Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: RA, Spondyloarthritis, & OA
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Reduction in pain and fatigue, maintenance of physical functioning, and improvement in health-related quality of life (HRQoL) are vital aspects of successful treatment for patients (pts) with RA. In phase 3 clinical trials, filgotinib (FIL)—a potent, selective, oral, small molecule Janus kinase 1 inhibitor—improved signs and symptoms of RA when used in combination with MTX in pts with inadequate response to MTX (MTX-IR; FINCH 1 study [F1]), or to a biologic (b)DMARD (bDMARD-IR; FINCH 2 study [F2]).1,2 This is a post hoc analysis of functional status in both studies, with a focus on patient-reported outcomes using the Short Form-36 (SF-36) and HAQ-Disability Index (HAQ-DI).
Methods: All pts met 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria for RA. F1 pts were randomized 3:3:2:3 to receive once-daily FIL 200 mg, FIL 100 mg, adalimumab (ADA), or placebo (PBO) for up to 52 weeks (W) on a weekly stable background dose of MTX; at W24, pts receiving PBO were rerandomized 1:1 to FIL 200 or 100 mg. F2 pts were randomized 1:1:1 to receive once-daily FIL 200 mg, FIL 100 mg, or PBO for up to 24W on a stable background dose of permitted conventional synthetic (cs)DMARD(s). SF-36 was assessed at baseline and by visit on W4, 12, 24, 36, and 52. HAQ-DI was assessed at baseline and by visit on W2, 4, 8, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 24, 26, 30, 36, 44, and 52. The proportion of pts achieving HAQ-DI ≤0.5 was compared for FIL vs PBO (F1/F2) and FIL vs ADA (F1) using logistic regression with treatment groups and stratification factors in the model. Comparisons of change from baseline in SF-36 domains between FIL vs PBO and FIL vs ADA were conducted using mixed-effects model for repeated measures (MMRM) including treatment group, visit, treatment group by visit interaction, stratification factors, and baseline value as fixed effects; and subjects as random effect. All analyses were exploratory without multiplicity adjustment, and nominal P values are reported.
Results: Improvements in SF-36 domains in all FIL arms were observed as early as W4 and were sustained or increased through end of study (Fig 1). Nominally statistically significant improvements across all SF-36 domain scores occurred for pts on FIL 200 mg vs PBO at W4, 12, and 24 in F1, and 7/8 domains at W4 and 12 in F2; substantial improvements were evident particularly for bodily pain, physical functioning, and role-functional (Fig 1). The proportion of pts with HAQ-DI ≤0.5 was nominally statistically significantly higher in each FIL arm vs PBO early in treatment (W2 for F1 and W8 for F2) and for FIL 200 mg vs ADA at W4, 8, 36, and 52 (F1) (Fig 2).
Conclusion: FIL provided rapid and sustained improvements across multiple aspects of pts’ HRQoL captured by SF-36 and HAQ-DI when used in combination with csDMARD for treatment of MTX-IR or bDMARD-IR RA. Improvements in physical activities were observed with both HAQ-DI and SF-36. Furthermore, FIL meaningfully reduced HAQ-DI score to near-normal levels in relatively treatment-resistant bDMARD-IR patients, in addition to more MTX-IR pts on FIL 200 mg reaching this state by end of study when compared to pts on ADA. These results suggest that FIL can improve the daily lives of pts with advanced RA.
References
- Combe et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019; 78 (Suppl 2): A77.
- Genovese et al. JAMA. 2019; 322(4):315─25.
