Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by immune cell infiltration into the synovial membrane of the joint, where they engage stromal cells such as synovial fibroblasts in a persistent proinflammatory feedback loop. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) and interleukin 17 (IL17) are elevated in RA and activate synovial fibroblasts. Chronically activated fibroblasts proliferate, degrade joint cartilage, and recruit additional immune cells. We found that stimulation of fibroblasts with IL17 alone produced little response compared to TNF, but the combination of IL17 and TNF synergistically increased chemokine and cytokine gene expression. The purpose of this study is to define the transcriptional network controlling the synergistic response to IL17 and TNF.
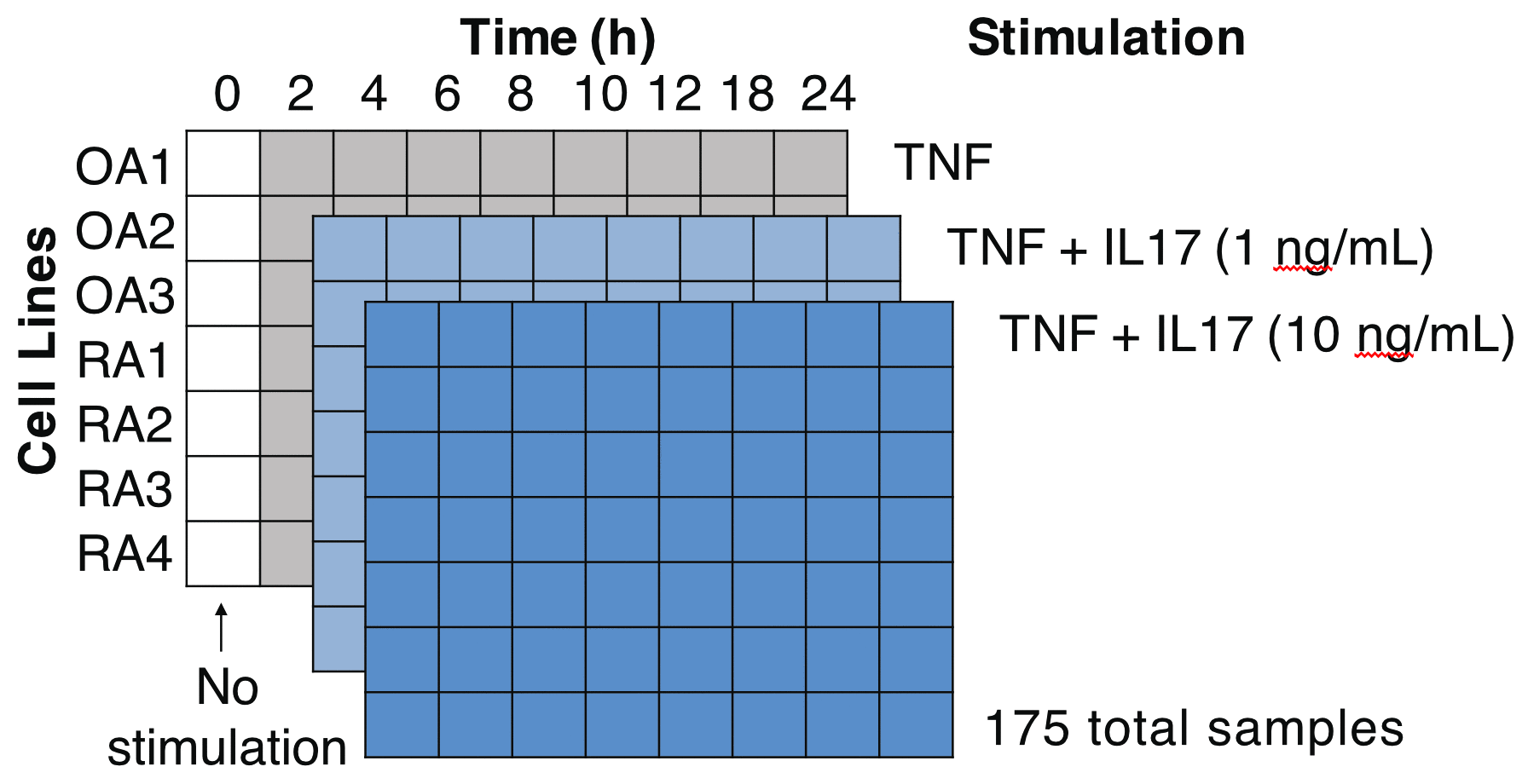
Methods: We assessed transcriptional changes over time and IL17 doses. We did 175 Smart-seq2TM RNA-seq experiments on synovial fibroblast cell lines from knee joint tissues obtained from 4 RA and 3 osteoarthritis (OA) donors. For each donor, we did a time series with 8 time points over 24 hours and 3 IL17 doses (0, 1, and 10 ng/mL) in combination with TNF (1 ng/mL). We repeated a subset of these RNA-seq experiments after siRNA silencing of specific transcription factors, this time with fewer time points and independent cell lines.
