Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Osteonecrosis (ON) complicates approximately 15-20% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) on an average of six years after diagnosis. However, a small subgroup of patients will develop ON early, sometimes in a few weeks after treatment initiation. It is possible that these patients display an increased “end-organ sensitivity” and, in turn, an increased responsiveness to the administered treatment (particularly glucocorticosteroids). The aim of this study was to evaluate if patients who develop early ON will achieve better control of their disease over time compared to individuals with late ON.
Methods: Inception patients (enrolled in the Lupus Clinic within 18 months of diagnosis) who developed symptomatic ON were retrieved from the electronic database and divided into four quartiles based on the time to ON development. Patients in the first quartile were compared to individuals of the remaining three quartiles as per the demographic, clinical, immunological and therapeutic characteristics. Outcomes also included the adjusted mean SLE Disease Activity Index-2000 (SLEDAI-2K) from diagnosis until the development of ON and the severity of ON (affected joints/patient at ON diagnosis, at 12 months after ON and at the last visit). Descriptive statistics were used.
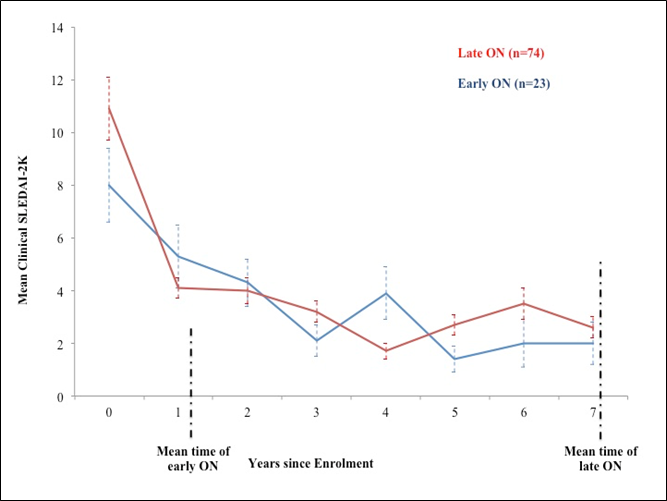
Results: Ninety-seven inception patients developed ON (time range 0.1-19.9 years from diagnosis). Twenty-three patients developed ON within 1.3 years after diagnosis (1st quartile, mean 1.2±0.6 years) whereas 74 developed ON later (2nd-4th quartiles, mean 7.4±5.2 years). There were no significant differences regarding age, sex distribution and race/ethnicity between the two groups. Initial SLEDAI-2K was higher in the patients with late ON (12.9±10.2 vs. 9.6±7, p< 0.001) as well as the initial prednisone dose (39.2±25.6 vs. 26.9±17.2, p< 0.001). For the first 12 months since diagnosis (approximately the time of early ON development), the average daily prednisone dose was similar between groups (21.6±12.1 vs. 21.3±10.7mg/day) as well as the cumulative prednisone dose (10.5±7.1 vs. 9.4±5.5grams). The evolution of the mean clinical SLEDAI-2K for seven years from diagnosis (approximately the time of late ON development) in the two groups is shown in the figure.
Concerning ON severity, this was comparable between groups both at ON diagnosis (1.46 vs. 1.43 affected joints/patient), at 12 months after ON (1.78 vs. 1.91 affected joints/patient) and at the last visit (3.3 vs. 2.87 affected joints/patient).
Conclusion: The early ON group had a lower disease activity score, lower initial steroid dose and a similar cumulative dose at one year, but developed ON within 1.3 years of diagnosis. Thus, other factors, such as genetic predisposition and organ responsiveness may be implicated in early development of ON.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tselios K, Gladman D, Su J, Urowitz M. Factors Implicated in the Development of Early Osteonecrosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-implicated-in-the-development-of-early-osteonecrosis-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-implicated-in-the-development-of-early-osteonecrosis-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/