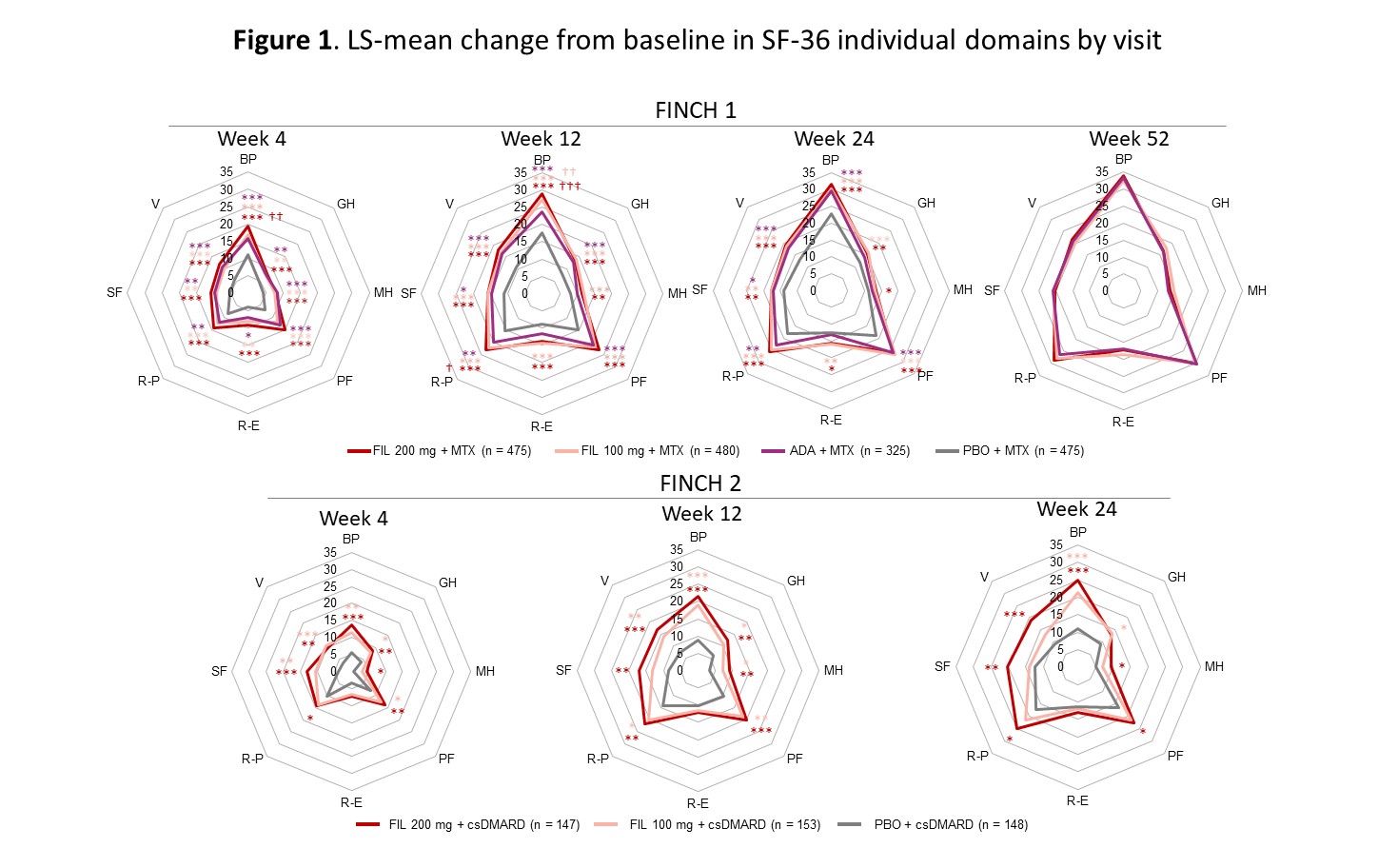 Concentric octagons represent the LS-mean change from baseline in the SF-36 domain score. Comparison with PBO: ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. Comparison with ADA: †††P < 0.001, ††P < 0.01. All are nominal P-values (not adjusted for multiplicity) and were from the MMRM including treatment, visit (as categorical), treatment by visit, stratification factors, and baseline value as fixed effects; and subjects as random effect. In FINCH 1, patients on PBO were rerandomized to FIL 200 or 100 mg at week 24. The FINCH 2 study ended at week 24. ADA, adalimumab; BP, bodily pain; csDMARD, conventional synthetic DMARD; FIL, filgotinib; GH, general health; LS, least squares; MH, mental health; MMRM, mixed-effects model for repeated measures; PBO, placebo; PF, physical functioning; R-E, role-emotional; R-P, role-physical; SF, social functioning; SF-36, Short Form-36; V, vitality.
Concentric octagons represent the LS-mean change from baseline in the SF-36 domain score. Comparison with PBO: ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. Comparison with ADA: †††P < 0.001, ††P < 0.01. All are nominal P-values (not adjusted for multiplicity) and were from the MMRM including treatment, visit (as categorical), treatment by visit, stratification factors, and baseline value as fixed effects; and subjects as random effect. In FINCH 1, patients on PBO were rerandomized to FIL 200 or 100 mg at week 24. The FINCH 2 study ended at week 24. ADA, adalimumab; BP, bodily pain; csDMARD, conventional synthetic DMARD; FIL, filgotinib; GH, general health; LS, least squares; MH, mental health; MMRM, mixed-effects model for repeated measures; PBO, placebo; PF, physical functioning; R-E, role-emotional; R-P, role-physical; SF, social functioning; SF-36, Short Form-36; V, vitality.