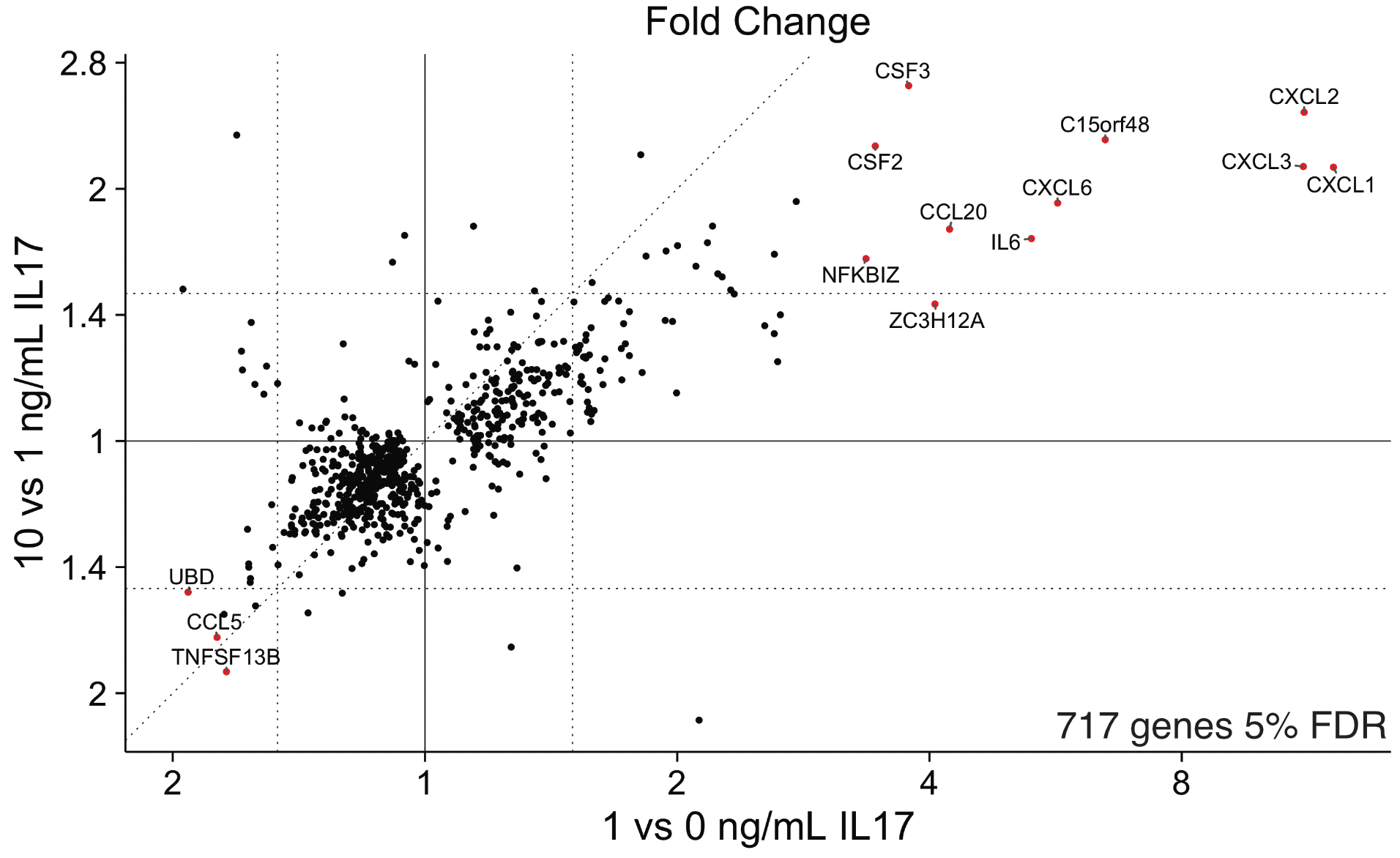
Results: We identified 813 genes at 5% false discovery rate (FDR) and >1.5 fold change between RA and OA, including two homeobox genes HOXC10 and HOXD11. Statistical analysis with linear models revealed 34 genes at 5% FDR and >1.5 fold change that respond to IL17 in a dose dependent manner, 10 of which are also differently expressed between RA and OA. We identified motifs enriched in these 34 genes’ promoters representing binding sites for known transcription factors (TFs) such as NFKB p65 (Rel A) and CEBP. We also found a novel transcription factor, CUX1. Two CUX1 target genes, CXCL2 and CXCL3, are highly dose-responsive to IL17 and these targets have CUX1 peaks in their promoters in ENCODE ChIP-seq data. Finally, exon level differential expression analysis revealed IL17 dose-dependent exon inclusion of 38 exons in 21 genes at 5% FDR, including an exon in NFkappaB inhibitor zeta (NFKBIZ) for an ankyrin repeat that likely binds to NFKB. Analysis of siRNA silencing experiments is ongoing.
Conclusion: IL17 and TNF costimulation activates a different transcriptional network than TNF or IL17 alone. A specific set of genes responds to dose of IL17, and putative transcription factors controlling these genes include NFKB p65 (Rel A), CEBP, and CUX1.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Slowikowski K, Nguyen H, Watts G, Mizoguchi F, Noss EH, Brenner M, Raychaudhuri S. Finding Transcriptional Regulators Central to RA with Transcriptomics of IL17 Dose Response, Time Series, and siRNA Silencing in Stromal Cells [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/finding-transcriptional-regulators-central-to-ra-with-transcriptomics-of-il17-dose-response-time-series-and-sirna-silencing-in-stromal-cells/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/finding-transcriptional-regulators-central-to-ra-with-transcriptomics-of-il17-dose-response-time-series-and-sirna-silencing-in-stromal-cells/