Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Abstracts: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment II: PsA
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: Subgroup analysis from different clinical trials and real-world data suggest, that there are differences in baseline characteristics, clinical phenotypes, and treatment responses in female patients compared to males. Especially in psoriatic arthritis, which is a heterogeneous disease, only little is known about gender differences. We conducted an investigator-initiated, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (IIT) in active PsA to examine if outcomes of treatment with ustekinumab (UST) in combination with MTX (either newly initiated or ongoing) were different from UST only (+Placebo; PBO). We used this data to investigate gender differences in focus on baseline characteristics and treatment responses to UST only and to UST+MTX combinational therapy.
Methods: A total of 186 patients with active PsA (defined as TJC >/=4, SJC >/=4 [68/66 joint count] and DAS28 >/=3.2) were screened for eligibility. 173 patients were randomized to UST+MTX (new or ongoing) or UST+PBO. 166 patients (mITT population) were included in this subgroup analysis. Patients were stratified according to gender. Demographic data and disease activity status (joint count [TJC/SJC], enthesitis [LEI], dactylitis count, PASI, BSA), QoL (EQ5D, DLQI), and function (HAQ) were compared between the groups. Response rates (pain response, ACR response) were evaluated at week 24.
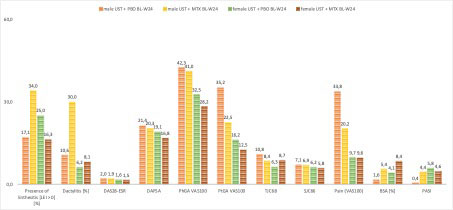
Results: Of the 166 patients included in this subgroup analysis, 41,6% were female. Demographic data including years since the onset of PsA, age, and BMI were well balanced between the groups. Skin involvement (BSA, PASI) was higher in the groups of UST+MTX treatment, especially in the female group with a BSA of 9.6% and PASI of 5.3. Enthesitis was more frequent in the female groups whereas dactylitis was more prominent in the male groups. Other disease activity features such as DAS28, DAPSA, TJC [68], SJC [66], and pain (VAS 100) showed comparable levels at baseline (table 1). Treatment response features are shown in Figures 1 and 2. Differences are found between the male and female groups, especially in the resolution of enthesitis, dactylitis, and pain. With a focus on pain reduction and ACR response rates, higher levels of reduction are achieved in the male groups compared to females. Here, the UST+MTX therapy shows less difference from baseline in the achievement of treatment responses whereas male patients have a higher improvement for resolution of enthesitis and dactylitis by combining UST+MTX compared to baseline.
Conclusion: Data from an RCT was analyzed in focus on gender differences in baseline characteristics and treatment responses to UST+MTX or UST-only therapy over 24-weeks. In comparison to the male cohort, females show a decreased response in the resolution of pain, enthesitis, dactylitis, and ACR response rates. Different from males, females seem not to benefit from a UST+MTX combinational treatment for the improvement of enthesitis and dactylitis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Koehm M, Foldenauer A, Rossmanith T, Kellner H, Kiltz U, Rech J, Burmester G, Kofler D, Brandt-Juergens J, Finzel S, Bergner R, Sieburg M, Behrens F. Female Psoriatic Arthritis Patients Show Differences in Treatment Response to IL12/23 Inhibition in Combination with or Without MTX Compared to Male – Results from a Multicenter Investigator-initiated Randomized Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/female-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-show-differences-in-treatment-response-to-il12-23-inhibition-in-combination-with-or-without-mtx-compared-to-male-results-from-a-multicenter-investigator-i/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/female-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-show-differences-in-treatment-response-to-il12-23-inhibition-in-combination-with-or-without-mtx-compared-to-male-results-from-a-multicenter-investigator-i/