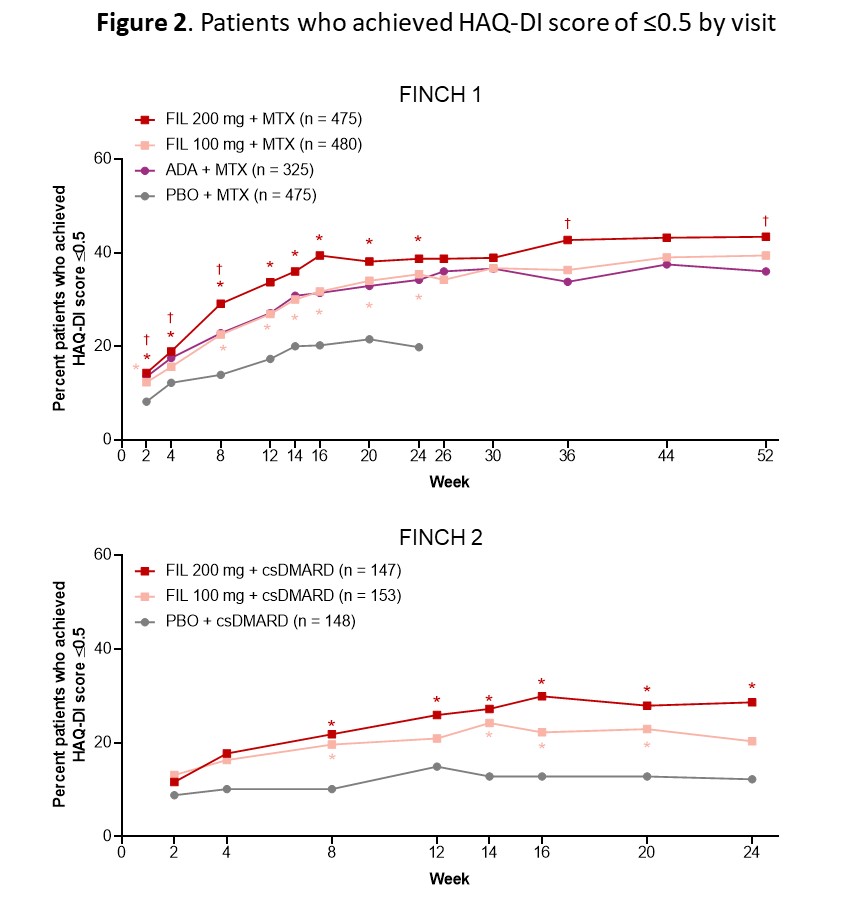 Comparison with PBO: *P < 0.05. Comparison with ADA: †P < 0.05. All are nominal P-values (not adjusted for multiplicity) and were from logistic regression with treatment groups and stratification factors in the model. A non-responder imputation was used. In FINCH 1, patients on PBO were rerandomized to FIL 200 or 100 mg at week 24. The FINCH 2 study ended at week 24. ADA, adalimumab; csDMARD, conventional synthetic DMARD; FIL, filgotinib; HAQ-DI, HAQ-Disability Index; PBO, placebo.
Comparison with PBO: *P < 0.05. Comparison with ADA: †P < 0.05. All are nominal P-values (not adjusted for multiplicity) and were from logistic regression with treatment groups and stratification factors in the model. A non-responder imputation was used. In FINCH 1, patients on PBO were rerandomized to FIL 200 or 100 mg at week 24. The FINCH 2 study ended at week 24. ADA, adalimumab; csDMARD, conventional synthetic DMARD; FIL, filgotinib; HAQ-DI, HAQ-Disability Index; PBO, placebo.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bingham III C, Walker D, Nash P, Lee S, Ye L, Hu H, Khalid J, Combe B. Filgotinib Significantly Improved Patient-reported Health-related Quality of Life for Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Post Hoc Analysis of SF-36 and HAQ-DI from Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/filgotinib-significantly-improved-patient-reported-health-related-quality-of-life-for-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-sf-36-and-haq-di-from-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/filgotinib-significantly-improved-patient-reported-health-related-quality-of-life-for-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-sf-36-and-haq-di-from-phase-3-studies/
