all in IL1i/IL-6i arm), including 6 episodes of MAS. One patient died of acute liver failure.
Conclusion: Treatment practices have changed tremendously since the CARRA sJIA CTPs were initially developed. Initial biologic therapy is now the most common treatment approach among sJIA patients enrolled in the CARRA Registry. A substantial proportion of patients not initially started on biologics subsequently started a biologic within the first few months following diagnosis. Excellent treatment outcomes were observed in 57% to 75% of FROST patients overall, depending on the outcome definition.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Beukelman T, Tomlinson G, Nigrovic P, Dennos A, Del Gaizo V, Riordan M, Schanberg L, Mohan S, Pfeifer E, Kimura Y. FiRst Line Options for Systemic JIA Treatment (FROST): Results from a Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) Registry Consensus Treatment Plan Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/first-line-options-for-systemic-jia-treatment-frost-results-from-a-childhood-arthritis-and-rheumatology-research-alliance-carra-registry-consensus-treatment-plan-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/first-line-options-for-systemic-jia-treatment-frost-results-from-a-childhood-arthritis-and-rheumatology-research-alliance-carra-registry-consensus-treatment-plan-observational-study/