Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Heart failure (HF) is a leading
cause of excess deaths in RA. We previously found an association between left
ventricular mass index (LVMI) and anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPA)
in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients without CVD. Our objective was to validate
these findings in a different RA cohort of patients without CVD.
Methods: Seventy-four patients without
known CVD from underwent 3D Echocardiography and concurrent serum testing of a
panel of 30 specific ACPAs using a custom Bio-Plex bead array. With a high ACPA
level defined as ≥ 75th percentile, a cross-sectional analysis
of the association of specific ACPAs and LVMI was performed. Traditional CVD
risk factors and RA characteristics were adjusted for.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 54
years (±13), with 85% being females and 36% self-identified as non-Hispanic White.
The median disease duration was 7 years (IQR: 3-17), 67% had a positive
anti-CCP antibody, and the mean current RA disease activity, based on the DAS28-CRP,
was 3.9 (IQR: 2.9-4.5). Forty percent were hypertensive, 11% had diabetes, and
7% were current smokers. Except for a higher proportion of patients with
rheumatoid factor level> 40units, no differences were seen between those
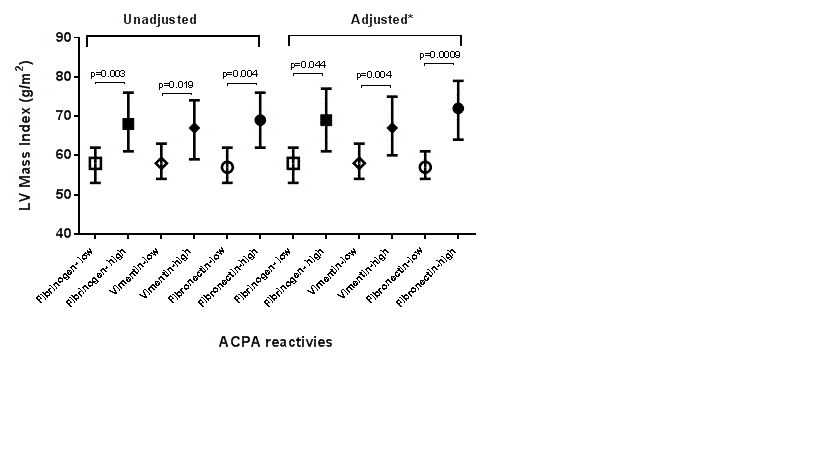
with high vs. low anti-CCP titers. High anti-citrullinated fibrinogen, anti-citrullinated
vimentin, and anti-citrullinated fibronectin antibody levels were associated
with a higher LVMI compared to low levels of these antibodies (68 vs. 58 g/m2,
p=0.02; 67 vs. 58 g/m2, p=0.003; and 69 vs. 57 g/m2,
p=0.004; respectively). These associations remained significant in the
adjusted analyses (69 vs. 58 g/m2, p=0.04; 67 vs. 58 g/m2,
p=0.004; 72 vs. 57 g/m2, p=0.009; respectively) (figure 1).
Conclusion: In concordance with our previous findings, specific ACPAs were associated with a
higher LVMI in RA patients without CVD. This independent association suggests a
link between autoimmunity and cardiac structure in RA.
Figure 1. Association of ACPA status with Left Ventricular mass
index.
Figure 1. High anti-citrullinated-vimentin, anti-citrullinated-fibrinogen,
and anti-citrullinated fibronectin antibody levels were associated with higher
LVMI. *Adjusted for hypertension.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Geraldino-Pardilla L, Giles JT, Sokolove J, Zartoshti A, Robinson W, Bathon JM. Fine Specificity of Anti-Citrullinated Peptide Antibodies Is Associated with Left Ventricular Mass Index in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients without Cardiovascular Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fine-specificity-of-anti-citrullinated-peptide-antibodies-is-associated-with-left-ventricular-mass-index-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-without-cardiovascular-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fine-specificity-of-anti-citrullinated-peptide-antibodies-is-associated-with-left-ventricular-mass-index-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-without-cardiovascular-disease/